Maison >interface Web >tutoriel HTML >Qu'est-ce que le HTML ?
Qu'est-ce que le HTML ?
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBoriginal
- 2024-09-04 16:12:30913parcourir
HyperText Markup Language, ou HTML, est un langage qui permet la création de sites Web visibles par toute personne connectée à Internet. Selon une enquête, plus de 55 % des personnes interrogées ont déclaré utiliser HTML.
De plus, l’apprentissage du HTML est généralement la première étape du parcours de tout développeur Web. Un développeur Web moyen gagne 61 718 $ par an, et les meilleurs développeurs franchissent la barre des 103 000 $.
L'hypertexte est le moyen d'accéder à Internet en cliquant sur un texte appelé hyperliens qui mènera à la page suivante.

Points clés à retenir
- Le code de base se compose d'une déclaration doctype, d'une balise HTML, d'une balise head, d'une balise titre et d'une balise body.
- Il peut fonctionner sur n'importe quel système d'exploitation, tel que Windows, Mac et Linux, et sur n'importe quel navigateur, tel que Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox et Safari.
- Il a également diverses applications, telles que la création de blogs personnels, de tableaux détaillés, de formulaires d'inscription, de pages de destination, de newsletters et de portfolios en ligne.
- Les avantages sont qu'il s'agit d'un standard ouvert, facile à apprendre, convivial pour les débutants avec un excellent support communautaire et convivial pour les moteurs de recherche.
- Les inconvénients incluent une sécurité médiocre, un manque de flexibilité de conception, des résultats incohérents sur différents navigateurs et des fonctionnalités limitées.
Sous-ensembles de HTML
1. XHTML (langage de balisage hypertexte extensible)
- XHTML est un langage de balisage basé sur XML, ce qui signifie qu'il adhère à des règles syntaxiques et sémantiques strictes.
- XHTML était le successeur de HTML 4, visant à rendre le langage plus modulaire et extensible.
- Les documents XHTML doivent être bien formés et valides, ce qui les rend plus difficiles à créer, plus cohérents et accessibles à un plus large éventail d'appareils.
2. SGML (langage de balisage généralisé standard)
- SGML est un métalangage utilisé pour définir des langages de balisage, dont HTML.
- SGML fournit une syntaxe standard pour décrire la structure et le contenu d'un document, ce qui le rend utile pour l'échange d'informations entre différents systèmes.
- SGML est un système complexe et puissant, mais sa syntaxe et sa complexité le rendent moins largement utilisé que les langages de balisage plus simples comme HTML.
3. DHTML (HTML dynamique)
- DHTML fait référence à l'utilisation de HTML, CSS et JavaScript pour créer des pages Web dynamiques et interactives.
- DHTML permet de manipuler le contenu, la mise en page et le comportement d'une page Web en réponse aux actions de l'utilisateur sans nécessiter une actualisation de la page.
- DHTML est largement utilisé pour créer des effets dynamiques, tels que des menus déroulants, des info-bulles et des diaporamas.
- Il peut également créer des animations et des jeux simples.
4. TTML2 (Langage de balisage de texte temporisé 2)
- TTML2 est un langage de balisage utilisé pour représenter le contenu textuel chronométré, tel que les légendes et les sous-titres, de manière standardisée.
- TTML2 fournit un ensemble complet de fonctionnalités pour le formatage et le style du texte chronométré, y compris la prise en charge de plusieurs langues et styles de police.
- TTML2 est un outil important pour garantir l'accessibilité du contenu multimédia pour les utilisateurs sourds et malentendants et pour améliorer la convivialité du contenu vidéo pour tous les utilisateurs.
Modèle HTML
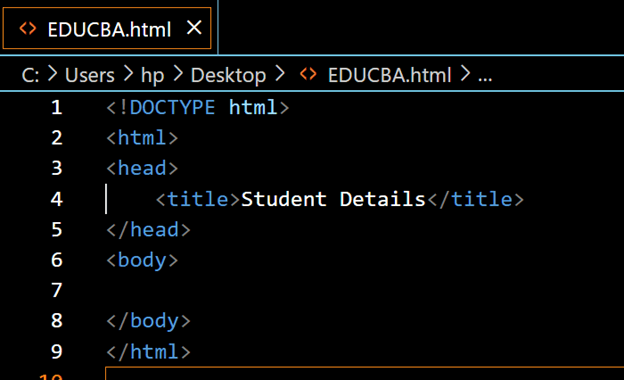
Chaque page HTML a un modèle de base. Il se compose des sections suivantes :
Déclaration de type de document : La première ligne d'un document HTML est la déclaration doctype ou type de document, qui définit la version de HTML utilisée.
Syntaxe :
<!DOCTYPE html>
Élément : L'élément est l'élément racine d'un document HTML, contenant tous les autres éléments.
Syntaxe :
<html>...</html>
Élément Head : L'élément head contient des informations sur le document, telles que le titre, les métadonnées et des liens vers des ressources externes telles que des feuilles de style.
Syntaxe :
<head>...</head>
Élément Titre : L'élément titre définit le titre du document, qui s'affiche dans la barre de titre du navigateur.
Syntaxe :
<title>Name of Web Page</title>
Élément Body : L'élément body contient le contenu principal du document, y compris le texte, les images et d'autres médias.
Syntaxe :
<body>...</body>
En dehors de ces balises de base, plusieurs autres éléments peuvent aider à ajouter du contenu pour créer un superbe site Web. Ce sont-
Titres : Les titres (H1, H2, H3, etc.) permettent de structurer le contenu et de hiérarchiser les informations.
Syntaxe :
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
Paragraphes : Les paragraphes (
) aident à définir des blocs de texte.
Syntaxe :
<p>Hello World</p>
Liens : Les liens () permettent aux utilisateurs de naviguer vers d'autres pages Web ou vers d'autres ressources.
Syntaxe :
<a href="https://www.EDUCBA.com">Link to EDUCBA website</a>
Images: Images () can provide visual content in a document.
Syntax:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Image Description">
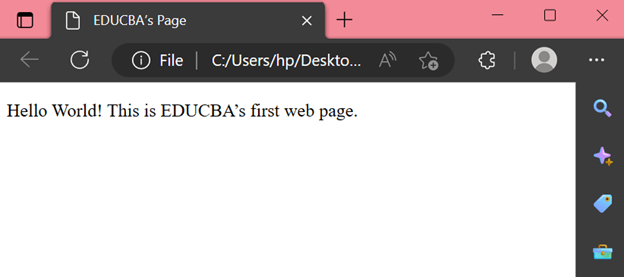
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>EDUCBA’s Page Hello World! This is EDUCBA’s first web page.
Output:
How to Create an HTML Table?
There are specific table tags to create a table – mainly,
| , | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.
Pre-requisites for HTML TableFor an absolute beginner, it is essential to know what the different table tags do before writing a basic code.
|