在进行无限极分类中最常用的算法就是“递归”,熟悉PHP语言的朋友肯定知道,PHP不擅长递归 ,而且递归次数有限(100次左右,因操作系统和配置而异)。
所以本文将会给大家带来几种不使用递归实现无限级分类的代码。供大家来学习使用。
第一种:
无限级分类在开发中经常使用,例如:部门结构、文章分类。无限级分类的难点在于“输出”和“查询”,例如
将文章分类输出为ff6d136ddc5fdfeffaf53ff6ee95f185列表形式;
查找分类A下面所有分类包含的文章。
1.实现原理
几种常见的实现方法,各有利弊。其中“改进前序遍历树”数据结构,便于输出和查询,但是在移动分类和常规理解上有些复杂。
2.数据结构
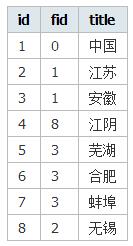
<?php $list = array( array('id'=>1, 'fid'=>0, 'title' => '中国'), array('id'=>2, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '江苏'), array('id'=>3, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '安徽'), array('id'=>4, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '江阴'), array('id'=>5, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '芜湖'), array('id'=>6, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '合肥'), array('id'=>7, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '蚌埠'), array('id'=>8, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '无锡') ); ?>
由于所有的递归均可以使用循环实现,本文根据PHP语言特点编写了一套关于“无限级”分类的函数,相比递归实现而言效率更高。
3.输出ul列表形式
将上述数据输出为下面的HTML
<ul> <li class="first-child"> <p>江苏</p> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <p>无锡</p> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <p>江阴</p> </li> </ul> </li> </ul> </li> <li class="last-child"> <p>安徽</p> <ul> <li class="first-child"><p>芜湖</p></li> <li><p>合肥</p></li> <li class="last-child"><p>蚌埠</p></li> </ul> </li> </ul>
这种HTML结构在前端使用(使用JavaScript和CSS构造可折叠树)十分方便。具体实现程序如下:
<ul><?php echo get_tree_ul($list, 1); ?></ul>
4.输出option列表形式
<select> <option value="2">江苏</option> <option value="8"> 无锡</option> <option value="4"> 江阴</option> <option value="3">安徽</option> <option value="5"> 芜湖</option> <option value="6"> 合肥</option> <option value="7"> 蚌埠</option> </select>
具体实现程序如下:
<select>
<?php
// get_tree_option()返回数组,并为每个元素增加了“深度”(即depth)列,直接输出即可
$options = get_tree_option($list, 1);
foreach($options as $op) {
echo '<option value="' . $op['id'] .'">' . str_repeat(" ", $op['depth'] * 4) . $op['title'] . '<;/option>';
}
?>
<;/select>5. 查找某一分类的所有子类
<?php $children = get_tree_child($list, 0); echo implode(',', $children); // 输出:1,3,2,7,6,5,8,4 ?>
6. 查找某一分类的所有父类
<?php $children = get_tree_parent($list, 4); echo implode(',', $children); //8, 2, 10 ?>
7. 相关函数
<?php
function get_tree_child($data, $fid) {
$result = array();
$fids = array($fid);
do {
$cids = array();
$flag = false;
foreach($fids as $fid) {
for($i = count($data) - 1; $i >=0 ; $i--) {
$node = $data[$i];
if($node['fid'] == $fid) {
array_splice($data, $i , 1);
$result[] = $node['id'];
$cids[] = $node['id'];
$flag = true;
}
}
}
$fids = $cids;
} while($flag === true);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_parent($data, $id) {
$result = array();
$obj = array();
foreach($data as $node) {
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
while($value) {
$id = null;
foreach($data as $node) {
if($node['id'] == $value['fid']) {
$id = $node['id'];
$result[] = $node['id'];
break;
}
}
if($id === null) {
$result[] = $value['fid'];
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
}
unset($obj);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_ul($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added_left = array();
$added_right= array();
$html_left = array();
$html_right = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
$cids = $child[$id];
$length = count($cids);
for($i = $length - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $cids[$i]);
}
$obj[$cids[$length - 1]]['isLastChild'] = true;
$obj[$cids[0]]['isFirstChild'] = true;
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_left[$id])) {
if(isset($node['isFirstChild']) && isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child last-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isFirstChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="last-child">';
} else {
$html_left[] = '<li>';
}
$html_left[] = ($flag === true) ? "<p>{$node['title']}</p><ul>" : "<p>{$node['title']}</p>";
$added_left[$id] = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_right[$id])) {
$html_right[] = ($flag === true) ? '</ul></li>' : '</li>';
$added_right[$id] = true;
}
if ($flag == false) {
if($node) {
$cids = $child[$node['fid']];
for ($i = count($cids) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($cids[$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
}
}
array_push($html_left, array_pop($html_right));
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $html_left;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return implode('', $html_left);
}
function get_tree_option($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added = array();
$options = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
$depth = -1;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
for($i = count($child[$id]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $child[$id][$i]);
}
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added[$id])) {
$node['depth'] = $depth;
$options[] = $node;
$added[$id] = true;
}
if($flag == true){
$depth++;
} else {
if($node) {
for ($i = count($child[$node['fid']]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($child[$node['fid']][$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
$depth--;
}
}
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $options;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return $options;
}
?>第二种:
这是使用TP来制作的无限级分类。
算法复杂度为T(n)=O(2n),只遍历两次数组.
关键代码其实只有一行
$return[$v['pid']]['child'][$v['id']] = &$return[$k];
但是为了实现较为复杂的扩展,这里添加一些额外的信息
//索引要和ID一致,这不是废话么
//pid是父元素
//不要出现死循环嵌套,就是AB互为父子
//不要出现相同name
$list[0]=['id'=>0,'pid'=>-1,'name'=>'A@0'];//-1用于后面的根目录判断
$list[1]=['id'=>1,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@1'];
$list[2]=['id'=>2,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@2'];
$list[3]=['id'=>3,'pid'=>2,'name'=>'A@3'];
$list[4]=['id'=>4,'pid'=>3,'name'=>'A@4'];
$list[5]=['id'=>5,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@5'];
$list[6]=['id'=>6,'pid'=>1,'name'=>'A@6'];
//先初始化目录
$return=[];
foreach($list as $v)
$return[$v['name']]=[];
//将每个目录与父目录进行拼接,并找到根目录
foreach($list as $k=>$v)
{
if($v['pid']>=0)
$return[$list[$v['pid']]['name']][$v['name']]=&$return[$v['name']];
else
$parent=$v['name'];
}
//打印根目录
print_r($return[$parent]);输出1
Array(
[A@1] => Array
(
[A@6] => Array
(
)
)
[A@2] => Array
(
[A@3] => Array
(
[A@4] => Array
(
)
)
)
[A@5] => Array
(
)
)代码2
/**
* Created by PhpStorm.
* User: Nikaidou-Shinku
* Date: 16/9/14
* Time: 17:12
*/
$list[] = ['id' => 0, 'pid' => -1, 'name' => 'A@0'];//-1用于后面的根目录判断
$list[] = ['id' => 1, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@1'];
$list[] = ['id' => 2, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@2'];
$list[] = ['id' => 3, 'pid' => 2, 'name' => 'A@3'];
$list[] = ['id' => 4, 'pid' => 3, 'name' => 'A@4'];
$list[] = ['id' => 5, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@5'];
$list[] = ['id' => 6, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => 'A@6'];
//先初始化目录
$return = [];
$parent = '';
foreach ($list as $v)
$return[$v['id']] = [
'id' => $v['id'],
'name' => $v['name'],
'pid' => $v['pid'],
'child' => '',
];
//将每个目录与父目录进行拼接,并找到根目录
foreach ($return as $k => $v) {
if ($v['pid'] >= 0)
$return[$v['pid']]['child'][$v['id']] = &$return[$k];
else
$parent = &$return[$k];
}
//打印根目录
var_export($parent);输出2
$aa=[
'id' => 0,
'name' => 'A@0',
'pid' => -1,
'child' =>
[
1 =>
[
'id' => 1,
'name' => 'A@1',
'pid' => 0,
'child' =>
[
6 =>
[
'id' => 6,
'name' => 'A@6',
'pid' => 1,
'child' => '',
],
],
],
2 =>
[
'id' => 2,
'name' => 'A@2',
'pid' => 0,
'child' =>
[
3 =>
[
'id' => 3,
'name' => 'A@3',
'pid' => 2,
'child' =>
[
4 =>
[
'id' => 4,
'name' => 'A@4',
'pid' => 3,
'child' => '',
],
],
],
],
],
5 =>
[
'id' => 5,
'name' => 'A@5',
'pid' => 0,
'child' => '',
],
],
]第三种:
接下来这个无限级分类更为的简单。可以简化成使用5行代码就可以完成。
function generateTree($items){
$tree = array();
foreach($items as $item){
if(isset($items[$item['pid']])){
$items[$item['pid']]['son'][] = &$items[$item['id']];
}else{
$tree[] = &$items[$item['id']];
}
}
return $tree;
}
$items = array(
1 => array('id' => 1, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => '安徽省'),
2 => array('id' => 2, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => '浙江省'),
3 => array('id' => 3, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => '合肥市'),
4 => array('id' => 4, 'pid' => 3, 'name' => '长丰县'),
5 => array('id' => 5, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => '安庆市'),
);
print_r(generateTree($items));可以看到下面打印的结果:
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[pid] => 0
[name] => 安徽省
[son] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 3
[pid] => 1
[name] => 合肥市
[son] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 4
[pid] => 3
[name] => 长丰县
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 5
[pid] => 1
[name] => 安庆市
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 2
[pid] => 0
[name] => 浙江省
)
)上面生成树方法还可以精简到5行:
function generateTree($items){
foreach($items as $item)
$items[$item['pid']]['son'][$item['id']] = &$items[$item['id']];
return isset($items[0]['son']) ? $items[0]['son'] : array();
}但是上面的代码有个问题就是对数据库结构有点要求,每个节点要指明其父节点是谁,虽然实用性不高,但是还是能给大家带来启发,学习下不同类型的无限级分类。
 Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PMLaravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AMThe PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PMLaravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PMDo you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PMArticle discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PMPHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
 How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AM
How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AMLaravel's service container and service providers are fundamental to its architecture. This article explores service containers, details service provider creation, registration, and demonstrates practical usage with examples. We'll begin with an ove
 Customizing/Extending Frameworks: How to add custom functionality.Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Customizing/Extending Frameworks: How to add custom functionality.Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:12 PMThe article discusses adding custom functionality to frameworks, focusing on understanding architecture, identifying extension points, and best practices for integration and debugging.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






