 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial Java data structure and algorithm: practical optimization of microservice architecture
Java data structure and algorithm: practical optimization of microservice architecture
Java Data Structures and Algorithms: How to Optimize in Microservice Architecture
Introduction
In a microservices architecture, optimizing data structures and algorithms is crucial to improve system performance and scalability. This article explores how to use appropriate data structures to optimize common microservices architecture patterns and provides real-world examples.
Data structure
- Arrays and linked lists: Used to store and access linear data. Arrays provide fast access, while linked lists have advantages in inserting and deleting elements.
- Stacks and queues: Last-in-first-out (LIFO) and first-in-first-out (FIFO) structures are used to temporarily store data.
- Hash table: Use key-value pairs to store data and provide fast retrieval.
- Trees and graphs: Used to store and navigate complex data structures.
Real example
Scenario 1: Storing authentication information in the gateway microservice
Problem : Highly concurrent requests require fast access to authentication information.
Solution: Use a hash table to store user ID and token pairs. This structure allows fast lookups with O(1) time complexity.
Scenario 2: Storing pending tasks in the message queue
Problem: It is necessary to ensure that tasks are executed in FIFO order.
Solution: Use a queue to store tasks. The first-in-first-out mechanism ensures that tasks are processed in order.
Scenario 3: Storing popular data in a cache service
Problem: Frequently accessed data needs to be retrieved as quickly as possible.
Solution: Use an array or linked list to store popular data. These structures provide fast sequential access.
Algorithm
- Sort algorithm: Used to sort data, such as merge sort and quick sort.
- Search algorithm: Used to find specific elements in a data structure, such as binary search.
- Graph algorithms: Used to process graph structures, such as breadth-first search and depth-first search.
Real example
Scenario 4: Searching for text in a search service
Question: Need to search large amounts of text efficiently.
Solution: Use the trie data structure. This structure supports prefix searches and fast matching.
Scenario 5: Calculating similarity in a recommendation system
Problem: Need to calculate the similarity between users to recommend content to them .
Solution: Use cosine similarity or Jaccard similarity algorithm. These algorithms measure the similarity of two vectors.
Scenario 6: Selecting the best service instance in the routing service
Problem: It is necessary to select the best performing service instance from a set of service instances Example.
Solution: Use Dijkstra's algorithm or A* algorithm. These algorithms find the shortest path in a weight graph that represents the latency between service instances.
Conclusion
Using appropriate data structures and algorithms is crucial to optimizing microservices architecture. By carefully considering the performance requirements of different use cases, developers can significantly improve system performance, scalability, and reliability.
The above is the detailed content of Java data structure and algorithm: practical optimization of microservice architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM特斯拉是一个典型的AI公司,过去一年训练了75000个神经网络,意味着每8分钟就要出一个新的模型,共有281个模型用到了特斯拉的车上。接下来我们分几个方面来解读特斯拉FSD的算法和模型进展。01 感知 Occupancy Network特斯拉今年在感知方面的一个重点技术是Occupancy Network (占据网络)。研究机器人技术的同学肯定对occupancy grid不会陌生,occupancy表示空间中每个3D体素(voxel)是否被占据,可以是0/1二元表示,也可以是[0, 1]之间的
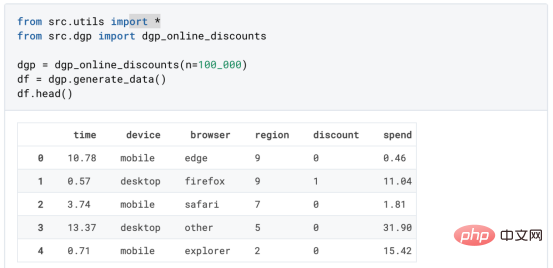 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
 因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM
因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM导读:因果推断是数据科学的一个重要分支,在互联网和工业界的产品迭代、算法和激励策略的评估中都扮演者重要的角色,结合数据、实验或者统计计量模型来计算新的改变带来的收益,是决策制定的基础。然而,因果推断并不是一件简单的事情。首先,在日常生活中,人们常常把相关和因果混为一谈。相关往往代表着两个变量具有同时增长或者降低的趋势,但是因果意味着我们想要知道对一个变量施加改变的时候会发生什么样的结果,或者说我们期望得到反事实的结果,如果过去做了不一样的动作,未来是否会发生改变?然而难点在于,反事实的数据往往是
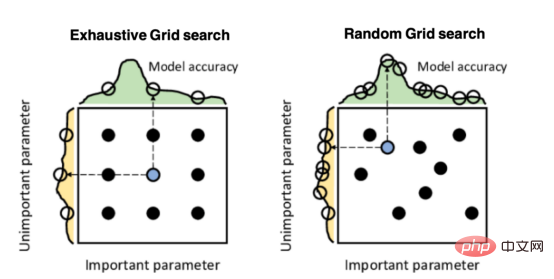 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
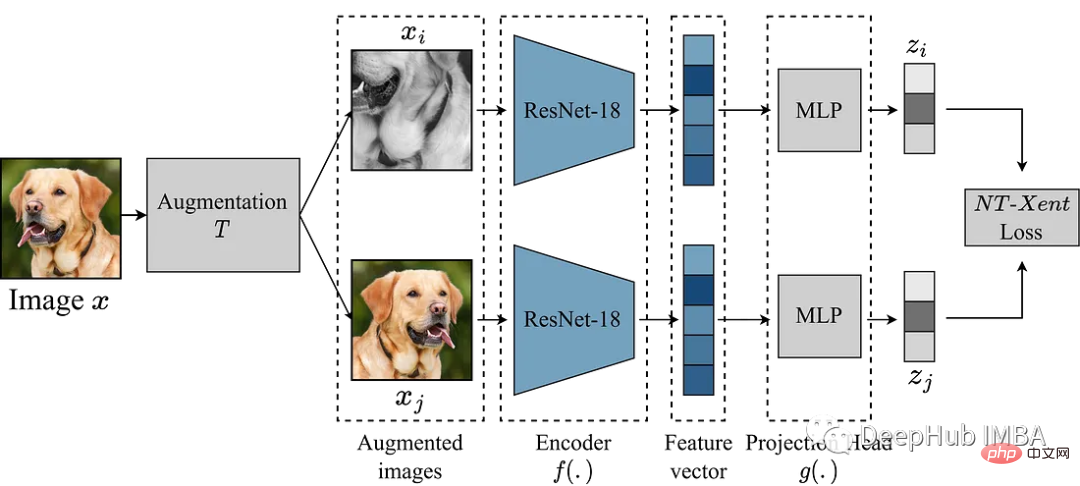 使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PMSimCLR(Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Representations)是一种学习图像表示的自监督技术。 与传统的监督学习方法不同,SimCLR 不依赖标记数据来学习有用的表示。 它利用对比学习框架来学习一组有用的特征,这些特征可以从未标记的图像中捕获高级语义信息。SimCLR 已被证明在各种图像分类基准上优于最先进的无监督学习方法。 并且它学习到的表示可以很容易地转移到下游任务,例如对象检测、语义分割和小样本学习,只需在较小的标记
 盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM
盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM一、盒马供应链介绍1、盒马商业模式盒马是一个技术创新的公司,更是一个消费驱动的公司,回归消费者价值:买的到、买的好、买的方便、买的放心、买的开心。盒马包含盒马鲜生、X 会员店、盒马超云、盒马邻里等多种业务模式,其中最核心的商业模式是线上线下一体化,最快 30 分钟到家的 O2O(即盒马鲜生)模式。2、盒马经营品类介绍盒马精选全球品质商品,追求极致新鲜;结合品类特点和消费者购物体验预期,为不同品类选择最为高效的经营模式。盒马生鲜的销售占比达 60%~70%,是最核心的品类,该品类的特点是用户预期时
 人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM10 月 5 日,AlphaTensor 横空出世,DeepMind 宣布其解决了数学领域 50 年来一个悬而未决的数学算法问题,即矩阵乘法。AlphaTensor 成为首个用于为矩阵乘法等数学问题发现新颖、高效且可证明正确的算法的 AI 系统。论文《Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning》也登上了 Nature 封面。然而,AlphaTensor 的记录仅保持了一周,便被人类
 研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM译者 | 李睿 审校 | 孙淑娟随着机器学习成为人们每天都在使用的很多应用程序的一部分,人们越来越关注如何识别和解决机器学习模型的安全和隐私方面的威胁。 然而,不同机器学习范式面临的安全威胁各不相同,机器学习安全的某些领域仍未得到充分研究。尤其是强化学习算法的安全性近年来并未受到太多关注。 加拿大的麦吉尔大学、机器学习实验室(MILA)和滑铁卢大学的研究人员开展了一项新研究,主要侧重于深度强化学习算法的隐私威胁。研究人员提出了一个框架,用于测试强化学习模型对成员推理攻击的脆弱性。 研究


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!





