Achetez-moi un café☕
*Mon message explique MS COCO.
CocoDetection() peut utiliser l'ensemble de données MS COCO comme indiqué ci-dessous. * Ceci concerne train2017 avec captions_train2017.json, instances_train2017.json et person_keypoints_train2017.json, val2017 avec captions_val2017.json, instances_val2017.json et person_keypoints_val2017.json et test2017 avec image_info_test2017.json et image_info_test-dev2017.json :
from torchvision.datasets import CocoDetection
cap_train2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/train2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/captions_train2017.json"
)
ins_train2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/train2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/instances_train2017.json"
)
pk_train2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/train2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/person_keypoints_train2017.json"
)
len(cap_train2017_data), len(ins_train2017_data), len(pk_train2017_data)
# (118287, 118287, 118287)
cap_val2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/val2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/captions_val2017.json"
)
ins_val2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/val2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/instances_val2017.json"
)
pk_val2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/val2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/trainval2017/person_keypoints_val2017.json"
)
len(cap_val2017_data), len(ins_val2017_data), len(pk_val2017_data)
# (5000, 5000, 5000)
test2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/test2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/test2017/image_info_test2017.json"
)
testdev2017_data = CocoDetection(
root="data/coco/imgs/test2017",
annFile="data/coco/anns/test2017/image_info_test-dev2017.json"
)
len(test2017_data), len(testdev2017_data)
# (40670, 20288)
cap_train2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x428">,
# [{'image_id': 30, 'id': 695774,
# 'caption': 'A flower vase is sitting on a porch stand.'},
# {'image_id': 30, 'id': 696557,
# 'caption': 'White vase with different colored flowers sitting inside of it. '},
# {'image_id': 30, 'id': 699041,
# 'caption': 'a white vase with many flowers on a stage'},
# {'image_id': 30, 'id': 701216,
# 'caption': 'A white vase filled with different colored flowers.'},
# {'image_id': 30, 'id': 702428,
# 'caption': 'A vase with red and white flowers outside on a sunny day.'}])
cap_train2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">,
# [{'image_id': 294, 'id': 549895,
# 'caption': 'A man standing in front of a microwave next to pots and pans.'},
# {'image_id': 294, 'id': 556411,
# 'caption': 'A man displaying pots and utensils on a wall.'},
# {'image_id': 294, 'id': 556507,
# 'caption': 'A man stands in a kitchen and motions towards pots and pans. '},
# {'image_id': 294, 'id': 556993,
# 'caption': 'a man poses in front of some pots and pans '},
# {'image_id': 294, 'id': 560728,
# 'caption': 'A man pointing to pots hanging from a pegboard on a gray wall.'}])
cap_train2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="480x640">,
# [{'image_id': 370, 'id': 468271,
# 'caption': 'A little girl holding wet broccoli in her hand. '},
# {'image_id': 370, 'id': 471646,
# 'caption': 'The young child is happily holding a fresh vegetable. '},
# {'image_id': 370, 'id': 475471,
# 'caption': 'A little girl holds a hand full of wet broccoli. '},
# {'image_id': 370, 'id': 475663,
# 'caption': 'A little girl holds a piece of broccoli towards the camera.'},
# {'image_id': 370, 'id': 822588,
# 'caption': 'a small kid holds on to some vegetables '}])
ins_train2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x428">,
# [{'segmentation': [[267.38, 330.14, 281.81, ..., 269.3, 329.18]],
# 'area': 47675.66289999999, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 30,
# 'bbox': [204.86, 31.02, 254.88, 324.12], 'category_id': 64,
# 'id': 291613},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 86, 'id': 1155486}])
ins_train2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">,
# [{'segmentation': [[27.7, 423.27, 27.7, ..., 28.66, 427.0]],
# 'area': 64624.86664999999, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 294,
# 'bbox': [27.7, 69.83, 364.91, 357.17], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 470246},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 50, 'id': 708187},
# ...
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 50, 'id': 2217190}])
ins_train2017_data[67]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="480x640">,
# [{'segmentation': [[90.81, 155.68, 90.81, ..., 98.02, 207.57]],
# 'area': 137679.34520000007, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 370,
# 'bbox': [90.81, 24.5, 389.19, 615.5], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 436109},
# {'segmentation': [[257.51, 446.79, 242.45, ..., 262.02, 460.34]],
# 'area': 43818.18095, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 370,
# 'bbox': [242.45, 257.05, 237.55, 243.95], 'category_id': 56,
# 'id': 1060727}])
pk_train2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x428">, [])
pk_train2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">,
# [{'segmentation': [[27.7, 423.27, 27.7, ..., 28.66, 427]],
# 'num_keypoints': 11, 'area': 64624.86665, 'iscrowd': 0,
# 'keypoints': [149, 133, 2, 159, ..., 0, 0], 'image_id': 294,
# 'bbox': [27.7, 69.83, 364.91, 357.17], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 470246}])
pk_train2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="480x640">,
# [{'segmentation': [[90.81, 155.68, 90.81, ..., 98.02, 207.57]],
# 'num_keypoints': 12, 'area': 137679.3452, 'iscrowd': 0,
# 'keypoints': [229, 171, 2, 263, ..., 0, 0], 'image_id': 370,
# 'bbox': [90.81, 24.5, 389.19, 615.5], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 436109}])
cap_val2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x483">,
# [{'image_id': 632, 'id': 301804,
# 'caption': 'Bedroom scene with a bookcase, blue comforter and window.'},
# {'image_id': 632, 'id': 302791,
# 'caption': 'A bedroom with a bookshelf full of books.'},
# {'image_id': 632, 'id': 305425,
# 'caption': 'This room has a bed with blue sheets and a large bookcase'},
# {'image_id': 632, 'id': 305953,
# 'caption': 'A bed and a mirror in a small room.'},
# {'image_id': 632, 'id': 306511,
# 'caption': 'a bed room with a neatly made bed a window and a book shelf'}])
cap_val2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x480">,
# [{'image_id': 5001, 'id': 542124,
# 'caption': 'A group of people cutting a ribbon on a street.'},
# {'image_id': 5001, 'id': 545685,
# 'caption': 'A man uses a pair of big scissors to cut a pink ribbon.'},
# {'image_id': 5001, 'id': 549285,
# 'caption': 'A man cutting a ribbon at a ceremony '},
# {'image_id': 5001, 'id': 549666,
# 'caption': 'A group of people on the sidewalk watching two young children.'},
# {'image_id': 5001, 'id': 549696,
# 'caption': 'A group of people holding a large pair of scissors to a ribbon.'}])
cap_val2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="375x500">,
# [{'image_id': 6763, 'id': 708378,
# 'caption': 'A man and a women posing next to one another in front of a table.'},
# {'image_id': 6763, 'id': 709983,
# 'caption': 'A man and woman hugging in a restaurant'},
# {'image_id': 6763, 'id': 711438,
# 'caption': 'A man and woman standing next to a table.'},
# {'image_id': 6763, 'id': 711723,
# 'caption': 'A happy man and woman pose for a picture.'},
# {'image_id': 6763, 'id': 714720,
# 'caption': 'A man and woman posing for a picture in a sports bar.'}])
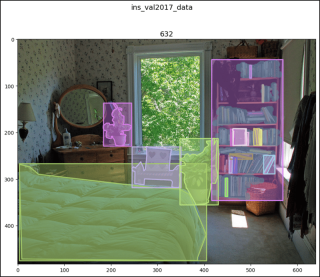
ins_val2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x483">,
# [{'segmentation': [[5.45, 269.03, 25.08, ..., 3.27, 266.85]],
# 'area': 64019.87940000001, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 632,
# 'bbox': [3.27, 266.85, 401.23, 208.25], 'category_id': 65,
# 'id': 315724},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 64, 'id': 1610466},
# ...
# {'segmentation': {'counts': [201255, 6, 328, 6, 142, ..., 4, 34074],
# 'size': [483, 640]}, 'area': 20933, 'iscrowd': 1, 'image_id': 632,
# 'bbox': [416, 43, 153, 303], 'category_id': 84,
# 'id': 908400000632}])
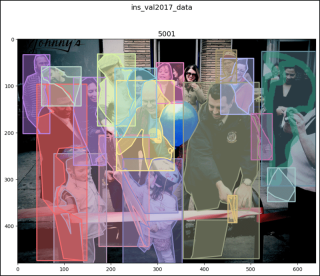
ins_val2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x480">,
# [{'segmentation': [[210.34, 204.76, 227.6, ..., 195.24, 211.24]],
# 'area': 5645.972500000001, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 5001,
# 'bbox': [173.66, 204.76, 107.87, 238.39], 'category_id': 87,
# 'id': 1158531},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 1201627},
# ...
# {'segmentation': {'counts': [251128, 24, 451, 32, 446, ..., 43, 353],
# 'size': [480, 640]}, 'area': 10841, 'iscrowd': 1, 'image_id': 5001,
# 'bbox': [523, 26, 116, 288], 'category_id': 1, 'id': 900100005001}])
ins_val2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="375x500">,
# [{'segmentation': [[232.06, 92.6, 369.96, ..., 223.09, 93.72]],
# 'area': 11265.648799999995, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 6763
# 'bbox': [219.73, 64.57, 151.35, 126.69], 'category_id': 72,
# 'id': 30601},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 197649},
# ...
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 1228674}])
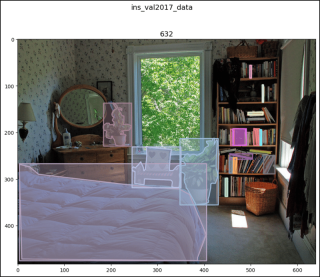
pk_val2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x483">, [])
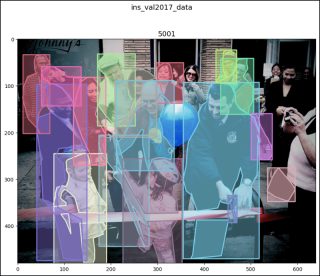
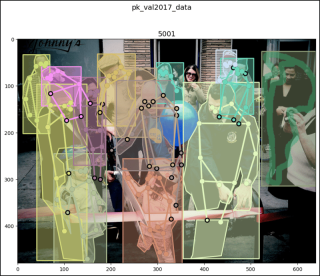
pk_val2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x480">,
# [{'segmentation': [[42.07, 190.11, 45.3, ..., 48.54, 201.98]],
# 'num_keypoints': 8, 'area': 5156.63, 'iscrowd': 0,
# 'keypoints': [58, 56, 2, 61, ..., 0, 0], 'image_id': 5001,
# 'bbox': [10.79, 32.63, 58.24, 169.35], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 1201627},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 1220394},
# ...
# {'segmentation': {'counts': [251128, 24, 451, 32, 446, ..., 43, 353], # 'size': [480, 640]}, 'num_keypoints': 0, 'area': 10841,
# 'iscrowd': 1, 'keypoints': [0, 0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0],
# 'image_id': 5001, 'bbox': [523, 26, 116, 288],
# 'category_id': 1, 'id': 900100005001}])
pk_val2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="375x500">,
# [{'segmentation': [[94.38, 462.92, 141.57, ..., 100.27, 459.94]],
# 'num_keypoints': 10, 'area': 36153.48825, 'iscrowd': 0,
# 'keypoints': [228, 202, 2, 252, ..., 0, 0], 'image_id': 6763,
# 'bbox': [79.48, 131.87, 254.23, 331.05], 'category_id': 1,
# 'id': 197649},
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 212640},
# ...
# {'segmentation': ..., 'category_id': 1, 'id': 1228674}])
test2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">, [])
test2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x406">, [])
test2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">, [])
testdev2017_data[2]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x427">, [])
testdev2017_data[47]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="480x640">, [])
testdev2017_data[64]
# (<pil.image.image image mode="RGB" size="640x480">, [])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon, Rectangle
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask
# `show_images1()` doesn't work very well for the images with
# segmentations and keypoints so for them, use `show_images2()` which
# more uses the original coco functions.
def show_images1(data, ims, main_title=None):
file = data.root.split('/')[-1]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(14, 8))
fig.suptitle(t=main_title, y=0.9, fontsize=14)
x_crd = 0.02
for i, axis in zip(ims, axes.ravel()):
if data[i][1] and "caption" in data[i][1][0]:
im, anns = data[i]
axis.imshow(X=im)
axis.set_title(label=anns[0]["image_id"])
y_crd = 0.0
for ann in anns:
text_list = ann["caption"].split()
if len(text_list) > 9:
text = " ".join(text_list[0:10]) + " ..."
else:
text = " ".join(text_list)
plt.figtext(x=x_crd, y=y_crd, fontsize=10,
s=f'{ann["id"]}:\n{text}')
y_crd -= 0.06
x_crd += 0.325
if i == 2 and file == "val2017":
x_crd += 0.06
if data[i][1] and "segmentation" in data[i][1][0]:
im, anns = data[i]
axis.imshow(X=im)
axis.set_title(label=anns[0]["image_id"])
for ann in anns:
if "counts" in ann['segmentation']:
seg = ann['segmentation']
# rle is Run Length Encoding.
uncompressed_rle = [seg['counts']]
height, width = seg['size']
compressed_rle = mask.frPyObjects(pyobj=uncompressed_rle,
h=height, w=width)
# rld is Run Length Decoding.
compressed_rld = mask.decode(rleObjs=compressed_rle)
y_plts, x_plts = np.nonzero(a=np.squeeze(a=compressed_rld))
axis.plot(x_plts, y_plts, color='yellow')
else:
for seg in ann['segmentation']:
seg_arrs = np.split(ary=np.array(seg),
indices_or_sections=len(seg)/2)
poly = Polygon(xy=seg_arrs,
facecolor="lightgreen", alpha=0.7)
axis.add_patch(p=poly)
x_plts = [seg_arr[0] for seg_arr in seg_arrs]
y_plts = [seg_arr[1] for seg_arr in seg_arrs]
axis.plot(x_plts, y_plts, color='yellow')
x, y, w, h = ann['bbox']
rect = Rectangle(xy=(x, y), width=w, height=h,
linewidth=3, edgecolor='r',
facecolor='none', zorder=2)
axis.add_patch(p=rect)
if data[i][1] and 'keypoints' in data[i][1][0]:
kps = ann['keypoints']
kps_arrs = np.split(ary=np.array(kps),
indices_or_sections=len(kps)/3)
x_plts = [kps_arr[0] for kps_arr in kps_arrs]
y_plts = [kps_arr[1] for kps_arr in kps_arrs]
nonzeros_x_plts = []
nonzeros_y_plts = []
for x_plt, y_plt in zip(x_plts, y_plts):
if x_plt == 0 and y_plt == 0:
continue
nonzeros_x_plts.append(x_plt)
nonzeros_y_plts.append(y_plt)
axis.scatter(x=nonzeros_x_plts, y=nonzeros_y_plts,
color='yellow')
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ Bad result ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
# axis.plot(nonzeros_x_plts, nonzeros_y_plts)
if not data[i][1]:
im, _ = data[i]
axis.imshow(X=im)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
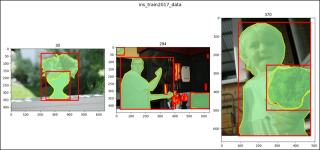
ims = (2, 47, 64)
show_images1(data=cap_train2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="cap_train2017_data")
show_images1(data=ins_train2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="ins_train2017_data")
show_images1(data=pk_train2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="pk_train2017_data")
print()
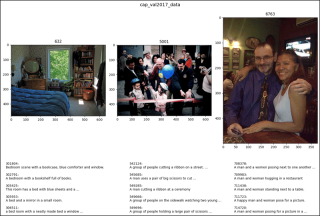
show_images1(data=cap_val2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="cap_val2017_data")
show_images1(data=ins_val2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="ins_val2017_data")
show_images1(data=pk_val2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="pk_val2017_data")
print()
show_images(data=test2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="test2017_data")
show_images(data=testdev2017_data, ims=ims,
main_title="testdev2017_data")
# `show_images2()` works very well for the images with segmentations and
# keypoints.
def show_images2(data, index, main_title=None):
img_set = data[index]
img, img_anns = img_set
if img_anns and "segmentation" in img_anns[0]:
img_id = img_anns[0]['image_id']
coco = data.coco
def show_image(imgIds, areaRng=[],
iscrowd=None, draw_bbox=False):
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 8))
plt.imshow(X=img)
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=1, fontsize=14)
plt.title(label=img_id, fontsize=14)
anns_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id,
areaRng=areaRng, iscrowd=iscrowd)
anns = coco.loadAnns(ids=anns_ids)
coco.showAnns(anns=anns, draw_bbox=draw_bbox)
plt.show()
show_image(imgIds=img_id, draw_bbox=True)
show_image(imgIds=img_id, draw_bbox=False)
show_image(imgIds=img_id, iscrowd=False, draw_bbox=True)
show_image(imgIds=img_id, areaRng=[0, 5000], draw_bbox=True)
elif img_anns and not "segmentation" in img_anns[0]:
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 8))
img_id = img_anns[0]['image_id']
plt.imshow(X=img)
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=1, fontsize=14)
plt.title(label=img_id, fontsize=14)
plt.show()
elif not img_anns:
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 8))
plt.imshow(X=img)
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=1, fontsize=14)
plt.show()
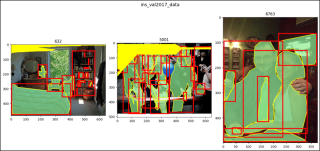
show_images2(data=ins_val2017_data, index=2,
main_title="ins_val2017_data")
print()
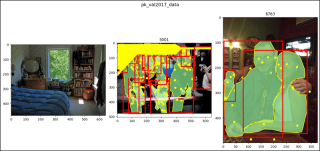
show_images2(data=pk_val2017_data, index=2,
main_title="pk_val2017_data")
print()
show_images2(data=ins_val2017_data, index=47,
main_title="ins_val2017_data")
print()
show_images2(data=pk_val2017_data, index=47,
main_title="pk_val2017_data")
</pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image></pil.image.image>












Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Apprendre Python: 2 heures d'étude quotidienne est-elle suffisante?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Apprendre Python: 2 heures d'étude quotidienne est-elle suffisante?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMEst-ce suffisant pour apprendre Python pendant deux heures par jour? Cela dépend de vos objectifs et de vos méthodes d'apprentissage. 1) Élaborer un plan d'apprentissage clair, 2) Sélectionnez les ressources et méthodes d'apprentissage appropriées, 3) la pratique et l'examen et la consolidation de la pratique pratique et de l'examen et de la consolidation, et vous pouvez progressivement maîtriser les connaissances de base et les fonctions avancées de Python au cours de cette période.
 Python pour le développement Web: applications clésApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python pour le développement Web: applications clésApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMLes applications clés de Python dans le développement Web incluent l'utilisation des cadres Django et Flask, le développement de l'API, l'analyse et la visualisation des données, l'apprentissage automatique et l'IA et l'optimisation des performances. 1. Framework Django et Flask: Django convient au développement rapide d'applications complexes, et Flask convient aux projets petits ou hautement personnalisés. 2. Développement de l'API: Utilisez Flask ou DjangorestFramework pour construire RestulAPI. 3. Analyse et visualisation des données: utilisez Python pour traiter les données et les afficher via l'interface Web. 4. Apprentissage automatique et AI: Python est utilisé pour créer des applications Web intelligentes. 5. Optimisation des performances: optimisée par la programmation, la mise en cache et le code asynchrones
 Python vs. C: Explorer les performances et l'efficacitéApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C: Explorer les performances et l'efficacitéApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython est meilleur que C dans l'efficacité du développement, mais C est plus élevé dans les performances d'exécution. 1. La syntaxe concise de Python et les bibliothèques riches améliorent l'efficacité du développement. Les caractéristiques de type compilation et le contrôle du matériel de CC améliorent les performances d'exécution. Lorsque vous faites un choix, vous devez peser la vitesse de développement et l'efficacité de l'exécution en fonction des besoins du projet.
 Python en action: exemples du monde réelApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python en action: exemples du monde réelApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMLes applications du monde réel de Python incluent l'analyse des données, le développement Web, l'intelligence artificielle et l'automatisation. 1) Dans l'analyse des données, Python utilise des pandas et du matplotlib pour traiter et visualiser les données. 2) Dans le développement Web, les cadres Django et Flask simplifient la création d'applications Web. 3) Dans le domaine de l'intelligence artificielle, Tensorflow et Pytorch sont utilisés pour construire et former des modèles. 4) En termes d'automatisation, les scripts Python peuvent être utilisés pour des tâches telles que la copie de fichiers.
 Les principales utilisations de Python: un aperçu completApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Les principales utilisations de Python: un aperçu completApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython est largement utilisé dans les domaines de la science des données, du développement Web et des scripts d'automatisation. 1) Dans la science des données, Python simplifie le traitement et l'analyse des données à travers des bibliothèques telles que Numpy et Pandas. 2) Dans le développement Web, les cadres Django et Flask permettent aux développeurs de créer rapidement des applications. 3) Dans les scripts automatisés, la simplicité de Python et la bibliothèque standard le rendent idéal.
 Le but principal de Python: flexibilité et facilité d'utilisationApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Le but principal de Python: flexibilité et facilité d'utilisationApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AMLa flexibilité de Python se reflète dans les systèmes de prise en charge et de type dynamique multi-paradigmes, tandis que la facilité d'utilisation provient d'une syntaxe simple et d'une bibliothèque standard riche. 1. Flexibilité: prend en charge la programmation orientée objet, fonctionnelle et procédurale, et les systèmes de type dynamique améliorent l'efficacité de développement. 2. Facilité d'utilisation: La grammaire est proche du langage naturel, la bibliothèque standard couvre un large éventail de fonctions et simplifie le processus de développement.
 Python: la puissance de la programmation polyvalenteApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python: la puissance de la programmation polyvalenteApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython est très favorisé pour sa simplicité et son pouvoir, adaptés à tous les besoins des débutants aux développeurs avancés. Sa polyvalence se reflète dans: 1) Facile à apprendre et à utiliser, syntaxe simple; 2) Bibliothèques et cadres riches, tels que Numpy, Pandas, etc.; 3) Support multiplateforme, qui peut être exécuté sur une variété de systèmes d'exploitation; 4) Convient aux tâches de script et d'automatisation pour améliorer l'efficacité du travail.
 Apprendre le python en 2 heures par jour: un guide pratiqueApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Apprendre le python en 2 heures par jour: un guide pratiqueApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMOui, apprenez Python en deux heures par jour. 1. Élaborer un plan d'étude raisonnable, 2. Sélectionnez les bonnes ressources d'apprentissage, 3. Consolider les connaissances apprises par la pratique. Ces étapes peuvent vous aider à maîtriser Python en peu de temps.


Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Version Mac de WebStorm
Outils de développement JavaScript utiles

Télécharger la version Mac de l'éditeur Atom
L'éditeur open source le plus populaire

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) est une application Web PHP/MySQL très vulnérable. Ses principaux objectifs sont d'aider les professionnels de la sécurité à tester leurs compétences et leurs outils dans un environnement juridique, d'aider les développeurs Web à mieux comprendre le processus de sécurisation des applications Web et d'aider les enseignants/étudiants à enseigner/apprendre dans un environnement de classe. Application Web sécurité. L'objectif de DVWA est de mettre en pratique certaines des vulnérabilités Web les plus courantes via une interface simple et directe, avec différents degrés de difficulté. Veuillez noter que ce logiciel

SublimeText3 version anglaise
Recommandé : version Win, prend en charge les invites de code !

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)





