One article to clarify what is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?
- 王林forward
- 2024-05-06 08:00:121339browse
Currently, sharding, Layer 2 and cross-chain bridges are being used as breakthroughs to try to solve the dilemma caused by the impossible triangle of blockchain.
What is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?
The Blockchain Impossible Triangle, also known as the Blockchain Trilemma and Blockchain Trilemma, refers to the design and implementation of the Blockchain. The dilemma faced by the three key elements - decentralization, security and scalability.
These three elements are in conflict with each other. According to current technology, it is difficult for us to implement all three elements simultaneously in one system.
Simply put, with the current technical status, no blockchain can be decentralized, secure and fast at the same time. Achieve at most one or two of these.
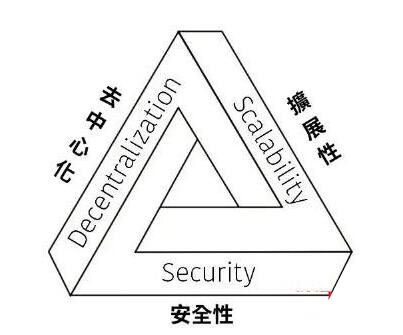
Blockchain Impossible Triangle
Element 1: Decentralization Decentralization
means that the nodes that maintain the network are scattered everywhere , and no node can individually control or manipulate the entire network. Decentralization is to prevent single points of failure and avoid monopoly control by central institutions.
Element 2: SecuritySecurity
Security means that the data in the blockchain cannot be changed once it is written, and the encryption algorithm is used to protect the information from unauthorized persons. Tampering or reading.
means that the blockchain system needs to have sufficient defense capabilities against various attacks, including preventing double-spending attacks and ensuring the irreversibility of transactions.
Element Three: Scalability Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability of the blockchain network to effectively handle a large number of transactions and users. However, in reality, when many existing blockchains develop to a certain scale, since each node needs to process all transactions, the transaction speed will decrease and cannot achieve efficient scalability.
So in the blockchain impossible triangle, some people call the scalability part "fast" or "speed".
Blockchain Impossible Triangle in Practical Application
Bitcoin
Bitcoin places its focus on security and decentralization, thus leading to Bitcoin The scalability of the coin is limited. Because Bitcoin’s block size and block time settings limit its transaction processing capabilities. When demand is high, this can lead to transaction delays and rising fees.
Ethereum
Ethereum also focuses on security and decentralization, and as a smart contract platform, it needs to ensure that user assets and protocols are safe. Therefore, the scalability of Ethereum is poor, especially when the application volume of DeFi and NFT increases significantly, the problems of transaction delays and rising fees are particularly prominent.
EOS and Solana
These two blockchain projects mainly focus on scalability and are therefore very efficient in terms of processing speed and throughput. In order to achieve such performance, they made some compromises in the degree of centralization of the network, such as limiting the number of validators.
Polygon
Polygon is a Layer 2 solution that improves scalability by providing an Ethereum-compatible chain. But this solution also requires sacrificing decentralization to a certain extent, such as shifting part of the transaction verification work to a few nodes.
The impact of the impossible triangle of blockchain
- Limitations of blockchain applications: Many blockchain applications (such as DeFi, DApp, etc.) require a certain degree of decentralization and security to ensure its operation. In order to achieve these goals, it is usually necessary to sacrifice some scalability, which makes these applications likely to encounter performance bottlenecks when facing large-scale users.
- Blockchain choices and trade-offs: Different blockchains will make different choices based on their goals and usage. For example, Bitcoin and Ethereum chose decentralization and security at the expense of certain scalability. On the other hand, some new blockchain platforms (such as EOS, Solana, etc.) choose to sacrifice a certain degree of decentralization to achieve higher scalability.
- The driving force of blockchain innovation: The Impossible Triangle of blockchain is also an important factor driving technological innovation. To solve this dilemma, many projects are working on new consensus algorithms, sharding technology, Layer 2 solutions, etc. to improve the performance of the blockchain. This effort promotes the continued development and progress of blockchain technology.
- Long-term development and trust of blockchain: The blockchain impossible triangle reminds us that the balance between blockchain’s scalability, security and decentralization not only affects its performance in the short term , and also affects its ability to build trust and achieve sustainable development in the long term. This has important implications for our understanding and assessment of the potential and limitations of blockchain technology.
A breakthrough to solve the impossible triangle of blockchain?
Solving the challenges of the impossible triangle of blockchain requires innovative technical solutions. The following are some possible solutions currently being explored:
Sharding
Sharding is a technology that can divide the network into multiple parts. Each shard can independently process transactions and smart contracts. This approach can greatly increase the scalability of the blockchain while maintaining a certain degree of decentralization and security. Ethereum 2.0 is an example of trying to use sharding to solve the impossible triangle problem.
Ethereum is the most well-known blockchain platform that uses sharding technology. Ethereum 2.0 plans to increase its processing power by introducing sharding technology. When sharding is completed, each shard will be able to process transactions independently, thereby greatly increasing the transaction speed of Ethereum.
Layer 2 solutions
These solutions build a secondary blockchain on top of the existing blockchain (also known as "Layer1") , to improve scalability. These Layer 2 solutions can speed up transaction processing and reduce transaction fees without compromising the security or decentralized nature of the underlying blockchain.
Lightning Network is an example of a major Layer 2 solution. The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain that allows users to conduct instant, large-scale and small-amount transactions without recording every transaction on the main blockchain.
Cross-chain interoperability
This method refers to allowing different blockchains to communicate and operate with each other. In this way, the resources and advantages of different blockchains can be combined to solve the impossible triangle problem.
Some cross-chain bridge protocols, such as Stargate, Cosmos and Polkadot, are exploring this approach.
Summary
No matter how much we appreciate the revolutionary potential of blockchain, we must recognize that this technology also faces some important challenges. The Impossible Triangle does not mean that the development path of blockchain technology has been completely closed. On the contrary, it provides a thinking framework that allows us to understand the limitations of blockchain more clearly and inspires us to find new ways to overcome these limitations. methods to promote the development of technology.
Whether we are observers, developers or users, we all look forward to witnessing how blockchain technology unlocks new possibilities and realizes its true potential. I believe that in the near future, we will be able to use blockchain technology that is decentralized, secure, and fast.
The above is the detailed content of One article to clarify what is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

