Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Minuterie en Java
Minuterie en Java
- PHPzoriginal
- 2024-08-30 15:53:07503parcourir
Timer en Java est disponible en Java. Le package util étend la classe Object et implémente les interfaces sérialisables et clonables. La classe timer contient des méthodes utilisées pour effectuer des activités liées au timing. La classe Timer en Java est utilisée pour effectuer la planification des tâches en fonction du temps. Les threads Java utilisent les méthodes de la classe Timer pour planifier une tâche telle que l'exécution d'une section de code après un certain instant, ou l'exécution répétée de code après un certain temps prédéfini. Chaque objet Timer est lié à un thread d'exécution en arrière-plan distinct qui est responsable de l'exécution de toutes les tâches associées au thread. Il est à noter que la classe timer en Java est thread-safe ; c'est-à-dire qu'à la fois, un seul thread peut exécuter la méthode de classe Timer. La classe Timer utilise également le tas binaire comme structure de données sous-jacente pour stocker les tâches.
Commencez votre cours de développement de logiciels libres
Développement Web, langages de programmation, tests de logiciels et autres
Syntaxe du minuteur en Java
Voici une syntaxe de base sur la façon dont la classe Timer est utilisée en Java :
Syntaxe :
// create a class extending TimerTask
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
//define run method
public void run()
{
// Write Code to be executed by Timer
}
}
class MainClass{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//create timer instance
Timer timer = new Timer();
// create Timer class instance
TimerTask task = new TimerHelper ();
// call timer method
timer.schedule(task, 3000,6000);
//first argument is timer object
// second argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be first executed
// Third argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be executed regularly.
}
}
Explication de la syntaxe ci-dessus : La syntaxe montre comment une classe Timer est utilisée en Java. L'utilisation d'une classe timer implique de créer une classe étendant TimerTask et d'y définir la méthode d'exécution. La méthode run contient une logique qui doit être exécutée en fonction du temps. Vous trouverez ci-dessous la déclaration de la classe Timer :
public class Timer extends Object implements Serializable, Cloneable
Méthodes de classe Timer en Java
Nous allons maintenant voir quelles sont les différentes méthodes et champs disponibles dans la classe Java Timer. Voici la liste des méthodes couramment utilisées disponibles dans la classe Timer :
|
Description | ||||||||||||||||||
| programme d'annulation publique (tâche TimerTask, Date date) | Planifie une tâche à exécuter à la date définie. | ||||||||||||||||||
| planification publique vide (tâche TimerTask, date firstTime, longue période) | Le premier argument est TimerTask à exécuter ; le deuxième argument est le temps après lequel la tâche est exécutée pour la première fois, et le troisième argument est les secondes en millisecondes après lesquelles la tâche sera exécutée régulièrement. | ||||||||||||||||||
| public int purge() | Utilisé pour supprimer toutes les tâches annulées de la file d'attente du minuteur. | ||||||||||||||||||
| public void Cancel() | Annulez le minuteur. | ||||||||||||||||||
| planification d'annulation publique (tâche TimeTask, long délai) | Planifie l'exécution de la tâche après le temps spécifié en millisecondes. | ||||||||||||||||||
| planification d'annulation publique (tâche TimeTask, long délai, longue période) | Le premier argument est TimerTask à exécuter ; le deuxième argument est le temps en millisecondes après lequel la tâche est exécutée pour la première fois, et le troisième argument est le temps en millisecondes après lequel la tâche sera exécutée régulièrement. | ||||||||||||||||||
| public void planningAtFixedRate (tâche TimerTask, Date firstTime, longue période) | Le premier argument est TimerTask à exécuter ; le deuxième argument est le temps après lequel la tâche est exécutée pour la première fois, et le troisième argument est les secondes en millisecondes après lesquelles la tâche sera exécutée régulièrement. | ||||||||||||||||||
| public void planningAtFixedRate (tâche TimeTask, long délai, longue période) | Le premier argument est TimerTask à exécuter ; le deuxième argument est le temps en millisecondes après lequel la tâche est exécutée pour la première fois, et le troisième argument est le temps en millisecondes après lequel la tâche sera exécutée régulièrement. |
From the above-stated methods, we have found two methods that are similar in working but different in the name; they are schedule and scheduleAtFixedRate. The difference between the two is that in the case of fixed-rate execution, each execution is scheduled in accordance with the initial execution. If there is a delay in execution, then two or more executions will occur in quick succession to overcome the delay.
Constructors in Timer Class
The timer class contains four constructors for instantiating timer object.
- Timer(): Creates a new Timer Object.
- Timer(boolean isDaemon): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread specified to run as a daemon.
- Timer(String name): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread name.
- Timer(String name, boolean isDaemon): This method is a combination of the above two constructors.
One of the above four listed constructors can be called depending on our requirements.
Examples of Implementing Timer in Java
Below is the example of Timer in Java:
Example #1
To start things, let us see a basic example of Timer class. In this example, we will demonstrate the use of the schedule method of the Timer class.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask timerhelper = new TimerHelper();
timer.schedule(timerhelper, 3000, 2000);
}
}
Explanation of the above code: The above code will execute the run method for the first time after 3 seconds as the first argument is 3000, and after every 2 seconds, the run method will be executed regularly. Here is the output that will be displayed:
Output:
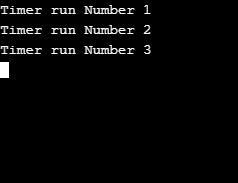
Example #2
In this example, we will see how to terminate a timer thread after a given number of timer runs.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
if(counter ==3){
this.cancel();
System.out.println("Now Cancelling Thread!!!!!");
return;
}
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask helper = new TimerHelper();
helper.schedule(task, 3000, 2000);
}
}
In the above example, the timer will cancel after the three times run method is called using the timer class’s cancel method.
Output:
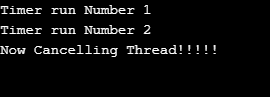
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

