Maison >développement back-end >Tutoriel Python >Explication détaillée d'exemples de dessin de graphiques avec python
Explication détaillée d'exemples de dessin de graphiques avec python
- PHP中文网original
- 2017-06-20 15:55:325526parcourir
1. Environnement
Système : windows10
version python : python3.6.1
Bibliothèques utilisées : matplotlib, numpy
2. Plusieurs façons pour la bibliothèque numpy de générer des nombres aléatoires
3. >import numpy as npnumpy.random
rand(d0, d1, ..., dn) Dans [2] : x=np.random.rand(2,5)
rand(d0, d1, ..., dn) In [2]: x=np.random.rand(2,5)
In [3]: x
Out[3]:
array([[ 0.84286554, 0.50007593, 0.66500549, 0.97387807, 0.03993009],
[ 0.46391661, 0.50717355, 0.21527461, 0.92692517, 0.2567891 ]])randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)查询结果为标准正态分布
In [4]: x=np.random.randn(2,5)
In [5]: x
Out[5]:
array([[-0.77195196, 0.26651203, -0.35045793, -0.0210377 , 0.89749635],
[-0.20229338, 1.44852833, -0.10858996, -1.65034606, -0.39793635]])randint(low,high,size) 生成low到high之间(半开区间 [low, high)),size个数据
In [6]: x=np.random.randint(1,8,4)
In [7]: x
Out[7]: array([4, 4, 2, 7])random_integers(low,high,size) 生成low到high之间(闭区间 [low, high)),size个数据
In [10]: x=np.random.random_integers(2,10,5)
In [11]: x
Out[11]: array([7, 4, 5, 4, 2])Entrée [3] : x
Sortie[3] :
array([[ 0.84286554, 0.50007593, 0.66500549, 0.97387807, 0.03993009],
[ 0.46391661, 0. 50717355, 1527461 , 0.92692517, 0.2567891 ]])le résultat de la requête randn(d0, d1, ..., dn) est une distribution normale standard td>
Sortie[5] :
tableau( [[-0.77195196, 0.26651203, -0.35045793, -0.0210377, 0.89749635],
[-0.20229338, 1.44852833, -0.10858996, -1.650346 06, -0. 39793635]])randint(low,high,size) Générer entre bas et haut (intervalle semi-ouvert [bas, haut)), taille des donnéesDans [ 6] : x=np.random.randint(1,8,4)
Dans [7] : x
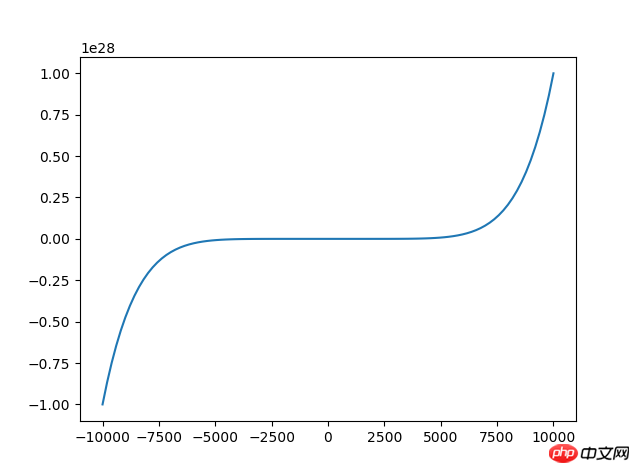
Out[7] : array([4, 4, 2 , 7])random_integers(low,high,size) Générer entre bas et haut (intervalle fermé [low, high)) , données de taille <code class="language-python hljs"># 来源:百度网盘搜索 <br/>x=np.linspace(<span class="hljs-number">-10000,<span class="hljs-number">10000,<span class="hljs-number">100) <span class="hljs-comment">#将-10到10等区间分成100份 y=x**<span class="hljs-number">2+x**<span class="hljs-number">3+x**<span class="hljs-number">7 plt.plot(x,y) plt.show()</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></code>Dans [10] : x=np.random.random_integers(2,10,5)Dans [11] : x
Out[11 ] : array([7, 4, 5, 4, 2])
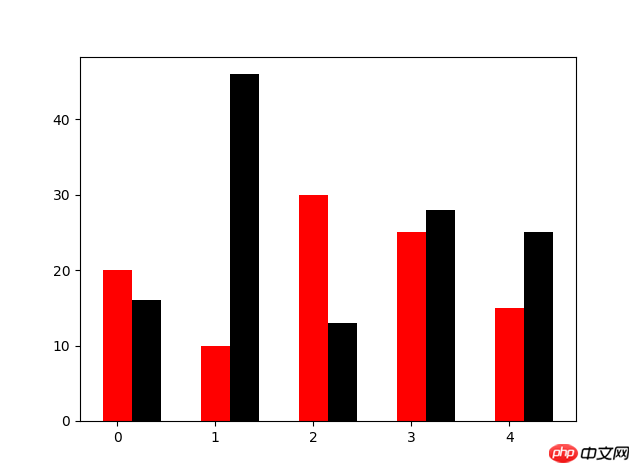
N=5 y=[20,10,30,25,15] y1=np.random.randint(10,50,5) x=np.random.randint(10,1000,N) index=np.arange(N) plt.bar(left=index,height=y,color='red',width=0.3) plt.bar(left=index+0.3,height=y1,color='black',width=0.3) plt.show()
4. Graphique linéaire
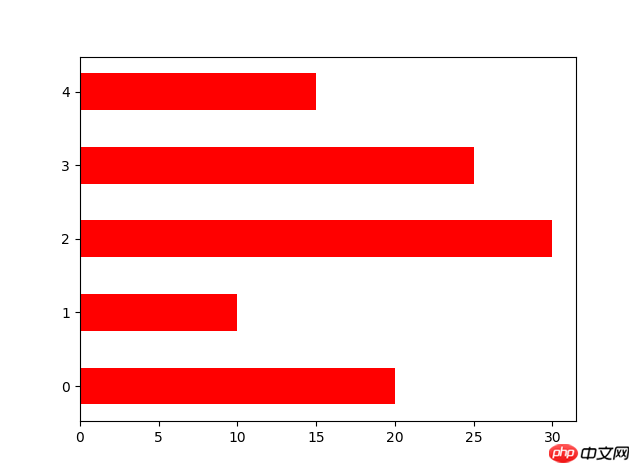
N=5 y=[20,10,30,25,15] y1=np.random.randint(10,50,5) x=np.random.randint(10,1000,N) index=np.arange(N)# plt.bar(left=index,height=y,color='red',width=0.3)# plt.bar(left=index+0.3,height=y1,color='black',width=0.3)#plt.barh() 加了h就是横向的条形图,不用设置orientation plt.bar(left=0,bottom=index,width=y,color='red',height=0.5,orientation='horizontal') plt.show()Graphique linéaire Le graphique utilise la fonction de tracé
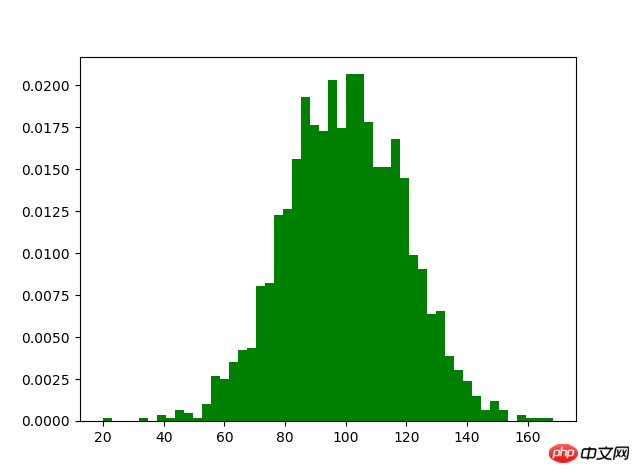
m1=100 sigma=20 x=m1+sigma*np.random.randn(2000) plt.hist(x,bins=50,color="green",normed=True) plt.show()5. Graphique à barres
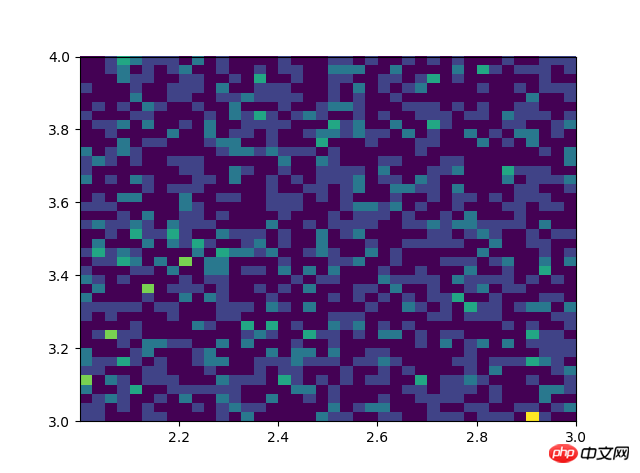
# #双变量的直方图# #颜色越深频率越高# #研究双变量的联合分布#双变量的直方图#颜色越深频率越高#研究双变量的联合分布 x=np.random.rand(1000)+2 y=np.random.rand(1000)+3 plt.hist2d(x,y,bins=40) plt.show()l'orientation définit un graphique à barres horizontales
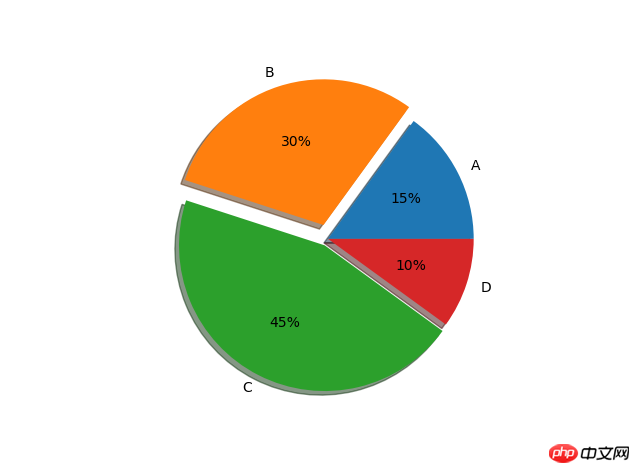
#设置x,y轴比例为1:1,从而达到一个正的圆#labels标签参数,x是对应的数据列表,autopct显示每一个区域占的比例,explode突出显示某一块,shadow阴影Histogrammelabes=['A','B','C','D'] fracs=[15,30,45,10] explode=[0,0.1,0.05,0]#设置x,y轴比例为1:1,从而达到一个正的圆 plt.axes(aspect=1)#labels标签参数,x是对应的数据列表,autopct显示每一个区域占的比例,explode突出显示某一块,shadow阴影 plt.pie(x=fracs,labels=labes,autopct="%.0f%%",explode=explode,shadow=True) plt.show()
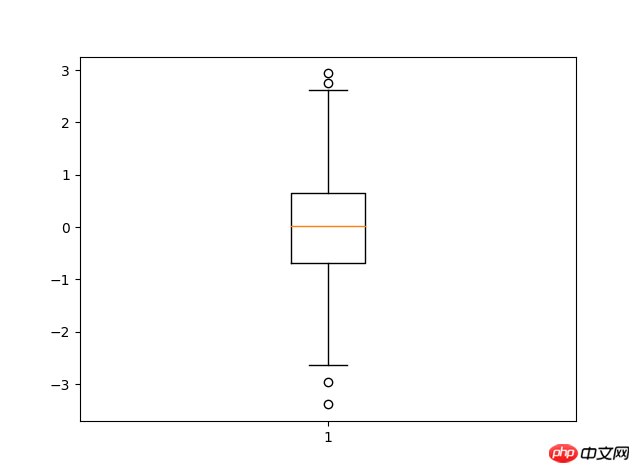
8. Box plotimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdata=np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=1000)#sym 点的形状,whis虚线的长度plt.boxplot(data,sym="o",whis=1.5)plt.show()#sym 点的形状,whis虚线的长度7.
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!


 Générer entre bas et haut (intervalle semi-ouvert [bas, haut)), taille des donnéesDans [ 6] : x=np.random.randint(1,8,4)
Générer entre bas et haut (intervalle semi-ouvert [bas, haut)), taille des donnéesDans [ 6] : x=np.random.randint(1,8,4)