What is liquidity staking? How does it work? What is the difference between liquidity staking and entrusted staking? Liquid staking allows stakers to maintain the liquidity of their staked tokens through the use of alternative tokens, which they can use to earn additional income through DeFi protocols.
Today, the editor of this website will introduce to you in detail what is liquid staking? How liquidity staking works, and the difference between liquidity staking and entrusted staking. Hope you all like it!

1. What is liquidity staking?

Liquid staking allows stakers to maintain the liquidity of their staked tokens by using alternative tokens, which they can use to earn additional income through DeFi protocols.
Before we dive into liquidity staking, let’s first understand staking and the issues associated with it. Staking refers to the process of locking cryptocurrency in a blockchain network to maintain it, which enables stakers to earn profits. However, pledged assets often become illiquid during the staking period as they cannot be traded or transferred.
Liquidity staking enables cryptocurrency holders to participate in staking without giving up control of their holdings. This changes the way users perform staking. Projects such as Lido have introduced liquidity staking, providing tokenization of pledged assets in the form of tokens and derivatives.
It allows users to gain the advantages of staking while retaining the flexibility to trade these tokens in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or transfer them to other users.

#2. Is there a difference between entrusted staking and liquidity staking?
Network users in Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) vote to choose their preferred delegator. However, the purpose of liquid staking is to allow stakers to circumvent minimum staking thresholds and mechanisms to lock up tokens.
Although DPoS borrows the basic concept of Proof of Stake, the way it is executed is different. In DPoS, network users have the power to elect representatives called “witnesses” or “block producers” to validate blocks. The number of representatives participating in the consensus process is limited and can be adjusted by voting. Network users in DPoS can pool their tokens into a staking pool and use their combined voting power to vote for preferred representatives.
Liquidity staking, on the other hand, aims to lower the investment threshold and provide stakers with a way to circumvent the token locking mechanism. Blockchains often have minimum requirements for staking. For example, Ethereum requires anyone who wants to set up a validator node to stake at least 32 Ethereum (ETH). It also requires specific computer hardware, software, time and expertise, which in turn requires significant investment.

3. What is staking as a service?
Staking-as-a-Service is a platform that acts as an intermediary, connecting the blockchain’s consensus mechanism with cryptocurrency holders who wish to contribute to the functionality of the network.
Staking-as-a-Service is a platform or service that enables users to entrust their crypto assets to a third party, who then participates in staking on the user’s behalf, typically charging a fee or sharing in rewards. According to JPMorgan Chase, the pledge services industry will expand to $40 billion by 2025. Cryptocurrency staking services will play an important role in this emerging economy, and liquidity staking will become an integral part of it.
Staking-as-a-service platforms can be classified into custodial and non-custodial based on the degree of decentralization, which plays an important role in safeguarding the best interests of stakeholders and maintaining transparency. To facilitate decentralized governance, key decisions are made by Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
Managed Staking as a Service involves extensive management of the staking process. The staking services provided by cryptocurrency exchanges are custodial. Rewards flow first to staking providers and then to stakers.
In a non-custodial staking-as-a-service model, validators charge a commission to anyone who wants to participate in staking. In PoS networks that support native delegation, stakers’ reward shares are sent directly to them without the involvement of validators.
4. How Liquidity Staking Works
Liquidity Staking aims to eliminate the staking threshold and allow holders to profit from liquidity tokens.
The staking pool allows users to combine several small pledges into one large pledge using smart contracts, which provide each staker with corresponding liquid tokens (representing their share of the staking pool).
This mechanism eliminates the threshold for becoming a staker. Liquid staking goes a step further, allowing stakers to double their returns. On the one hand, they earn from the staked tokens, and on the other hand, they earn from the liquidity tokens by conducting financial activities such as trading, lending or any other activities without affecting their original staked positions. profit.
Using Lido as a case study will help us better understand how liquidity staking works. Lido is a liquid staking solution for PoS currencies, supporting multiple PoS blockchains including Ethereum, Solana, Kusama, Polkadot, and Polygon. Lido provides an innovative solution to the barriers posed by traditional PoS staking by effectively lowering the barriers to entry and costs associated with locking assets in a single protocol.

#Lido is a staking pool based on smart contracts. Users who deposit assets into the platform will stake them on the Lido blockchain through the protocol. Lido allows ETH holders to stake a fraction of the minimum threshold (32 ETH) to earn block rewards. After depositing funds into Lido's staking pool smart contract, users receive Lido Staked ETH (stETH), an ERC-20 compatible token that is minted on deposits and destroyed on withdrawals.
The protocol distributes staked ETH to validators (node operators) within the Lido network, which is then deposited into the Ethereum beacon chain for verification. These funds are then protected by a smart contract, which is inaccessible to validators. ETH deposited through the Lido staking protocol is divided into sets of 32 ETH among active node operators on the network.
These operators utilize public verification keys to verify transactions involving user-staking assets. This mechanism allows users’ staked assets to be spread across multiple validators, thereby reducing the risks associated with single points of failure and single validator staking.
Stakers who deposit Solana (SOL) tokens, Polygon (MATIC), Polkadot (DOT), and Kusama KSM via a set of smart contracts in Lido will receive stSOL, stMATIC, stDOT, and stKSM respectively. stToken can be used to earn DeFi yields, provide liquidity, trade on decentralized exchanges (DEX), and many other use cases.
5. Are there any risks in the liquidity staking platform?
As with any product or service in the cryptocurrency space, technical threats and market volatility need to be considered when dealing with liquidity staking.
Technical Threats
PoS blockchain is still relatively new, and there is always the possibility of protocol errors or vulnerabilities that could lead to assets being lost or exploited. Relying on validators for staking also creates counterparty risk.
Market Risk
Liquidity staking unlocks staked assets, allowing stakers to earn rewards from DeFi applications. However, this also brings the risk of losing ground on both fronts during market downturns.
Keeping the liquidity staking platform open source and regularly audited can help prevent threats to a certain extent. Having a bounty program for the platform can also help minimize bugs.
Conducting comprehensive due diligence is critical to addressing the risks associated with market volatility. This includes studying historical market data, assessing the financial health of potential investments, understanding the regulatory environment, and developing a diversified investment strategy.
The above is the detailed content of What do you understand about liquidity staking? How does it work?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 怎么理解流动性质押?它是怎么运作的May 06, 2024 am 09:10 AM
怎么理解流动性质押?它是怎么运作的May 06, 2024 am 09:10 AM什么是流动性质押?它是如何运作的?流动性质押和委托质押有何区别呢?流动质押允许质押者通过使用替代代币来保持质押代币的流动性,他们可以使用替代代币通过DeFi协议赚取额外收益。今天本站小编给大家详细介绍什么是流动性质押?流动性质押的运作方式,以及流动性质押和委托质押的区别。希望大家喜欢!一、什么是流动性质押?流动质押允许质押者通过使用替代代币来保持质押代币的流动性,他们可以使用替代代币通过DeFi协议赚取额外收益。在深入了解流动性质押之前,让我们先了解一下质押以及与之相关的问题。质押是指将加密货币
 区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM
区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM不是。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript、Go都可以实现区块链的开发;区块链技术涉及的面很广,而编程语言只是一种手段,把设计理念用代码呈现出来,做成产品服务用户。
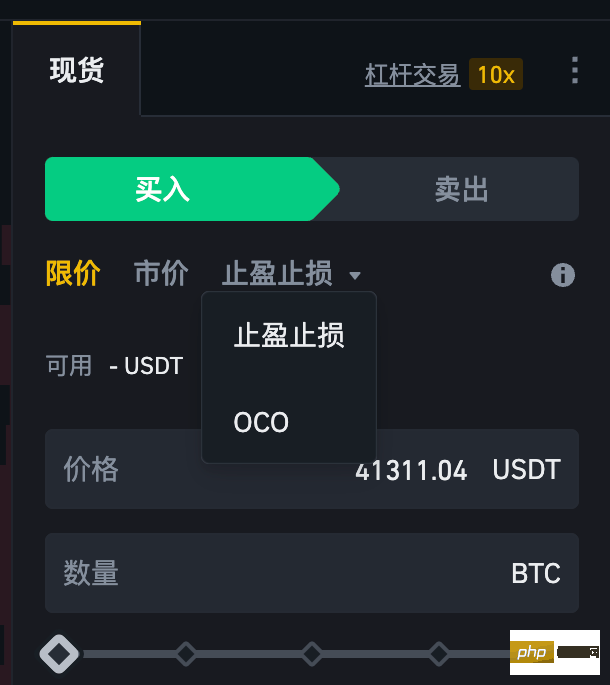 什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM
什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM二选一订单(OneCancelstheOther,简称OCO)可让您同时下达两个订单。它结合了限价单和限价止损单,但只能执行其中一个。换句话说,只要其中的限价单被部分或全部成交、止盈止损单被触发,另一个订单将自动取消。请注意,取消其中一个订单也会同时取消另一个订单。在币安交易平台进行交易时,您可以将二选一订单作为交易自动化的基本形式。这个功能可让您选择同时下达两个限价单,从而有助于止盈和最大程度减少潜在损失。如何使用二选一订单?登录您的币安帐户之后,请前往基本交易界面,找到下图所示的交易区域。点
 为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM
为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM原因:1、Go语言具有部署简单、性能优秀、并行执行性能好、良好语言设计、内置大量库、团队牛逼等优势。2、以太坊和超级账本都选择使用Go作为开发语言;这两大超级区块链的影响力很大,不仅在生态中占据了大的坑位,事实上还隐性的制定了区块链的标准。
 go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM可以开发。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如go语言、Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript都可以实现区块链的开发。Go语言是为了解决分布式计算,而区块链是典型的分布式数据存储系统,因此go语言能开发区块链。且Go易学易用,能很好的满足区块链行开发需要的“执行效率高、高并发、跨平台,网络开发要求高”等特点。
 深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM区块链技术的出现,使得数字货币的应用成为可能,也在许多领域得到了广泛应用。随着区块链技术领域的扩大,开发人员对于更好的应用程序编写方式的需求也高涨起来。于是,一个叫做Go语言(简称Golang)的编程语言悄悄兴起,成为了区块链开发人员的最爱。Go语言是谷歌公司开发的一种系统级编程语言,自诞生以来,一直着重强调程序设计的简捷和高效。Go语言的优点包括:静态类型
 Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AM
Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AMJava是一种广泛使用的编程语言,它被许多公司和组织用作开发各种应用程序的工具。最近几年来,区块链和加密货币技术在全球范围内引起了大量的关注。Java的灵活性和多功能性使得它成为开发区块链和加密货币应用程序的优秀选择。区块链技术是一种安全的、去中心化的数据库,它可以存储和共享交易记录,而无需任何中央机构的干涉。Java提供了许多区块链开发框架,例如H
 打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM
打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM随着区块链技术的发展和应用越来越广泛,有越来越多的人开始参与到区块链技术的开发中来。而要想打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,选择合适的开发语言和工具是非常重要的。Go语言正是一个很好的选择,因为它的性能很高,同时还有很多优秀的开源工具和库,能够大大提高开发效率。下面就来介绍一下如何打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,使用Go语言进行开发。一、选择Go语言在选择开发语言

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







