Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Compréhension approfondie de la configuration de sources multi-données Spring
Compréhension approfondie de la configuration de sources multi-données Spring
- 高洛峰original
- 2017-01-24 10:35:461408parcourir
Nous rencontrons souvent le problème des sources de données multiples dans les projets, notamment des projets tels que la synchronisation des données ou les tâches planifiées. Le plus gros problème pour plusieurs sources de données n’est pas de configurer plusieurs sources de données, mais de savoir comment changer de source de données de manière flexible et dynamique. Par exemple, dans un projet de framework Spring et Hibernate, nous configurons souvent une dataSource pour se connecter à la base de données dans la configuration Spring, puis la lions à sessionFactory, puis spécifions la sessionFactory dans le code de la couche dao pour effectuer les opérations de base de données.

Comme le montre l'image ci-dessus, chaque bloc est désigné et lié. S'il existe plusieurs sources de données, cela ne peut être que comme indiqué dans l'image ci-dessous.

On peut voir que deux SessionFactory sont codées en dur dans le code de la couche Dao, donc s'il y a une autre source de données dans le futur, le code devra être modifié pour ajouter une SessionFactory. Évidemment, cela ne respecte pas le principe d'ouverture et de fermeture.
Alors l'approche correcte devrait être
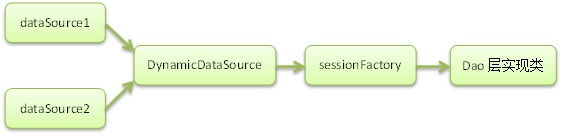
Le code est le suivant :
1.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:jms="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms" xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:oxm="http://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms http://www.springframework.org/schema/jms/spring-jms-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm http://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm/spring-oxm-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.1.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com"></context:component-scan>
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:com/resource/config.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSourceOne" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${dbOne.jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${dbOne.jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${dbOne.jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${dbOne.jdbc.password}" />
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${dbOne.jdbc.initialPoolSize}" />
<property name="minPoolSize" value="${dbOne.jdbc.minPoolSize}" />
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${dbOne.jdbc.maxPoolSize}" />
</bean>
<bean id="dataSourceTwo" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.password}" />
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.initialPoolSize}" />
<property name="minPoolSize" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.minPoolSize}" />
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${dbTwo.jdbc.maxPoolSize}" />
</bean>
<bean id="dynamicDataSource" class="com.core.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<entry value-ref="dataSourceOne" key="dataSourceOne"></entry>
<entry value-ref="dataSourceTwo" key="dataSourceTwo"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSourceOne">
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dynamicDataSource" />
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.current_session_context_class">org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.SpringSessionContext</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">false</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hbm2ddl.auto">create</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>com.po</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="transactionPointCut" expression="execution(* com.dao..*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="transactionPointCut" />
</aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="dataSourceAspect" ref="dataSourceInterceptor">
<aop:pointcut id="daoOne" expression="execution(* com.dao.one.*.*(..))" />
<aop:pointcut id="daoTwo" expression="execution(* com.dao.two.*.*(..))" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="daoOne" method="setdataSourceOne" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="daoTwo" method="setdataSourceTwo" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>2. DynamicDataSource.class
package com.core;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource{
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DatabaseContextHolder.getCustomerType();
}
}3. DatabaseContextHolder.class
package com.core;
public class DatabaseContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void setCustomerType(String customerType) {
contextHolder.set(customerType);
}
public static String getCustomerType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearCustomerType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}4. >5. Classe d'entité po
package com.core;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class DataSourceInterceptor {
public void setdataSourceOne(JoinPoint jp) {
DatabaseContextHolder.setCustomerType("dataSourceOne");
}
public void setdataSourceTwo(JoinPoint jp) {
DatabaseContextHolder.setCustomerType("dataSourceTwo");
}
}6. BrandDaoImpl.classpackage com.po;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "BTSF_BRAND", schema = "hotel")
public class Brand {
private String id;
private String names;
private String url;
@Id
@Column(name = "ID", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 10)
public String getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "NAMES", nullable = false, length = 50)
public String getNames() {
return this.names;
}
public void setNames(String names) {
this.names = names;
}
@Column(name = "URL", length = 200)
public String getUrl() {
return this.url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
}package com.po;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "CITY", schema = "car")
public class City {
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Id
@Column(name = "ID", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "NAMES", nullable = false, length = 50)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}7. 🎜>
package com.dao.one;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.po.Brand;
@Repository
public class BrandDaoImpl implements IBrandDao {
@Resource
protected SessionFactory sessionFactory;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List<Brand> findAll() {
String hql = "from Brand";
Query query = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createQuery(hql);
return query.list();
}
}8. DaoTest.classpackage com.dao.two;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.po.City;
@Repository
public class CityDaoImpl implements ICityDao {
@Resource
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List<City> find() {
String hql = "from City";
Query query = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createQuery(hql);
return query.list();
}
}
Utilisez aop pour modifier dynamiquement la source de données. Lorsque nous devons ajouter une source de données, il nous suffit d'ajouter la configuration aop dans le fichier de configuration applicationContext et de créer un nouveau DataSourceInterceptor. sans changer aucun code. package com.test;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.transaction.TransactionConfiguration;
import com.dao.one.IBrandDao;
import com.dao.two.ICityDao;
import com.po.Brand;
import com.po.City;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:com/resource/applicationContext.xml")
@TransactionConfiguration(transactionManager = "transactionManager", defaultRollback = false)
public class DaoTest {
@Resource
private IBrandDao brandDao;
@Resource
private ICityDao cityDao;
@Test
public void testList() {
List<Brand> brands = brandDao.findAll();
System.out.println(brands.size());
List<City> cities = cityDao.find();
System.out.println(cities.size());
}
}Ce qui précède représente l'intégralité du contenu de cet article. J'espère qu'il sera utile à l'apprentissage de chacun. J'espère également que tout le monde soutiendra le site Web PHP chinois. Pour une compréhension plus approfondie des articles liés à la configuration de sources multi-données Spring, veuillez prêter attention au site Web PHP chinois ! 
