Detailed explanation of JavaScript closures_Basic knowledge
In the last article, we gave an overview of pre-interpretation. Before writing this blog post, we planned to write a few classic cases. Considering that those cases are relatively comprehensive, we wrote this blog post step by step, so that we can It is also easier to start learning and deepening JavaScript.
Preface
A colleague went for an interview, and the interviewer asked a question: Can you write a closure and let me take a look? So my colleague quickly wrote the following code:
function fn(){
alert('Hello JavaScript Closure!!!'); // Damn it, the E text is not good, so I had to find a translator to write out the closure words
}
fn();
Then the interviewer shook his head and said: "How can this be called closure?" In the end, the two couldn't argue, and the colleague left decisively. What the hell is the interviewer doing? (This story is purely fictitious, any similarity is purely coincidental)
Closure may be a "high-end and difficult-to-learn" technology in the eyes of many people. Perhaps in the eyes of many people, it is the only one that counts as closure:
Example 1:
function fn() {
Return function () {
alert('Example 1');
}
}
fn()();
Example 1 PS: This doesn’t look very advanced, it seems like this person is not very good!
Example 2:
;(function () {
alert('Example 2');
})();
Example 2 PS: This one looks more advanced than the previous one, and a semicolon is added before the first bracket. Why add a semicolon? Well, let’s leave this question here for now and will talk about it later.
Example 3:
~function fn() {
alert('Example 3')
}();
Example 3 PS: This is the most advanced, it’s amazing. I don’t read much, so don’t lie to me!
I don’t read much, so I can only write these three kinds of "closures". I believe fellow bloggers can write more and better "closures"; please stop my nonsense now and continue my research. It seems that someone already knows the mechanism of function operation. It must be the scope. I really don’t want to add this scope to the title. It always feels almost meaningless. These things are originally together. Why? Want to repeat it? Old habit, code first:
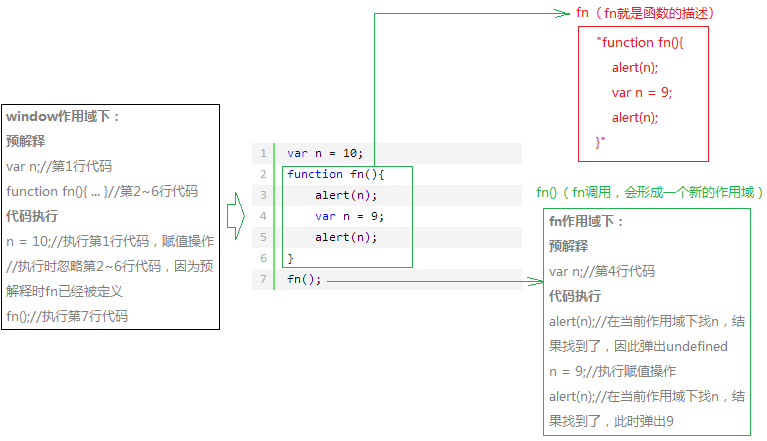
var n = 10;
function fn(){
alert(n);
var n = 9;
alert(n);
}
fn();
To put it simply, let’s draw a picture (the author will only use the drawing software that comes with Windows. If there is a better one, please recommend it) to analyze it:
Analysis 1
From the picture we see two scopes, one is the window scope (top-level scope), and the other is a private scope formed when fn is called; then what is a scope, the scope is actually code execution environment. For example, a student's learning environment is school, which is equivalent to his scope. If this student is very naughty and often goes to an Internet cafe to play games at night, it is equivalent to forming a private environment, and this scope is the Internet cafe. All right! This chestnut looks so damn like the masturbator himself that I couldn't help but sigh: "If you don't work hard when you are young, you will get kicked when you grow up." Back to the topic, in fact, the definition of function fn is a description pointing to a piece of code (red box in the picture). When fn is called (green box in the picture), a scope will be formed. Of course, in this scope The code will also be pre-interpreted before execution. I will not tell you that this scope will be destroyed after it is executed. Calling this fn again will also form a new scope, and then pre-interpretation before execution, and then the code is executed. Destroyed after final execution.
Understanding closures
We know that when a function is called, it will form a private scope (execution environment), and this private scope is a closure. Looking back, is closure still the legendary "tall and difficult to master"? Let's look back at the first interview story and the three examples I wrote. They are actually closures. To be precise, those three examples are all common forms of closures.
Application scenarios
Now there is such a requirement: there is a ul tag in the HTML page, and there are 5 li tags under the ul. It is required to click on any li, and the index (index starts from 0) position of the clicked li will pop up, and the HTML structure As follows:
- List 1
- List 2
- List 3
- List 4
- List 5
Being smart, I quickly wrote the following code:
var lis = document.getElementById('ul').getElementsByTagName('li');
for (var i = 0, len = lis.length; i lis[i].onclick = function () {
alert(i);
};
}
Final test to see if this requirement is perfectly realized:
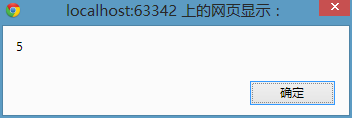
I found that no matter how many times I click, this result will eventually pop up, and the expected result is: click on list 1 to pop up 0, click on list 2 to pop up 1, click on list 3 to pop up 2... I just want to use this picture at this moment To describe my current mood:

(What it looks like when the prototype fails to run as designed during demonstration)
How can this be done? Why does 5 always pop up? It's theoretically correct! Let’s draw a picture to analyze it:

In fact, the onclick we just give to each li is actually a saved description string of a function. The content of this string is the content in the red box in the picture above. If you still don’t believe it, I have a picture with the truth:

Enter: lis[4].onclick in the Chrome console, the value is the function description. When we click on the fifth list, it is actually equivalent to lis[4].onclick(), calling this function description. We know that the function will form a private scope when it is called and executed. In this private scope The scope is also pre-interpreted first, and then the code is executed. At this time, i is found. There is no i in the current private scope, and then i is found in the window scope, so 5 pops up every time you click.
Obviously the above code cannot meet this requirement. It is incorrect for us to write the code like this. Let’s think about the cause of the problem? In fact, the reason is that every time you click, you read the i under the window. At this time, the value of i is already 5, so you have the following code:
Method 1:
var lis = document.getElementById('ul').getElementsByTagName('li');
function fn(i) {
Return function () {
alert(i);
}
}
for (var i = 0, len = lis.length; i lis[i].onclick = fn(i);
}
Method 2:
var lis = document.getElementById('ul').getElementsByTagName('li');
for (var i = 0, len = lis.length; i ;(function (i) {
lis[i].onclick = function () {
alert(i);
};
})(i);
}
Method 3:
var lis = document.getElementById('ul').getElementsByTagName('li');
for (var i = 0, len = lis.length; i lis[i].onclick = function fn(i) {
return function () {
alert(i);
}
}(i);
}
I wrote three methods in one breath. The idea is the same, which is to store the variable i in a private variable. Here I will only talk about the second method. Of course, if you understand one of them, you will understand the rest. As usual, we draw pictures to analyze step by step:

I described the entire code execution in detail. It should be noted that the onclick attribute of each li must occupy the (function(i){…})(i) scope. When this function is executed, it will not will be destroyed because it is occupied by an external li (this li is under the window scope), so this scope will not be destroyed. When any li is clicked, function(){ alert(i); } will be executed and a scope will be formed. This scope does not have i, and it will go to the (function(){ ... })(i) scope. Find i, and finally find i in the formal parameter. The value of this formal parameter i is passed in during the for loop; this example cleverly uses closures to store values, which perfectly solves the problem.
PS: I just mentioned why a semicolon is added in front of (function(i){ … })(i). The reason is to prevent the previous statement from forgetting to add a semicolon, which will cause JavaScript errors during parsing. That’s all. . Of course, one of the above application scenarios is the implementation principle of Tabs. There can be other implementation methods, such as custom attribute methods and finding indexes through DOM node relationships. The main purpose of using this method is to deepen the understanding of closures.
Summary
Closures are not the legendary ones that are difficult to master. The core is to understand function definition and calling. When a function is called, a new private scope will be formed. When a certain scope is occupied by the outside, then this scope will will not be destroyed. Lu Zhu has read very little, so I would like to ask fellow bloggers to correct me if I am wrong. I would also like to thank everyone for their support of Lu Zhu’s articles.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use





