Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Une introduction à l'utilisation du lancement d'exceptions à l'aide du mot-clé throw dans la programmation Java
Une introduction à l'utilisation du lancement d'exceptions à l'aide du mot-clé throw dans la programmation Java
- 高洛峰original
- 2017-01-18 14:56:292612parcourir
throw lève une exception de manière plus directe :
if(age < 0){
throw new MyException("年龄不能为负数!");
}
Regardons un exemple :
package Test;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc";
if(s.equals("abc")) {
throw new NumberFormatException();
} else {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
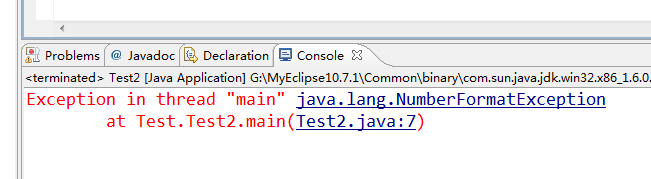
Le les résultats d'exécution sont les suivants :
En Java, vous pouvez déclarer une exception lors de la définition d'une méthode, puis vous pouvez utiliser throw pour lancer spécifiquement une exception lors de l'implémentation.
ppublic class Shoot { 创建类
static void pop() throws NegativeArraySizeException {
//定义方法并抛出NegativeArraySizeException异常
int [] arr = new int[-3];//创建数组
}
public static void main(String[] args) {//主方法
try {
pop(); //调用pop()方法
} catch (NegativeArraySizeException e) {
System.out.println("pop()方法抛出的异常");//输出异常信息
}
}
}Pour plus d'introduction à l'utilisation du lancement d'exceptions à l'aide du mot-clé throw dans la programmation Java, veuillez prêter attention au site Web PHP chinois pour les articles connexes !
Déclaration:
Le contenu de cet article est volontairement contribué par les internautes et les droits d'auteur appartiennent à l'auteur original. Ce site n'assume aucune responsabilité légale correspondante. Si vous trouvez un contenu suspecté de plagiat ou de contrefaçon, veuillez contacter admin@php.cn

