Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Tableau multidimensionnel en Java
Tableau multidimensionnel en Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBoriginal
- 2024-08-30 15:27:381262parcourir
Un guide complet sur les tableaux multidimensionnels en Java. Un tableau est une structure multidimensionnelle de données homogène qui est une collection d’éléments avec un type de données similaire. Ils sont stockés dans l'emplacement mémoire contigu. Dans le tableau, le premier élément est stocké dans l'index 0 ; le deuxième élément est stocké dans l'index 1, et ainsi de suite. Les tableaux peuvent être à une seule dimension ou à plusieurs dimensions. Dans ce document, nous examinerons les tableaux multidimensionnels en Java. Un tableau multidimensionnel est un tableau de tableaux pouvant contenir plusieurs lignes et colonnes. Voyons maintenant la syntaxe et l'implémentation d'un tableau multidimensionnel dans les sections suivantes.
PUBLICITÉ Cours populaire dans cette catégorie MAÎTRISÉE JAVA - Spécialisation | 78 séries de cours | 15 tests simulésSyntaxe :
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
- data_type : type de données du tableau, Exemple : int, char, float, etc.
- dimension : la dimension du tableau, Exemple : 1D, 2D, etc.
- array_name : Nom du tableau.
- taille1, taille2, …, tailleN : Tailles de la dimension.
Types de tableaux multidimensionnels en Java
Les tableaux multidimensionnels les plus courants en Java sont :
- Tableau bidimensionnel ou tableau 2D.
- Tableau tridimensionnel ou tableau 3D.
1. Tableau bidimensionnel
Les tableaux 2D sont couramment utilisés dans les jeux vidéo de plateforme comme Super Mario pour représenter un terrain ou un écran. Ils peuvent également être utilisés pour dessiner des échiquiers, représenter des structures comme une feuille de calcul, etc.
Code :
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
Exemple :
9 10
7 66
Il s'agit d'un tableau 2D avec deux lignes et deux colonnes.
2. Tableau tridimensionnel
Les tableaux tridimensionnels ne sont pas couramment utilisés dans les applications en temps réel. Par conséquent, les tableaux bidimensionnels sont également privilégiés dans les exemples de programmation.
Code :
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
Exemple :
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
Comment déclarer un tableau multidimensionnel en Java ?
Il est facile de comprendre le tableau multidimensionnel en Java si les tableaux normaux sont connus. Les tableaux multidimensionnels peuvent être déclarés comme indiqué ci-dessous :
Voyons d'abord la déclaration des tableaux 2D :
- int[][] array1 = new int[2][2]; //Tableau d'entiers bidimensionnels avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- String[][] array1 = new String[2][2]; //Tableau de chaînes bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- char[][] array1 = new char[2][2]; //Tableau de caractères bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- boolean[][] array1 = new boolean[2][2]; //Tableau booléen bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- double[][] array1 = new double[2][2]; //Double tableau bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- float[][] array1 = new float[2][2]; // Tableau flottant bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- long[][] array1 = new long[2][2]; //Tableau long bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- short[][] array1 = new short[2][2]; //Tableau court bidimensionnel avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
- byte[][] array1 = new byte[2][2]; // Tableau d'octets à deux dimensions avec 2 lignes et 2 colonnes.
Assurez-vous qu'une déclaration appropriée est créée lors de la programmation en Java.
Exemple n°1
Code :
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Sortie :

La déclaration du tableau tridimensionnel peut être discutée.
- int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Tableau tridimensionnel
Ces tableaux peuvent être de n’importe quel type de données. Vous trouverez ci-dessous quelques-uns des tableaux tridimensionnels avec différents types de données.
- int [][][] IntArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel d'entiers.
- octet[][][] ByteArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel d'octets.
- short[][][] ShortArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de Shorts.
- long[][][] LongArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de Longs.
- float[][][] FloatArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de Floats.
- double[][][] DoubleArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de Doubles.
- boolean[][][] BooleanArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de booléens.
- char[][][] CharArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de Chars.
- String[][][] StringArray; // déclaration d'un tableau tridimensionnel de chaînes.
Exemple n°2
Code :
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}
Sortie :

Comment initialiser le tableau multidimensionnel en Java ?
Les tableaux multidimensionnels peuvent être initialisés de plusieurs manières :
1. Declare and Create a Java Multidimensional Array
- int[][][] a= new int[3][5][4];
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
- a[0][1][0] = 15; // Initializing Array elements at position [0][1][0]
- a[1][2][0] = 45; // Initializing Array elements at position [1][2][0]
- a[2][1][1] = 65; // Initializing Array elements at position [2][1][1]
2. Directly Specify the Elements
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };
In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
3. Nested For Loop
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }
4. Assigning Values to One Row
int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Operations on Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Example #1
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Example #2
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
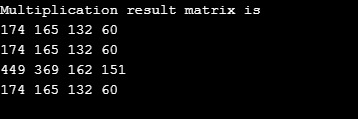
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Multidimensional Array in C
- 2D Arrays in Java
- 2D Arrays in C#
- Multidimensional Array in PHP
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

