Maison >développement back-end >tutoriel php >Guide rapide CakePHP
Guide rapide CakePHP
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBoriginal
- 2024-09-10 17:27:171591parcourir
CakePHP - Présentation
CakePHP est un framework MVC open source. Cela facilite grandement le développement, le déploiement et la maintenance des applications. CakePHP dispose d'un certain nombre de bibliothèques pour réduire la surcharge des tâches les plus courantes.
Avantages de CakePHP
Les avantages de l'utilisation de CakePHP sont répertoriés ci-dessous −
Open Source
Cadre MVC
Moteur de création de modèles
Opérations de mise en cache
URL conviviales pour les moteurs de recherche
Interactions faciles avec la base de données CRUD (créer, lire, mettre à jour, supprimer).
Bibliothèques et aides
Validation intégrée
Localisation
Composants de gestion des e-mails, des cookies, de la sécurité, des sessions et des demandes
Afficher les aides pour AJAX, JavaScript, les formulaires HTML et plus
Cycle de requête CakePHP
L'illustration suivante décrit le fonctionnement d'un cycle de vie de requête dans CakePHP −

Un cycle de requête CakePHP typique commence avec un utilisateur demandant une page ou une ressource dans votre application. À haut niveau, chaque demande passe par les étapes suivantes −
Les règles de réécriture du serveur Web dirigent la requête vers webroot / index.php.
Les fichiers de chargement automatique et d'amorçage de votre application sont exécutés.
Tous les filtres de répartition configurés peuvent gérer la demande et éventuellement générer une réponse.
Le répartiteur sélectionne le contrôleur et l'action appropriés en fonction des règles de routage.
L'action du contrôleur est appelée et le contrôleur interagit avec les modèles et composants requis.
Le contrôleur délègue la création de réponse à la Vue pour générer la sortie résultant des données du modèle.
La vue utilise des Helpers et des Cells pour générer le corps de la réponse et les en-têtes.
La réponse est renvoyée au client.
CakePHP - Installation
Dans ce chapitre, nous montrerons l'installation de CakePHP 4.0.3. La version minimale de PHP que nous devons installer est PHP 7.3.
Vous devez avoir installé PHP 7.3 et Composer avant de commencer l'installation de cakePHP.
Pour les utilisateurs Windows, installez ou mettez à jour le serveur WAMP avec la version PHP > 7.3.
Allez sur www.wampserver.com/en/download-wampserver-64bits/ et installez-le.
Pour les utilisateurs de Linux, veuillez vous référer au site Web Tutorials Point qui est disponible à l'adresse www.tutorialspoint.com/php7/php7_installation_linux.htm pour l'installation de PHP.
Installation de Composer
Allez sur composer sur https://getcomposer.org/download/ et cliquez sur télécharger selon le système d'exploitation (OS) de votre ordinateur et installez composer sur votre système. Ajoutez l'emplacement à la variable PATH pour les utilisateurs Windows, afin que vous puissiez utiliser composer à partir de n'importe quel répertoire.
Une fois que vous avez terminé d'installer Composer, commençons maintenant à installer CakePHP.
Installer CakePHP
Allez dans le dossier où se trouve wamp pour les utilisateurs Windows et dans le dossier www/, créez un dossier cakephp4/.
Pour les utilisateurs Linux, créez le dossier var/www/html/ puis créez le dossier cakephp4/.
cakephp4/ est le dossier dans lequel nous allons installer CakePHP.
Utilisez composer pour exécuter la commande suivante −
composer create-project --prefer-dist cakephp/app:4.0.3 cakephp4
C'est ce que vous devriez voir lorsque la commande s'exécute −

Une fois l'installation terminée, utilisez localhost pour ouvrir votre projet dans le navigateur.
Le chemin pour cela est http://localhost/cakephp.

CakePHP - Structure des dossiers
Ici, nous découvrirons la structure des dossiers et la convention de dénomination dans CakePHP. Commençons par comprendre la structure des dossiers.
Structure des dossiers
Jetez un œil à la capture d'écran suivante. Il montre la structure des dossiers de CakePHP.

Le tableau suivant décrit le rôle de chaque dossier dans CakePHP −
| Sr.Non | Nom et description du dossier |
|---|---|
| 1 |
poubelle Le dossier bin contient les exécutables de la console Cake. |
| 2 |
config Le dossier config contient les (quelques) fichiers de configuration utilisés par CakePHP. Les détails de connexion à la base de données, le démarrage, les fichiers de configuration de base et bien plus encore doivent être stockés ici. |
| 3 |
journaux Le dossier logs contient normalement vos fichiers journaux, en fonction de votre configuration de journaux. |
| 4 |
plugins Le dossier plugins est l'endroit où sont stockés les plugins utilisés par votre application. |
| 5 |
ressources Les fichiers à internationaliser dans le dossier local correspondant seront stockés ici. Par ex. locales/en_US. |
| 6 |
src Le dossier src sera l'endroit où vous exercerez votre magie. C’est là que seront placés les fichiers de votre application et que vous effectuerez l’essentiel du développement de votre application. Regardons d'un peu plus près les dossiers à l'intérieur de src.
|
| 7 |
modèles Les fichiers de présentation des modèles sont placés ici : éléments, pages d'erreur, mises en page et fichiers de modèles de vue. |
| 8 |
essais Le dossier tests sera l'endroit où vous placerez les cas de test pour votre application. |
| 9 |
tmp Le dossier tmp est l'endroit où CakePHP stocke les données temporaires. Les données réelles qu'il stocke dépendent de la façon dont CakePHP est configuré, mais ce dossier est généralement utilisé pour stocker les descriptions de modèles et parfois les informations de session. |
| 10 |
vendeur Le dossier vendor est l'endroit où CakePHP et d'autres dépendances d'application seront installés. Prenez l'engagement personnel de ne pas modifier les fichiers de ce dossier. Nous ne pouvons pas vous aider si vous avez modifié le noyau. |
| 11 |
webroot Le répertoire webroot est la racine du document public de votre application. Il contient tous les fichiers que vous souhaitez rendre accessibles au public. |
Naming Convention
Naming convention is not something mandatory to be followed, but is a good coding practice and will be very helpful as your project goes big.
Guide rapide CakePHP Convention
The controller class name has to be plural, PascalCased and the name has to end with Guide rapide CakePHP. For example, for Students class the name of the controller can be StudentsGuide rapide CakePHP. Public methods on Guide rapide CakePHPs are often exposed as ‘actions’ accessible through a web browser.
For example, the /users /view maps to the view() method of the UsersGuide rapide CakePHP out of the box. Protected or private methods cannot be accessed with routing.
File and Class Guide rapide CakePHP Convention
Mostly, we have seen that our class name file name is almost the same. This is similar in cakephp.
For example, the class StudentsGuide rapide CakePHP will have the file named as StudentsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. The files have to be saved as the module name and in the respective folders in app folder.
Database Conventions
The tables used for CakePHP models, mostly have names plural with underscore.
For example, student_details, student_marks. The field name has an underscore, if it is made up of two words, for example, first_name, last_name.
Model Conventions
For model, the classes are named as per database table, the names are plural, PascalCased and suffixed with Table.
For example, StudentDetailsTable, StudentMarksTable
View Conventions
For view templates, the files are based on controller functions.
For example, if the class StudentDetailsGuide rapide CakePHP has function showAll(), the view template will be named as show_all.php and saved inside template/yrmodule/show_all.php.
CakePHP - Project Configuration
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Guide rapide CakePHP, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
Configuration CakePHP comes with one configuration file by default, and we can modify it according to our needs. There is one dedicated folder “config” for this purpose. CakePHP comes with different configuration options.
Let us start by understanding the Environment Guide rapide CakePHP in CakePHP.
Environment Guide rapide CakePHP
Environment variables make the working of your application on different environments easy. For example, on dev server, test server, staging server and production server environment. For all these environments, you can make use of env() function to read the configuration for the environment you need and build your application.
In your config folder, you will come across config/.env.example. This file has all the variables that will be changed based on your environment. To start with, you can create a file in config folder i.e. config/.env and define those variables and use them. In case you need any additional variables, it can go in that file.
You can read your environment variable using env() function as shown below −
Example
$debug = env('APP_DEBUG', false);
The first one is the name of the environment variable you want and second value is the default value. The default value is used, if there is no value found for the environment variable.
General Configuration
The following table describes the role of various variables and how they affect your CakePHP application.
| Sr.No | Variable Guide rapide CakePHP & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
debug Changes CakePHP debugging output. false = Production mode. No error messages, errors, or warnings shown. true = Errors and warnings shown. |
| 2 |
App.namespace The namespace to find app classes under. |
| 3 |
App.baseUrl Un-comment this definition, if you don’t plan to use Apache’s mod_rewrite with CakePHP. Don’t forget to remove your .htaccess files too. |
| 4 |
App.base The base directory the app resides in. If false, this will be auto detected. |
| 5 |
App.encoding Define what encoding your application uses. This encoding is used to generate the charset in the layout, and encode entities. It should match the encoding values specified for your database. |
| 6 |
App.webroot The webroot directory. |
| 7 |
App.wwwRoot The file path to webroot. |
| 8 |
App.fullBaseUrl The fully qualified domain name (including protocol) to your application’s root. |
| 9 |
App.imageBaseUrl Web path to the public images directory under webroot. |
| 10 |
App.cssBaseUrl Web path to the public css directory under webroot. |
| 11 |
App.jsBaseUrl Web path to the public js directory under webroot. |
| 12 |
App.paths Configure paths for non-class based resources. Supports the plugins, templates, locales, subkeys, which allow the definition of paths for plugins, view templates and locale files respectively. |
| 13 |
Security.salt A random string used in hashing. This value is also used as the HMAC salt when doing symmetric encryption. |
| 14 |
Asset.timestamp Appends a timestamp, which is last modified time of the particular file at the end of asset files URLs (CSS, JavaScript, Image) when using proper helpers. The valid values are −
|
Databases Configuration
Database can be configured in config/app.php and config/app_local.php file. This file contains a default connection with provided parameters, which can be modified as per our choice.
The below snippet shows the default parameters and values, which should be modified as per the requirement.
Config/app_local.php
*/
'Datasources' => [
'default' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
'username' => 'my_app',
'password' => 'secret',
'database' => 'my_app',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL', null),
],
/*
* The test connection is used during the test suite.
*/
'test' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
//'port' => 'non_standard_port_number',
'username' => 'my_app',
'password' => 'secret',
'database' => 'test_myapp',
//'schema' => 'myapp',
],
],
Let us understand each parameter in detail in config/app_local.php.
| Host | The database server’s hostname (or IP address). |
|---|---|
| username | Database username |
| password | Database password. |
| database | Guide rapide CakePHP of Database. |
| Port | The TCP port or Unix socket used to connect to the server. |
config/app.php
'Datasources' => [
'default' => [
'classGuide rapide CakePHP' => Connection::class,
'driver' => Mysql::class,
'persistent' => false,
'timezone' => 'UTC',
//'encoding' => 'utf8mb4',
'flags' => [],
'cacheMetadata' => true,
'log' => false,
'quoteIdentifiers' => false,
//'init' => ['SET GLOBAL innodb_stats_on_metadata = 0'],
],
]
Let us understand each parameter in detail in config/app.php.
| Sr.No | Key & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
classGuide rapide CakePHP The fully namespaced class name of the class that represents the connection to a database server. This class is responsible for loading the database driver, providing SQL transaction mechanisms and preparing SQL statements among other things. |
| 2 |
driver The class name of the driver used to implement all specificities for a database engine. This can either be a short classname using plugin syntax, a fully namespaced name, or a constructed driver instance. Examples of short classnames are Mysql, Sqlite, Postgres, and Sqlserver. |
| 3 |
persistent Whether or not to use a persistent connection to the database. |
| 4 |
encoding Indicates the character set to use, when sending SQL statements to the server like ‘utf8’ etc. |
| 5 |
timezone Server timezone to set. |
| 6 |
init A list of queries that should be sent to the database server as and when the connection is created. |
| 7 | log
log Set to true to enable query logging. When enabled queries will be logged at a debug level with the queriesLog scope. |
| 8 |
quoteIdentifiers Set to true, if you are using reserved words or special characters in your table or column names. Enabling this setting will result in queries built using the Query Builder having identifiers quoted when creating SQL. It decreases performance. |
| 9 |
flags An associative array of PDO constants that should be passed to the underlying PDO instance. |
| 10 |
cacheMetadata Either boolean true, or a string containing the cache configuration to store meta data in. Having metadata caching disable is not advised and can result in very poor performance. |
Email Configuration
Email can be configured in file config/app.php. It is not required to define email configuration in config/app.php. Email can be used without it. Just use the respective methods to set all configurations separately or load an array of configs. Configuration for Email defaults is created using config() and configTransport().
Email Configuration Transport
By defining transports separately from delivery profiles, you can easily re-use transport configuration across multiple profiles. You can specify multiple configurations for production, development and testing. Each transport needs a classGuide rapide CakePHP. Valid options are as follows −
Mail − Send using PHP mail function
Smtp − Send using SMTP
Debug − Do not send the email, just return the result
You can add custom transports (or override existing transports) by adding the appropriate file to src/Mailer/Transport. Transports should be named YourTransport.php, where 'Your' is the name of the transport.
Following is the example of Email configuration transport.
'EmailTransport' => [
'default' => [
'classGuide rapide CakePHP' => 'Mail',
// The following keys are used in SMTP transports
'host' => 'localhost',
'port' => 25,
'timeout' => 30,
'username' => 'user',
'password' => 'secret',
'client' => null,
'tls' => null,
'url' => env('EMAIL_TRANSPORT_DEFAULT_URL', null),
],
],
Email Delivery Profiles
Delivery profiles allow you to predefine various properties about email messages from your application, and give the settings a name. This saves duplication across your application and makes maintenance and development easier. Each profile accepts a number of keys.
Following is an example of Email delivery profiles.
'Email' => [
'default' => [
'transport' => 'default',
'from' => 'you@localhost',
],
],
CakePHP - Routing
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing −
- Introduction to Routing
- Connecting Routes
- Passing Guide rapide CakePHP to Routes
- Generating urls
- Guide rapide CakePHP urls
Introduction to Routing
In this section, we will see how you can implement routes, how you can pass arguments from URL to controller’s action, how you can generate URLs, and how you can redirect to a specific URL. Normally, routes are implemented in file config/routes.php. Routing can be implemented in two ways −
- static method
- scoped route builder
Here, is an example presenting both the types.
// Using the scoped route builder.
Router::scope('/', function ($routes) {
$routes->connect('/', ['controller' => 'Guide rapide CakePHPs', 'action' => 'index']);
});
// Using the static method.
Router::connect('/', ['controller' => 'Guide rapide CakePHPs', 'action' => 'index']);
Both the methods will execute the index method of Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP. Out of the two methods, scoped route builder gives better performance.
Connecting Routes
Router::connect() method is used to connect routes. The following is the syntax of the method −
static Cake\Routing\Router::connect($route, $defaults =[], $options =[])
There are three arguments to the Router::connect() method −
The first argument is for the URL template you wish to match.
The second argument contains default values for your route elements.
The third argument contains options for the route, which generally contains regular expression rules.
Here, is the basic format of a route −
$routes->connect( 'URL template', ['default' => 'defaultValue'], ['option' => 'matchingRegex'] );
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown below.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('/', ['controller' => 'Tests', 'action' => 'show']);
$builder->connect('/pages/*', ['controller' => 'Pages', 'action' => 'display']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Core\Configure;
use Cake\Http\Exception\ForbiddenException;
use Cake\Http\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Cake\Http\Response;
use Cake\View\Exception\MissingTemplateException;
class TestsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function show()
{
}
}
Create a folder Tests under src/Template and under that folder, create a View file called show.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Tests/show.php
<h1>This is CakePHP tutorial and this is an example of connecting routes.</h1>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL which is available at http://localhost/cakephp4/
Output
The above URL will yield the following output.

Passed Guide rapide CakePHP
Passed arguments are the arguments which are passed in the URL. These arguments can be passed to controller’s action. These passed arguments are given to your controller in three ways.
As arguments to the action method
Following example shows, how we can pass arguments to the action of the controller. Visit the following URL at http://localhost/cakephp4/tests/value1/value2
This will match the following route line.
$builder->connect('tests/:arg1/:arg2', ['controller' => 'Tests', 'action' => 'show'],['pass' => ['arg1', 'arg2']]);
Here, the value1 from URL will be assigned to arg1 and value2 will be assigned to arg2.
As numericallyindexed array
Once the argument is passed to the controller’s action, you can get the argument with the following statement.
$args = $this->request->params[‘pass’]
The arguments passed to controller’s action will be stored in $args variable.
Using routing array
The argument can also be passed to action by the following statement −
$routes->connect('/', ['controller' => 'Tests', 'action' => 'show',5,6]);
The above statement will pass two arguments 5, and 6 to TestGuide rapide CakePHP’s show() method.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('tests/:arg1/:arg2', ['controller' => 'Tests', 'action' => 'show'],['pass' => ['arg1', 'arg2']]);
$builder->connect('/pages/*', ['controller' => 'Pages', 'action' => 'display']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/TestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Core\Configure;
use Cake\Http\Exception\ForbiddenException;
use Cake\Http\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Cake\Http\Response;
use Cake\View\Exception\MissingTemplateException;
class TestsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function show($arg1, $arg2) {
$this->set('argument1',$arg1);
$this->set('argument2',$arg2);
}
}
Create a folder Tests at src/Template and under that folder create a View file called show.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Tests/show.php.
<h1>This is CakePHP tutorial and this is an example of Passed arguments.</h1> <?php echo "Argument-1:".$argument1."<br/>"; echo "Argument-2:".$argument2."<br>"; ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL http://localhost/cakephp4/tests/Guide rapide CakePHP/Kunal
Output
Upon execution, the above URL will produce the following output.

Generating URLs
This is a cool feature of CakePHP. Using the generated URLs, we can easily change the structure of URL in the application without modifying the whole code.
url( string|array|null $url null , boolean $full false )
The above function will take two arguments −
The first argument is an array specifying any of the following - 'controller', 'action', 'plugin'. Additionally, you can provide routed elements or query string parameters. If string, it can be given the name of any valid url string.
If true, the full base URL will be prepended to the result. Default is false.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('/generate',['controller'=>'Generates','action'=>'show']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a GeneratesGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/GeneratesGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/GeneratesGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
21
use Cake\Core\Configure;
use Cake\Http\Exception\ForbiddenException;
use Cake\Http\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Cake\Http\Response;
use Cake\View\Exception\MissingTemplateException;
class GeneratesGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function show()
{
}
}
Create a folder Generates at src/Template and under that folder, create a View file called show.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Generates/show.php
<h1>This is CakePHP tutorial and this is an example of Generating URLs<h1> </h1> </h1>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/generate
Output
The above URL will produce the following output −

Guide rapide CakePHP Routing
Guide rapide CakePHP routing is useful, when we want to inform client applications that, this URL has been moved. The URL can be redirected using the following function −
static Cake\Routing\Router::redirect($route, $url, $options =[])
There are three arguments to the above function as follows −
A string describing the template of the route.
A URL to redirect to.
An array matching the named elements in the route to regular expressions which that element should match.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown below. Here, we have used controllers that were created previously.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('/generate',['controller'=>'Generates','action'=>'show']);
$builder->redirect('/redirect','https://tutorialspoint.com/');
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Execute the above example by visiting the following URLs.
URL 1 − http://localhost/cakephp4/generate
Output for URL 1

URL 2 − http://localhost/cakephp4/redirect
Output for URL 2
You will be redirected to https://tutorialspoint.com
CakePHP - Guide rapide CakePHPs
The controller as the name indicates controls the application. It acts like a bridge between models and views. Guide rapide CakePHPs handle request data, makes sure that correct models are called and right response or view is rendered.
Methods in the controllers’ class are called actions. Each controller follows naming conventions. The Guide rapide CakePHP class names are in plural form, Camel Cased, and end in Guide rapide CakePHP — PostsGuide rapide CakePHP.
AppGuide rapide CakePHP
The AppConttroller class is the parent class of all applications’ controllers. This class extends the Guide rapide CakePHP class of CakePHP. AppGuide rapide CakePHP is defined at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/AppGuide rapide CakePHP.php. The file contains the following code.
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP;
class AppGuide rapide CakePHP extends Guide rapide CakePHP {
public function initialize(): void {
parent::initialize();
$this->loadComponent('RequestHandler');
$this->loadComponent('Flash');
}
}
AppGuide rapide CakePHP can be used to load components that will be used in every controller of your application. The attributes and methods created in AppGuide rapide CakePHP will be available in all controllers that extend it. The initialize() method will be invoked at the end of controller’s constructor to load components.
Guide rapide CakePHP Actions
The methods in the controller class are called Actions. These actions are responsible for sending appropriate response for browser/user making the request. View is rendered by the name of action, i.e., the name of method in controller.
Example
class RecipesGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function view($id) {
// Action logic goes here.
}
public function share($customerId, $recipeId) {
// Action logic goes here.
}
public function search($query) {
// Action logic goes here.
}
}
As you can see in the above example, the RecipesGuide rapide CakePHP has 3 actions − View, Share, and Search.
Guide rapide CakePHPing
For redirecting a user to another action of the same controller, we can use the setAction() method. The following is the syntax for the setAction() method.
Cake\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP::setAction($action, $args...)
The following code will redirect the user to index action of the same controller.
$this->setAction('index');
The following example shows the usage of the above method.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('/redirect-controller',['controller'=>'Guide rapide CakePHPs','action'=>'action1']);
$builder->connect('/redirect-controller2',['controller'=>'Guide rapide CakePHPs','action'=>'action2']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Core\Configure;
use Cake\Http\Exception\ForbiddenException;
use Cake\Http\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Cake\Http\Response;
use Cake\View\Exception\MissingTemplateException;
class Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function action1() {
}
public function action2(){
echo "redirecting from action2";
$this->setAction('action1');
}
}
Create a directory Guide rapide CakePHPs at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called action1.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Guide rapide CakePHPs/action1.php
<h1>This is an example of how to redirect within controller.</h1>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL.
http://localhost/cakephp4/redirect-controller
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

Now, visit the following URL: http://localhost/cakephp4/redirect-controller2
The above URL will give you the following output.

Loading Models
In CakePHP, a model can be loaded using the loadModel() method. The following is the syntax for the loadModel() method −
Cake\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP::loadModel(string $modelClass, string $type)
There are two arguments to the above function as follows −
The first argument is the name of model class.
The second argument is the type of repository to load.
Example
If you want to load Guide rapide CakePHPs model in a controller, then it can be loaded by writing the following line in controller’s action.
$this->loadModel('Guide rapide CakePHPs');
CakePHP - Views
The letter “V” in the MVC is for Views. Views are responsible for sending output to user based on request. View Classes is a powerful way to speed up the development process.
View Templates
The View Templates file of CakePHP gets data from controller and then render the output so that it can be displayed properly to the user. We can use variables, various control structures in template.
Template files are stored in src/Template/, in a directory named after the controller that uses the files, and named after the action it corresponds to. For example, the Viewfile for the Products controller’s “view()” action, would normally be found in src/Template/Products/view.php.
In short, the name of the controller (ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP) is same as the name of the folder (Products) but without the word Guide rapide CakePHP and name of action/method (view()) of the controller (ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP) is same as the name of the View file(view.php).
View Guide rapide CakePHP
View variables are variables which get the value from controller. We can use as many variables in view templates as we want. We can use the set() method to pass values to variables in views. These set variables will be available in both the view and the layout your action renders. The following is the syntax of the set() method.
Cake\View\View::set(string $var, mixed $value)
This method takes two arguments − the name of the variable and its value.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
// Register scoped middleware for in scopes.
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('template',['controller'=>'Products','action'=>'view']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Core\Configure;
use Cake\Http\Exception\ForbiddenException;
use Cake\Http\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Cake\Http\Response;
use Cake\View\Exception\MissingTemplateException;
class ProductsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function view(){
$this->set('Product_Guide rapide CakePHP','XYZ');
}
}
Create a directory Products at src/Template and under that folder create a View file called view.php. Copy the following code in that file.
Value of variable is: <?php echo $Product_Guide rapide CakePHP; ? >
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL.
http://localhost/cakephp4/template
Output
The above URL will produce the following output.

CakePHP - Extending Views
Many times, while making web pages, we want to repeat certain part of pages in other pages. CakePHP has such facility by which one can extend view in another view and for this, we need not repeat the code again.
The extend() method is used to extend views in View file. This method takes one argument, i.e., the name of the view file with path. Don’t use extension .ctp while providing the name of the View file.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('extend',['controller'=>'Extends','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create an ExtendsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ExtendsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ExtendsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class ExtendsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
}
}
?>
Create a directory Extends at src/Template and under that folder create a View file called header.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Extends/header.php
<div align="center">
<h1>Common Header</h1>
</div>
= $this->fetch('content') ?>
Create another View under Extends directory called index.php. Copy the following code in that file. Here, we are extending the above view header.php.
src/Template/Extends/index.php
<?php $this->extend('header'); ?>
This is an example of extending view.
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL http://localhost/cakephp4/extend
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP - View Elements
Certain parts of the web pages are repeated on multiple web pages, but at different locations. CakePHP can help us reuse these repeated parts. These reusable parts are called Elements - help box, extra menu, etc. An element is basically a mini-view. We can also pass variables in elements.
Cake\View\View::element(string $elementPath, array $data, array $options =[]
There are three arguments to the above function as follows −
The first argument is the name of the template file in the /src/Template/element/ folder.
The second argument is the array of data to be made available to the rendered view.
The third argument is for the array of options. e.g. cache.
Out of the 3 arguments, the first one is compulsory, while the rest are optional.
Example
Create an element file at src/Template/element directory called helloworld.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/element/helloworld.php
<p>Hello World</p>
Create a folder Elems at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Elems/index.php
Element Example: <?php echo $this->element('helloworld'); ?>
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
$builder->connect('/element-example',['controller'=>'Elems','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create an ElemsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ElemsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ElemsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class ElemsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
}
}
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL http://localhost/cakephp4/element-example
Output
Upon execution, the above URL will give you the following output.

CakePHP - View Events
There are several callbacks/events that we can use with View Events. These events are helpful to perform several tasks before something happens or after something happens. The following is a list of callbacks that can be used with CakePHP −
| Sr.No | Event Function & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Helper::beforeRender(Event $event,$viewFile) The beforeRender method is called after the controller’s beforeRender method but before the controller renders view and layout. This receives the file being rendered as an argument. |
| 2 |
Helper::beforeRenderFile(Event $event, $viewFile) This method is called before each view file is rendered. This includes elements, views, parent views and layouts. |
| 3 |
Helper::afterRenderFile(Event $event, $viewFile, $content) This method is called after each View file is rendered. This includes elements, views, parent views and layouts. A callback can modify and return $content to change how the rendered content will be displayed in the browser. |
| 4 |
Helper::afterRender(Event $event, $viewFile) This method is called after the view has been rendered, but before the layout rendering has started. |
| 5 |
Helper::beforeLayout(Event $event, $layoutFile) This method is called before the layout rendering starts. This receives the layout filename as an argument. |
| 6 |
Helper::afterLayout(Event $event, $layoutFile) This method is called after the layout rendering is complete. This receives the layout filename as an argument. |
CakePHP - Working with Database
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
Further, we also need to configure our database in config/app_local.php file.
'Datasources' => [
'default' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
'username' => 'my_app',
'password' => 'secret',
'database' => 'my_app',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL', null),
],
/*
* The test connection is used during the test suite.
*/
'test' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
//'port' => 'non_standard_port_number',
'username' => 'my_app',
'password' => 'secret',
'database' => 'test_myapp',
//'schema' => 'myapp',
],
],
The default connection has following details −
'host' => 'localhost', 'username' => 'my_app', 'password' => 'secret', 'database' => 'my_app',
You can change the details, i.e. host, username, password and database as per your choice.
Once done, make sure it is updated in config/app_local.php in Datasources object.
Now, we will continue with above details, go to your phpmyadmin or mysql database and create user my_app as shown below −

Give the necessary privileges and save it. Now, we have the database details as per the configuration mentioned in app_local.php. When you check CakePHP home page, this is what you should get −

Now, we will create the following users’ table in the database.
CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
Insert a Record
To insert a record in database, we first need to get hold of a table using TableRegistry class. We can fetch the instance out of registry using get() method. The get() method will take the name of the database table as an argument.
This new instance is used to create new entity. Set necessary values with the instance of new entity. We now have to call the save() method with TableRegistry class’s instance which will insert new record in database.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/users/add', ['controller' => 'Users', 'action' => 'add']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/controller/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\ORM\TableRegistry;
use Cake\Datasource\ConnectionManager;
use Cake\Auth\DefaultPasswordHasher;
class UsersGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function add(){
if($this->request->is('post')){
$username = $this->request->getData('username');
$hashPswdObj = new DefaultPasswordHasher;
$password = $hashPswdObj->hash($this->request->getData('password'));
$users_table = TableRegistry::get('users');
$users = $users_table->newEntity($this->request->getData());
$users->username = $username;
$users->password = $password;
$this->set('users', $users);
if($users_table->save($users))
echo "User is added.";
}
}
}
?>
Create a directory Users at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called add.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Users/add.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/users/add'));
echo $this->Form->control('username');
echo $this->Form->control('password');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL. http://localhost/cakephp4/users/add
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

The data will be saved in the users table as shown below −

CakePHP - View a Record
To view records of database, we first need to get hold of a table using the TableRegistry class. We can fetch the instance out of registry using get() method. The get() method will take the name of the database table as argument.
Now, this new instance is used to find records from database using find() method. This method will return all records from the requested table.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/users', ['controller' => 'Users', 'action' => 'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/controller/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\ORM\TableRegistry;
use Cake\Datasource\ConnectionManager;
class UsersGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$users = TableRegistry::get('users');
$query = $users->find();
$this->set('results',$query);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Users at src/Template, ignore if already created, and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Users/index.ctp
<a href="add">Add User</a>
| ID | Username | Password | Edit | Delete | ".$row->id." | "; echo ""; echo " | ".$row->password." | "; echo "Edit | "; echo "Delete | "; endforeach; ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL http://localhost/cakephp4/users
Output
Upon execution, the above URL will give you the following output.

CakePHP - Update a Record
To update a record in database, we first need to get hold of a table using TableRegistry class. We can fetch the instance out of registry using the get() method. The get() method will take the name of the database table as an argument. Now, this new instance is used to get particular record that we want to update.
Call the get() method with this new instance, and pass the primary key to find a record, which will be saved in another instance. Use this instance, to set new values that you want to update and then, finally call the save() method with the TableRegistry class’s instance to update record.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/users/edit', ['controller' => 'Users', 'action' => 'edit']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/controller/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\ORM\TableRegistry;
use Cake\Datasource\ConnectionManager;
class UsersGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$users = TableRegistry::get('users');
$query = $users->find();
$this->set('results',$query);
}
public function edit($id){
if($this->request->is('post')){
$username = $this->request->getData('username');
$password = $this->request->getData('password');
$users_table = TableRegistry::get('users');
$users = $users_table->get($id);
$users->username = $username;
$users->password = $password;
if($users_table->save($users))
echo "User is udpated";
$this->setAction('index');
} else {
$users_table = TableRegistry::get('users')->find();
$users = $users_table->where(['id'=>$id])->first();
$this->set('username',$users->username);
$this->set('password',$users->password);
$this->set('id',$id);
}
}
}
?>
Create a directory Users at src/Template, ignore if already created, and under that directory create a view called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Users/index.php
<a href="add">Add User</a>
| ID | Username | Password | Edit | Delete | ".$row->id." | "; echo "".$row->username." | "; echo "".$row->password." | "; echo "Edit | "; echo "Delete | "; endforeach; ?>
Create another View file under the Users directory called edit.php and copy the following code in it.
src/Template/Users/edit.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/users/edit/'.$id));
echo $this->Form->control('username',['value'=>$username]);
echo $this->Form->control('password',['value'=>$password]);
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL and click on Edit link to edit record.
http://localhost/cakephp4/users
Output
After visiting the above URL, it will display the records in users table as shown below −
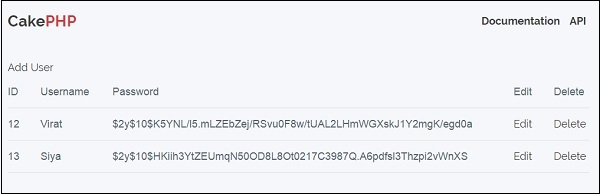
Click on Edit button and it will display you following screen −

Now, we will update the name Guide rapide CakePHP to Guide rapide CakePHP123 and submit the details. The next screen displayed will be as follows −

CakePHP - Delete a Record
To delete a record in database, we first need to get hold of a table using the TableRegistry class. We can fetch the instance out of registry using the get() method. The get() method will take the name of the database table as an argument. Now, this new instance is used to get particular record that we want to delete.
Call the get() method with this new instance and pass the primary key to find a record which will be saved in another instance. Use the TableRegistry class’s instance to call the delete method to delete record from database.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/users/delete', ['controller' => 'Users', 'action' => 'delete']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/controller/UsersGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\ORM\TableRegistry;
use Cake\Datasource\ConnectionManager;
class UsersGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$users = TableRegistry::get('users');
$query = $users->find();
$this->set('results',$query);
}
public function delete($id){
$users_table = TableRegistry::get('users');
$users = $users_table->get($id);
$users_table->delete($users);
echo "User deleted successfully.";
$this->setAction('index');
}
}
?>
Just create an empty View file under Users directory called delete.ctp.
src/Template/Users/delete.ctp
Create a directory Users at src/Template, ignore if already created, and under that directory create a Viewfile called index.ctp. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Users/index.ctp
<a href="add">Add User</a>
| ID | Username | Password | Edit | Delete | ".$row->id." | "; echo "".$row->username." | "; echo "".$row->password." | "; echo "Edit | "; echo "Delete | "; endforeach; ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL and click on Delete link to delete record.
http://localhost:85/CakePHP/users
Output
After visiting the above URL and clicking on the Delete link, you will receive the following output where you can delete record.

Click on Delete link to delete the record.

CakePHP - Services
This chapter deals with the information about the authentication process available in CakePHP.
Guide rapide CakePHP
Guide rapide CakePHP is the process of identifying the correct user. CakePHP supports three types of authentication.
FormAuthenticate − It allows you to authenticate users based on form POST data. Usually, this is a login form that users enter information into. This is default authentication method.
BasicAuthenticate − It allows you to authenticate users using Basic HTTP authentication
DigestAuthenticate − It allows you to authenticate users using Digest HTTP authentication.
Example for FormGuide rapide CakePHP
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Core\Plugin;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
use Cake\Routing\Router;
Router::defaultRouteClass('DashedRoute');
Router::scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $routes) {
$routes->connect('/auth',['controller'=>'Authexs','action'=>'index']);
$routes->connect('/login',['controller'=>'Authexs','action'=>'login']);
$routes->connect('/logout',['controller'=>'Authexs','action'=>'logout']);
$routes->fallbacks('DashedRoute');
});
Plugin::routes();
Change the code of AppGuide rapide CakePHP.php file as shown in the following program.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/AppGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Event\Event;
use Cake\Guide rapide CakePHP\Component\AuthComponent;
class AppGuide rapide CakePHP extends Guide rapide CakePHP {
public function initialize() {
parent::initialize();
$this->loadComponent('RequestHandler');
$this->loadComponent('Flash');
$this->loadComponent('Auth', [
'authenticate' => [
'Form' => [
'fields' => [
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'password'
]
]
],
'loginAction' => [
'controller' => 'Authexs',
'action' => 'login'
],
'loginGuide rapide CakePHP' => [
'controller' => 'Authexs',
'action' => 'index'
],
'logoutGuide rapide CakePHP' => [
'controller' => 'Authexs',
'action' => 'login'
]
]);
}
public function beforeFilter(Event $event) {
$this->Auth->allow(['index','view']);
$this->set('loggedIn', $this->Auth->user());
}
}
Create AuthexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/AuthexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/AuthexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\ORM\TableRegistry;
use Cake\Datasource\ConnectionManager;
use Cake\Event\Event;
use Cake\Auth\DefaultPasswordHasher;
class AuthexsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
var $components = array('Auth');
public function index(){
}
public function login(){
if($this->request->is('post')) {
$user = $this->Auth->identify();
if($user){
$this->Auth->setUser($user);
return $this->redirect($this->Auth->redirectUrl());
} else
$this->Flash->error('Your username or password is incorrect.');
}
}
public function logout(){
return $this->redirect($this->Auth->logout());
}
}
?>
Create a directory Authexs at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called login.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Authexs/login.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create();
echo $this->Form->control('username');
echo $this->Form->control('password');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Create another View file called logout.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Authexs/logout.php
You are successfully logged out.
Create another View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Authexs/index.php
You are successfully logged in.
<?php echo $this->Html->link('logout',[
"controller" => "Authexs","action" => "logout"
]);
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL.
http://localhost/cakephp4/auth
Sortie
Comme l'authentification a été mise en œuvre, et une fois que vous essayez de visiter l'URL ci-dessus, vous serez redirigé vers la page de connexion comme indiqué ci-dessous.

Après avoir fourni les informations d'identification correctes, vous serez connecté et redirigé vers l'écran comme indiqué ci-dessous.

Après avoir cliqué sur le lien déconnexion, vous serez à nouveau redirigé vers l'écran de connexion.
CakePHP - Gestion des erreurs et des exceptions
La panne du système doit être gérée efficacement pour le bon fonctionnement du système. CakePHP est livré avec un système de capture d'erreurs par défaut, qui imprime et enregistre les erreurs au fur et à mesure qu'elles se produisent. Ce même gestionnaire d'erreurs est utilisé pour intercepter les Exceptions.
Le gestionnaire d'erreurs affiche les erreurs lorsque le débogage est vrai et enregistre l'erreur lorsque le débogage est faux. CakePHP possède un certain nombre de classes d'exceptions et la gestion intégrée des exceptions capturera toute exception non interceptée et affichera une page utile.
Configuration des erreurs et des exceptions
Les erreurs et exceptions peuvent être configurées dans le fichier configapp.php. La gestion des erreurs accepte quelques options qui vous permettent d'adapter la gestion des erreurs à votre application -
| Option | Type de données | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| niveau d'erreur | int |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| trace | booléen | Inclure les traces de pile pour les erreurs dans les fichiers journaux. Les traces de pile seront incluses dans le journal après chaque erreur. Ceci est utile pour déterminer où et quand des erreurs sont générées. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| exceptionRenderer | chaîne | La classe responsable du rendu des exceptions non interceptées. Si vous choisissez une classe personnalisée, vous devez placer le fichier de cette classe dans src/Error. Cette classe doit implémenter une méthode render(). | |||||||||||||||||||||
| journal | booléen | Lorsque c'est vrai, les exceptions + leurs traces de pile seront enregistrées dans CakeLogLog. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| skipLog | tableau | Un tableau de noms de classes d'exceptions qui ne doivent pas être enregistrés. Ceci est utile pour supprimer les NotFoundExceptions ou d'autres messages de journaux courants mais sans intérêt. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| extraFatalErrorMemory | int | Définissez le nombre de mégaoctets pour augmenter la limite de mémoire lorsqu'une erreur fatale est rencontrée. Cela permet de respirer pour terminer la journalisation ou la gestion des erreurs. |
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/exception/:arg1/:arg2',
['controller'=>'Exps','action'=>'index'],
['pass' => ['arg1', 'arg2']]);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create ExpsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ExpsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ExpsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Core\Exception\Exception;
class ExpsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function index($arg1,$arg2) {
try{
$this->set('argument1',$arg1);
$this->set('argument2',$arg2);
if(($arg1 > 1 || $arg1 > 10) || ($arg2 10))
throw new Exception("One of the number is out of range [1-10].");
} catch(\Exception $ex){
echo $ex->getMessage();
}
}
}
?>
Create a directory Exps at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Exps/index.php
This is CakePHP tutorial and this is an example of Passed arguments.<br> Argument-1: =$argument1?><br> Argument-2: =$argument2?><br>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL.
http://localhost/cakephp4/exception/5/0
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP - Logging
Logging in CakePHP is a very easy task. You just have to use one function. You can log errors, exceptions, user activities, action taken by users, for any background process like cronjob. Logging data in CakePHP is easy. The log() function is provided by the LogTrait, which is the common ancestor for almost all CakePHP classes.
Logging Configuration
We can configure the log in file config/app.php. There is a log section in the file, where you can configure logging options as shown in the following screenshot.

By default, you will see two log levels − error and debug already configured for you. Each will handle different level of messages.
CakePHP supports various logging levels as shown below −
Emergency − System is unusable
Alert − Action must be taken immediately
Critical − Critical conditions
Error − Error conditions
Warning − Warning conditions
Notice − Normal but significant condition
Info − Informational messages
Debug − Debug-level messages
Writing to Log file
There are two ways by which, we can write in a Log file.
The first is to use the static write() method. The following is the syntax of the static write() method.
| Syntax | write( integer|string $level, mixed $message, string|array $context [] ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
The severity level of the message being written. The value must be an integer or string matching a known level. Message content to log. Additional data to be used for logging the message. The special scope key can be passed to be used for further filtering of the log engines to be used. If a string or a numerically index array is passed, it will be treated as the scope key. See Cake\Log\Log::config() for more information on logging scopes. |
| Returns | boolean |
| Description | Writes the given message and type to all of the configured log adapters. Configured adapters are passed both the $level and $message variables. $level is one of the following strings/values. |
The second is to use the log() shortcut function available on any using the LogTrait Calling log() will internally call Log::write() −
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',
['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('logex',['controller'=>'Logexs','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a LogexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LogexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LogexsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Log\Log;
class LogexsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
/*The first way to write to log file.*/
Log::write('debug',"Something didn't work.");
/*The second way to write to log file.*/
$this->log("Something didn't work.",'debug');
}
}
?>
Create a directory Logexs at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Logexs/index.php
Something is written in log file. Check log file logs\debug.log
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL.
http://localhost/cakephp4/logex
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

The logs will be added to log/debug.log file −

CakePHP - Form Handling
CakePHP provides various in built tags to handle HTML forms easily and securely. Like many other PHP frameworks, major elements of HTML are also generated using CakePHP. Following are the various functions used to generate HTML elements.
The following functions are used to generate select options −
| Syntax | _selectGuide rapide CakePHP( array $elementsarray(), array $parentsarray(), boolean $showParentsnull, array $attributesarray() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array |
| Description | Returns an array of formatted OPTION/OPTGROUP elements |
The following functions are used to generate HTML select element.
| Syntax | select( string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP, array $options array(), array $attributes array() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
Guide rapide CakePHP attribute of the SELECT Array of the OPTION elements (as 'value'=>'Text' pairs) to be used in the SELECT element. |
| Returns | Formatted SELECT element. |
| Description | Returns a formatted SELECT element. |
The following functions are used to generate button on HTML page.
| Syntax | Button(string $title, array $optionsarray() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | HTML button tag. |
| Description | Creates a tag. The type attribute defaults to type="submit". You can change it to a different value by using $options['type']. |
The following functions are used to generate checkbox on HTML page.
| Syntax | Checkbox(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP, array $optionsarray() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | An HTML text input element. |
| Description | Creates a checkbox input widget. |
Les fonctions suivantes sont utilisées pour créer un formulaire sur une page HTML.
| Syntaxe | create( mixte $modelnull , tableau $optionsarray() ) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
||||||||
| Retours | Une balise d'ouverture FORM formatée. | ||||||||
| Description | Renvoie un élément HTML FORM. |
| Syntax | file(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP, array $optionsarray() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | A generated file input. |
| Description | Creates file input widget. |
sur une page HTML.
| Syntaxe | fichier(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP, array $optionsarray() ) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
||||||||
| Retours | Une entrée de fichier générée. | ||||||||
| Description | Crée un widget de saisie de fichier.
|
Les fonctions suivantes sont utilisées pour créer un élément caché sur une page HTML.
| Syntaxe |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
||||||||
| Retours | Une entrée cachée générée
|
||||||||
| Description | Crée un champ de saisie masqué |
| Syntaxe | Input(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP , array $options array() ) |
|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
| Retours | Widget Formulaire complété |
| Description | Génère un élément de saisie de formulaire complet avec une étiquette et un div wrapper |
| Syntaxe | Radio(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP , array $optionsarray() , array $attributesarray() ) td> |
|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
| Retours | Ensemble de widgets radio terminé |
| Description | Crée un ensemble de widgets radio. Créera une légende et un ensemble de champs par défaut. Utilisez $options pour contrôler cela. |
| Syntaxe | Soumettre(string $caption null, array $options array() ) |
|---|---|
| Paramètres |
|
| Retours | Un bouton de soumission HTML |
| Description | Crée un élément de bouton de soumission. Cette méthode générera éléments qui peuvent être utilisés pour soumettre et réinitialiser des formulaires en utilisant $options. Les soumissions d'images peuvent être créées en fournissant un chemin d'image pour $caption. |
The following functions are used to generate textarea element on HTML page.
| Syntax | Textarea(string $fieldGuide rapide CakePHP , array $options array() ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | A generated HTML text input element |
| Description | Creates a textarea widget |
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following code.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('register',['controller'=>'Registrations','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a RegistrationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RegistrationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RegistrationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class RegistrationsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$country = array('India','United State of America','United Kingdom');
$this->set('country',$country);
$gender = array('Male','Female');
$this->set('gender',$gender);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Registrations at src/Template and under that directory, create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Registrations/index.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/register'));
echo '<label for="country">Country</label>';
echo $this->Form->select('country',$country);
echo '<label for="gender">Gender</label>';
echo $this->Form->radio('gender ',$gender);
echo '<label for="address">Address</label>';
echo $this->Form->textarea('address');
echo $this->Form->file('profilepic');
echo '<div>'.$this->Form->checkbox('terms').
'<label for="country">Terms ∓ Guide rapide CakePHPs</label>
</div>';
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/register
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP - Internationalization
Like many other frameworks, CakePHP also supports Internationalization. We need to follow these steps to go from single language to multiple language.
Step 1
Create a separate locales directory resources\locales.
Step 2
Create subdirectory for each language, under the directory src\Locale. The name of the subdirectory can be two letter ISO code of the language or full locale name like en_US, fr_FR etc.
Step 3
Create separate default.po file under each language subdirectory. This file contains entry in the form of msgid and msgstr, as shown in the following program.
msgid "msg" msgstr "CakePHP Internationalization example."
Here, the msgid is the key which will be used in the View template file and msgstr is the value which stores the translation.
Step 4
In the View template file, we can use the above msgid, as shown below which will be translated based on the set value of locale.
<?php echo __('msg'); ?>
The default locale can be set in the config/app.php file by the following line.
'defaultLocale' => env('APP_DEFAULT_LOCALE', 'en_US')
To change the local at runtime, we can use the following lines.
use Cake\I18n\I18n;
I18n::locale('de_DE');
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',
['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('locale',
['controller'=>'Localizations','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a LocalizationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LocalizationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LocalizationsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\I18n\I18n;
class LocalizationsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function index() {
if($this->request->is('post')) {
$locale = $this->request->getData('locale');
I18n::setLocale($locale);
}
}
}
?>
Create a locales directory at resources\locales. Create 3 directories called en_US, fr_FR, de_DE under the locales directory. Create a file under each directory called default.po. Copy the following code in the respective file.
resources/locales/en_US/default.po
msgid "msg" msgstr "CakePHP Internationalization example."
resources/locales/fr_FR/default.po
msgid "msg" msgstr "Exemple CakePHP internationalisation."
resources/locales/de_DE/default.po
msgid "msg" msgstr "CakePHP Internationalisierung Beispiel."
Create a directory Localizations at src/Template and under that directory, create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Localizations/index.php
Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/locale'));
echo $this->Form->radio("locale",
[
['value'=>'en_US','text'=>'Guide rapide CakePHP'],
['value'=>'de_DE','text'=>'German'],
['value'=>'fr_FR','text'=>'French'],
]
);
echo $this->Form->button('Change Language');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
<?php echo __('msg'); ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL. http://localhost/cakephp4/locale
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP provides Email class to manage email related functionalities. To use email functionality in any controller, we first need to load the Email class by writing the following line.
use Cake\Mailer\Email;
The Email class provides various useful methods which are described below.
| Syntax | From(string|array|null $email null, string|null $name null ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | It specifies from which email address; the email will be sent |
| Syntax | To(string|array|null $emailnull, string|null $namenull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | It specifies to whom the email will be sent |
| Syntax | Send(string|array|null $contentnull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array |
| Description | Send an email using the specified content, template and layout |
| Syntax | Subject(string|null $subjectnull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | Get/Set Subject |
| Syntax | Attachments(string|array|null $attachmentsnull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | Add attachments to the email message |
| Syntax | Bcc(string|array|null $emailnull, string|null $namenull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | Bcc |
| Syntax | cc( string|array|null $emailnull , string|null $namenull ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | array|$this |
| Description | Cc |
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/email',['controller'=>'Emails','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create an EmailsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/EmailsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/EmailsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Mailer\Email;
class EmailsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$email = new Email('default');
$email->to('abc@gmail.com')
->subject('About')
->send('My message');
}
}
?>
Create a directory Emails at src/Template and under that directory, create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Emails/index.php
Email Sent.
Before we send any email, we need to configure it. In the below screenshot, you can see that there are two transports, default and Gmail. We have used Gmail transport.
You need to replace the “GMAIL USERNAME” with your Gmail username and “APP PASSWORD” with your applications password. You need to turn on 2-step verification in Gmail and create a new APP password to send email.
config/app.php

Execute the above example by visiting the following URL − http://localhost/cakephp/email
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP - Session Management
Session allows us to manage unique users across requests, and stores data for specific users. Session data can be accessible anywhere, anyplace, where you have access to request object, i.e., sessions are accessible from controllers, views, helpers, cells, and components.
Accessing Session Object
Session object can be created by executing the following code.
$session = $this->request->session();
Writing Session Data
To write something in session, we can use the write() session method.
Session::write($key, $value)
The above method will take two arguments, the value and the key under, which the value will be stored.
Example
$session->write('name', 'Guide rapide CakePHP Gandhi');
Reading Session Data
To retrieve stored data from session, we can use the read() session method.
Session::read($key)
The above function will take only one argument, that is the key of the value, which was used at the time of writing session data. Once the correct key was provided, then the function will return its value.
Example
$session->read('name');
When you want to check whether, particular data exists in the session or not, then you can use the check() session method.
Session::check($key)
The above function will take only key as the argument.
Example
if ($session->check('name')) {
// name exists and is not null.
}
Delete Session Data
To delete data from session, we can use the delete() session method to delete the data.
Session::delete($key)
The above function will take only key of the value to be deleted from session.
Example
$session->delete('name');
When you want to read and then delete data from session then, we can use the consume() session method.
static Session::consume($key)
The above function will take only key as argument.
Example
$session->consume('name');
Destroying a Session
We need to destroy a user session, when the user logs out from the site and to destroy the session the destroy() method is used.
Session::destroy()
Example
$session->destroy();
Destroying session will remove all session data from server, but will not remove session cookie.
Renew a Session
In a situation, where you want to renew user session then, we can use the renew() session method.
Session::renew()
Example
$session->renew();
Complete Session
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('/session-object',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=>'index']);
$builder->connect('/session-read',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=>'retrieve_session_data']);
$builder->connect('/session-write',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=> 'write_session_data']);
$builder->connect('/session-check',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=>'check_session_data']);
$builder->connect('/session-delete',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=>'delete_session_data']);
$builder->connect('/session-destroy',['controller'=>'Sessions','action'=>'destroy_session_data']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a SessionsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/SessionsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/SessionsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class SessionsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function retrieveSessionData() {
//create session object
$session = $this->request->getSession();
//read data from session
$name = $session->read('name');
$this->set('name',$name);
}
public function writeSessionData(){
//create session object
$session = $this->request->getSession();
//write data in session
$session->write('name','Guide rapide CakePHP Gandhi');
}
public function checkSessionData(){
//create session object
$session = $this->request->getSession();
//check session data
$name = $session->check('name');
$address = $session->check('address');
$this->set('name',$name);
$this->set('address',$address);
}
public function deleteSessionData(){
//create session object
$session = $this->request->getSession();
//delete session data
$session->delete('name');
}
public function destroySessionData(){
//create session object
$session = $this->request->getSession();
//destroy session
$session->destroy();
}
}
?>
Create a directory Sessions at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called write_session_data.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Sessions/write_session_data.php
The data has been written in session.
Create another View file called retrieve_session_data.php under the same Sessions directory and copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Sessions/retrieve_session_data.php
Here is the data from session. Guide rapide CakePHP: =$name;?>
Create another View file called check_session_data.ctp under the same Sessions directory and copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Sessions/check_session_data.ctp
<?php if($name): ?> name exists in the session. <?php else: ?> name doesn't exist in the database <?php endif;?> <?php if($address): ?> address exists in the session. <?php else: ?> address doesn't exist in the database <?php endif;?>
Create another View file called delete_session_data.ctp, under the same Sessions directory and copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Sessions/delete_session_data.ctp
Data deleted from session.
Create another View file called destroy_session_data.ctp, under the same Sessions directory and copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Sessions/destroy_session_data.ctp
Session Guide rapide CakePHP.
Output
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL. This URL will help you write data in session.
http://localhost/cakephp4/session-write

Visit the following URL to read session data − http://localhost/cakephp4/session-read

Visit the following URL to check session data − http://localhost/cakephp4/session-check

Visit the following URL to delete session data − http://localhost/cakephp4/session-delete Visit the

Visit the following URL to destroy session data − http://localhost/cakephp4/session-destroy

CakePHP - Guide rapide CakePHP Management
Handling Guide rapide CakePHP with CakePHP is easy and secure. There is a Guide rapide CakePHPComponent class which is used for managing Guide rapide CakePHP. The class provides several methods for working with Guide rapide CakePHPs.
To work with cookies, add this 2 classes to your controller −
use Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP; use Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection;
The cookie object has to be created first to register a cookie.
$cookie = new Guide rapide CakePHP(name,value,expiration time,path,domain);
The name and value are mandatory and others are optional param.
Write Guide rapide CakePHP
Following is the syntax to write a cookie.
$cookie = new Guide rapide CakePHP(name,value,expiration time,path,domain);
The cookie created has to be added to cookieCollection as shown below −
$cookie = new Guide rapide CakePHP('name','XYZ');
$cookies = new Guide rapide CakePHPCollection([$cookie]);
If the cookie collection object is already created, the rest of the cookies can be added as shown below −
$cookies = $cookies->add($cookie);
Read Guide rapide CakePHP
To read cookie make use of get() method from cookiecollection.
Syntax
The syntax for read cookie is as follows −
Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection::get($name)
This will return you cookiecollection Interface, to get the value of the cookie, you will have to call the method getValue().
Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection Interface::getValue()
Check Guide rapide CakePHP
The has() method from cookieCollection will tell you, if the cookie is present or not.
Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection::has($name)
Example
echo $isPresent = $this->cookies->has('name');
Delete Guide rapide CakePHP
The remove() method is used to delete cookie. Following is the syntax of the remove() method.
Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection::remove($name)
The remove() method will take one argument, the name of cookie variable ($name) to delete.
Example 1
$test = $this->cookies->remove('name');
Example 2
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('cookie/testcookies',['controller'=>'Guide rapide CakePHPs','action'=>'testGuide rapide CakePHPs']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/Guide rapide CakePHPs/Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Http\Guide rapide CakePHP\Guide rapide CakePHPCollection;
class Guide rapide CakePHPsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public $cookies;
public function testGuide rapide CakePHPs() {
$cookie = new Guide rapide CakePHP('name','XYZ');
$this->cookies = new Guide rapide CakePHPCollection([$cookie]);
$cookie_val = $this->cookies->get('name');
$this->set('cookie_val',$cookie_val->getValue());
$isPresent = $this->cookies->has('name');
$this->set('isPresent',$isPresent);
$this->set('count', $this->cookies->count());
$test = $this->cookies->remove('name');
$this->set('count_afterdelete', $test->count());
}
}
?>
Create a directory Guide rapide CakePHPs at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called test_cookies.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Guide rapide CakePHP/test_cookies.php
The value of the cookie is: <?php echo $cookie_val; ?> <br> <?php if($isPresent): ?> The cookie is present. <?php else: ?> The cookie isn't present. <?php endif; ?> <br> <?php echo "The count of cookie before delete is :" .$count; ?> <br> <?php echo "The count of cookie after delete is :" .$count_afterdelete; ?>
Output
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL − http://localhost/cakephp4/cookie/testcookies

CakePHP - Security
Security is another important feature while building web applications. It assures the users of the website that, their data is secured. CakePHP provides some tools to secure your application.
Encryption and Decryption
Security library in CakePHP provides methods, by which we can encrypt and decrypt data. Following are the two methods, which are used for the same purpose.
static Cake\Utility\Security::encrypt($text, $key, $hmacSalt = null) static Cake\Utility\Security::decrypt($cipher, $key, $hmacSalt = null)
The encrypt method will take text and key as the argument to encrypt data and the return value will be the encrypted value with HMAC checksum.
To hash a data, hash() method is used. Following is the syntax of the hash() method.
static Cake\Utility\Security::hash($string, $type = NULL, $salt = false)
CSRF
CSRF stands for Cross Site Request Forgery. By enabling the CSRF Component, you get protection against attacks. CSRF is a common vulnerability in web applications.
It allows an attacker to capture and replay a previous request, and sometimes submit data requests using image tags or resources on other domains. The CSRF can be enabled by simply adding the CsrfComponent to your components array as shown below −
public function initialize(): void {
parent::initialize();
$this->loadComponent('Csrf');
}
The CsrfComponent integrates seamlessly with FormHelper. Each time you create a form with FormHelper, it will insert a hidden field containing the CSRF token.
While this is not recommended, you may want to disable the CsrfComponent on certain requests. You can do so by using the controller’s event dispatcher, during the beforeFilter() method.
public function beforeFilter(Event $event) {
$this->eventManager()->off($this->Csrf);
}
Security Component
Security Component applies tighter security to your application. It provides methods for various tasks like −
Restricting which HTTP methods your application accepts − You should always verify the HTTP method, being used before executing side-effects. You should check the HTTP method or use Cake\Network\Request::allowMethod() to ensure the correct HTTP method is used.
-
Form tampering protection − By default, the SecurityComponent prevents users from tampering with forms in specific ways. The SecurityComponent will prevent the following things −
Unknown fields cannot be added to the form.
Fields cannot be removed from the form.
Values in hidden inputs cannot be modified.
Requiring that SSL be used − All actions to require a SSL- secured
Limiting cross controller communication − We can restrict which controller can send request to this controller. We can also restrict which actions can send request to this controller’s action.
Example
Make changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',
['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('login',['controller'=>'Logins','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a LoginsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LoginsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/LoginsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class LoginsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function initialize() : void {
parent::initialize();
$this->loadComponent('Security');
}
public function index(){
}
}
?>
Create a directory Logins at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Logins/index.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/login'));
echo $this->Form->control('username');
echo $this->Form->control('password');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL − http://localhost/cakephp4/login
Output
Upon execution, you will receive the following output.

CakePHP - Validation
Often while making websites, we need to validate certain things before processing data further. CakePHP provides validation package, to build validators that can validate data with ease.
Validation Methods
CakePHP provides various validation methods in the Validation Class. Some of the most popular of them are listed below.
| Syntax | Add(string $field, array|string $name, array|Cake\Validation\ValidationRule $rule [] ) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Adds a new rule to a field's rule set. If second argument is an array, then rules list for the field will be replaced with second argument and third argument will be ignored. |
| Syntax | allowEmpty(string $field, boolean|string|callable $whentrue, string|null $messagenull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Allows a field to be empty. |
| Syntax | alphanumeric (string $field, string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null $whennull) |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add an alphanumeric rule to a field. |
| Syntax | creditCard(string $field , string $type'all', string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null $whennull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add a credit card rule to a field. |
| Syntax | Email(string $field , boolean $checkMXfalse, string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null, $whennull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add an email validation rule to a field. |
| Syntax | maxLength(string $field, integer $max, string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null $whennull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add a string length validation rule to a field. |
| Syntax | minLength(string $field, integer $min, string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null $whennull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add a string length validation rule to a field. |
| Syntax | notBlank(string $field, string|null $messagenull, string|callable|null $whennull) |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | $this |
| Description | Add a notBlank rule to a field. |
CakePHP - Creating Validators
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
use Cake\Validation\Validator; $validator = new Validator();
Validating Data
Once, we have created validator, we can use the validator object to validate data. The following code explains, how we can validate data for login webpage.
$validator->notEmpty('username', 'We need username.')->add(
'username', 'validFormat', ['rule' => 'email','message' => 'E-mail must be valid']);
$validator->notEmpty('password', 'We need password.');
$errors = $validator->errors($this->request->data());
Using the $validator object, we have first called the notEmpty() method, which will ensure that the username must not be empty. After that, we have chained the add() method to add one more validation for proper email format.
After that we have added validation for password field with notEmpty() method, which will confirm that password field must not be empty.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('validation',['controller'=>'Valids','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a ValidsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ValidsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/ValidsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Validation\Validator;
class ValidsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$validator = new Validator();
$validator->notEmpty('username', 'We need username.')->add(
'username', 'validFormat', ['rule' => 'email','message' => 'E-mail must be valid']);
$validator->notEmpty('password', 'We need password.');
$errors = $validator->errors($this->request->getData());
$this->set('errors',$errors);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Valids at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Valids/index.php
<?php if($errors) {
foreach($errors as $error)
foreach($error as $msg)
echo '<font color="red">'.$msg.'<br>';
} else {
echo "No errors.";
}
echo $this->Form->create(NULL,array('url'=>'/validation'));
echo $this->Form->control('username');
echo $this->Form->control('password');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/validation
Output
Click on the submit button without entering anything. You will receive the following output.

Http - Client
The http client can be used to make requests like GET, POST, PUT etc.
To work with http client, add the following −
use Cake\Http\Client;
Let us work on example to understand working of HTTP client.
HTTP GET Method
To get the data from give http url, you can do as follows −
$response = $http->get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users');
In case, you need to pass some query params, they can be passed as follows −
$response = $http->get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users', ["id", 1]);
To get the response, you can do as follows −
For normal text data −
$response->getBody();
For Json −
$response->getJson();
For Xml −
$response->getXml()
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('getData',['controller'=>'Requests','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Http\Client;
class RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$http = new Client();
$response = $http->get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users');
$stream = $response->getJson();
$this->set('response',$stream);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Requests at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Requests/index.php
<h3>All Users from url : https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users</h3>
<?php if($response) {
foreach($response as $res => $val) {
echo '<font color="gray">Guide rapide CakePHP: '.$val["name"].' Email -'.$val["email"].'</font><br>';
}
}
?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/getData
Output
Click on the submit button without entering anything. You will receive the following output.

HTTP POST Method
To work with post, you need to call $http client as follows −
$response = $http->post('yoururl', data);
Let us see one example on the same.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('postData',['controller'=>'Requests','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file. Ignore if already created.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\Http\Client;
class RequestsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$http = new Client();
$response = $http->post('https://postman-echo.com/post', [
'name'=> 'ABC',
'email' => 'xyz@gmail.com'
]);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Requests at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Requests/index.php
<h3>Testing Post Method</h3>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/postData
Output
Given below is the output of the code −

Similarly, you can try for PUT method.
$http = new Client();
$response = $http->put('https://postman-echo.com/post', [
'name'=> 'ABC',
'email' => 'xyz@gmail.com'
]);
CakePHP - Pagination
If we want to show a set of data that is huge, we can use pagination and this feature is available with cake php 4 which is very easy to use.
We have a table titled “articles” with following data −

Let us use pagination to display the data in the form of pages, instead of showing them all together.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('posts',['controller'=>'Posts','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a PostsGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/PostsGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file. Ignore, if already created.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/PostsGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
class PostsGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function index(){
$this->loadModel('articles');
$articles = $this->articles->find('all')->order(['articles.id ASC']);
$this->set('articles', $this->paginate($articles, ['limit'=> '3']));
}
}
?>
The data from articles table is fetched using −
$this->loadModel('articles');
$articles = $this->articles->find('all')->order(['articles.id ASC']);
To apply pagination and we would show the data with 3 per records and the same is done as follows −
$this->set('articles', $this->paginate($articles, ['limit'=> '3']));
This is enough to activate pagination on the articles tables.
Create a directory Posts at src/Template and under that directory create a Viewfile called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Posts/index.php
<div>
<?php foreach ($articles as $key=>$article) {?>
<a href="#">
<div>
<p>= $article->title ?> </p>
<p>= $article->details ?></p>
</div>
</a>
<br>
<?php }
?>
<ul class="pagination">
= $this->Paginator->prev("
= $this->Paginator->numbers() ?>
= $this->Paginator->next(">>") ?>
</ul>
</div>
The pagination for the list of pages is done as follows −
-
= $this->Paginator->prev("
= $this->Paginator->numbers() ?>
= $this->Paginator->next(">>") ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/posts
Output
When you run the code, you will see the following output −

Click on the numbers below, to switch to next page, or use the next or previous button.
For example

You will see that page=2 is appended to the page url in the browser.
CakePHP - Date and Time
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
To work with date and time, include the class in your controller
use Cake\I18n\FrozenTime;
Let us work, on an example and display date and time, using FrozenTime class.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('datetime',['controller'=>'Dates','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a DatesGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/DatesGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file. Ignore if already created.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/DatesGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\I18n\FrozenTime;
class DatesGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP{
public function index(){
$time = FrozenTime::now();
$now = FrozenTime::parse('now');
$_now = $now->i18nFormat('yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');
$this->set('timenow', $_now);
$now = FrozenTime::parse('now');
$nice = $now->nice();
$this->set('nicetime', $nice);
$hebrewdate = $now->i18nFormat(\IntlDateFormatter::FULL, null, 'en-IR@calendar=hebrew');
$this->set("hebrewdate",$hebrewdate);
$japanesedate = $now->i18nFormat(\IntlDateFormatter::FULL, null, 'en-IR@calendar=japanese');
$this->set("japanesedate",$japanesedate);
$time = FrozenTime::now();
$this->set("current_year",$time->year);
$this->set("current_month",$time->month);
$this->set("current_day",$time->day);
}
}
?>
Create a directory Dates at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Dates/index.php
<?php echo "The Current date and time is = ".$timenow; echo "<br/>"; echo "Using nice format available = ".$nicetime; echo "<br>"; echo "Date and Time as per Hebrew Calender =" .$hebrewdate; echo "<br>"; echo "Date and Time as per Japanese Calender =" .$japanesedate; echo "<br>"; echo "Current Year = ".$current_year; echo "<br>"; echo "Current Month = ".$current_month; echo "<br>"; echo "Current Day = ".$current_day; ?>
Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/datetime
Output
When you run the code, you will see the following output −

CakePHP - File upload
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
Example
Make Changes in the config/routes.php file, as shown in the following program.
config/routes.php
<?php use Cake\Http\Middleware\CsrfProtectionMiddleware;
use Cake\Routing\Route\DashedRoute;
use Cake\Routing\RouteBuilder;
$routes->setRouteClass(DashedRoute::class);
$routes->scope('/', function (RouteBuilder $builder) {
$builder->registerMiddleware('csrf', new CsrfProtectionMiddleware([
'httpOnly' => true,
]));
$builder->applyMiddleware('csrf');
//$builder->connect('/pages',['controller'=>'Pages','action'=>'display', 'home']);
$builder->connect('fileupload',['controller'=>'Files','action'=>'index']);
$builder->fallbacks();
});
Create a FilesGuide rapide CakePHP.php file at src/Guide rapide CakePHP/FilesGuide rapide CakePHP.php. Copy the following code in the controller file. Ignore, if already created.
Create uploads/ directory in src/. The files uploaded will be saved in uploads/ folder.
src/Guide rapide CakePHP/FilesGuide rapide CakePHP.php
<?php namespace App\Guide rapide CakePHP;
use App\Guide rapide CakePHP\AppGuide rapide CakePHP;
use Cake\View\Helper\FormHelper;
class FilesGuide rapide CakePHP extends AppGuide rapide CakePHP {
public function index(){
if ($this->request->is('post')) {
$fileobject = $this->request->getData('submittedfile');
$uploadPath = '../uploads/';
$destination = $uploadPath.$fileobject->getClientFilename();
// Existing files with the same name will be replaced.
$fileobject->moveTo($destination);
}
}
}
?>
Create a directory Files at src/Template and under that directory create a View file called index.php. Copy the following code in that file.
src/Template/Files/index.php
<?php echo $this->Form->create(NULL, ['type' => 'file']);
echo $this->l;Form->file('submittedfile');
echo $this->Form->button('Submit');
echo $this->Form->end();
$uploadPath ='../uploads/';
$files = scandir($uploadPath, 0);
echo "Files uploaded in uploads/ are:<br>";
for($i = 2; $i ";
?>
The files saved in uploads/ folder is listed for the user. Execute the above example by visiting the following URL −
http://localhost/cakephp4/fileupload −
Output
When you execute the above code, you should see the following output −

Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Comment utiliser cURL pour implémenter les requêtes Get et Post en PHP
- Comment utiliser cURL pour implémenter les requêtes Get et Post en PHP
- Comment utiliser cURL pour implémenter les requêtes Get et Post en PHP
- Comment utiliser cURL pour implémenter les requêtes Get et Post en PHP
- Tous les symboles d'expression dans les expressions régulières (résumé)

