Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Opérateurs de comparaison en Java
Opérateurs de comparaison en Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBoriginal
- 2024-08-30 15:19:30711parcourir
Les opérateurs sont considérés comme des caractères spéciaux ou des symboles utilisés pour effectuer certaines opérations sur des variables ou des valeurs (opérandes). En Java, plusieurs opérateurs sont utilisés pour manipuler les variables. Il comprend des opérateurs arithmétiques, des opérateurs au niveau du bit, des opérateurs de comparaison, des opérateurs logiques, divers. opérateurs, opérateurs d'affectation, etc. Dans cet article, nous aborderons plus de détails sur les opérateurs de comparaison en Java.
Opérateurs de comparaison en Java
Voici les différents opérateurs de comparaison en Java.
PUBLICITÉ Cours populaire dans cette catégorie MAÎTRISÉE JAVA - Spécialisation | 78 séries de cours | 15 tests simulés| Name of the Operator | Operator | Example |
| Equal to | = = | a= =b |
| Not equal to | != | a!=b |
| Less than | < | a |
| Greater than | > | a>b |
| Less than or equal to | <= | a<=b |
| Greater than or equal to | >= | a>=b |
1. Égal à
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur du côté gauche de l'opérateur est égale à la valeur du côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are equal; Return true if it is same, else returns false
System.out.println(x == y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 3 ; y = 5 ; Renvoie faux car ils ne sont pas égaux

Cas 2 : x = 4 ; y =4; Renvoie vrai car ils sont égaux

2. Pas égal à
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur du côté gauche de l'opérateur n'est pas égale à la valeur du côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are not equal; Return true if it is not equal, else returns false
System.out.println(x != y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 3 ; y =4; Renvoie vrai car ils ne sont pas égaux
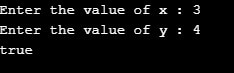
Cas 2 : x = 3 ; y = 3 ; Renvoie faux car ils sont égaux

3. Moins que
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur sur le côté gauche de l'opérateur est inférieure à la valeur sur le côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is less than y, else false
System.out.println(x < y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 4 ; y =6; Renvoie vrai car x est inférieur à y

Cas 2 : x = 44 ; y = 32 ; Renvoie faux car x n'est pas inférieur à y

4. Plus grand que
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur sur le côté gauche de l'opérateur est supérieure à la valeur sur le côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.<em>in</em>);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is greater than y, else false
System.out.println(x > y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 67 ; y = 66 ; Renvoie vrai car x est supérieur à y

Cas 2 : x = 43 ; y = 57 ; Renvoie faux car x est inférieur à y

5. Inférieur ou égal à
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur sur le côté gauche de l'opérateur est inférieure ou égale à la valeur sur le côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user and store it in variable y
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is less than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x <= y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 45 ; y = 45 ; Renvoie vrai car x est égal à y

Cas 2 : x = 45 ; y = 54 ; Renvoie vrai car x est inférieur à y

Cas 3 : x = 45 ; y = 43 ; Renvoie faux car x est supérieur à y

6. Supérieur ou égal à
Cet opérateur vérifie si la valeur sur le côté gauche de l'opérateur est supérieure ou égale à la valeur sur le côté droit.
Exemple :
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is greater than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x >= y);
}
}
Sortie :
Cas 1 : x = 54 ; y = 67 ; Renvoie faux car x est inférieur à y

Cas 2 : x = 45 ; y = 36 ; Renvoie vrai car x est supérieur à y

Cas 3 : x = 55 ; y = 55 ; Renvoie vrai car x est égal à y

Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Comment récupérer le PID d'un processus lancé à l'aide de ProcessBuilder en Java ?
- Comment puis-je contrôler efficacement la consommation de mémoire JVM ?
- Comment puis-je évaluer facilement des expressions mathématiques en Java ?
- Pourquoi est-ce que j'obtiens \'java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError\' lors de l'exécution de Java à partir de la ligne de commande ?
- Pourquoi est-il important de remplacer correctement les méthodes equals() et hashCode() lorsque vous travaillez avec HashMaps en Java ?

