 Backend Development
Backend Development Golang
Golang What are the synchronization mechanisms between golang functions and goroutine?
What are the synchronization mechanisms between golang functions and goroutine?Go language provides a variety of synchronization mechanisms, including mutex locks, read-write locks, condition variables and WaitGroup, to solve data inconsistencies or race conditions caused by concurrent access to shared resources. Mutex locks provide exclusive access to shared resources, read-write locks support multiple simultaneous reads and single writes, condition variables are used to coordinate waiting and notification between Goroutines, and WaitGroup is used to wait for a group of Goroutines to complete. For example, in the case of a shared buffer, a mutex can ensure that only one Goroutine accesses the buffer at a time, avoiding data corruption.

The synchronization mechanism of functions and Goroutines in Go language
In concurrent programming, the synchronization mechanism is crucial and is used to Ensure that concurrent access to shared resources does not cause data inconsistencies or race conditions. The Go language provides a variety of synchronization mechanisms. The following are the most commonly used mechanisms for synchronizing functions and Goroutines:
Mutex (Mutex)
Mutex locks provide Exclusive access to shared resources. When a Goroutine acquires a mutex, other Goroutines will be blocked until the Goroutine releases the mutex.
var mu sync.Mutex
func someFunction() {
mu.Lock()
// 对共享资源进行操作
mu.Unlock()
}Read-write lock (RWMutex)
Read-write lock allows multiple Goroutines to read shared resources at the same time, but only one Goroutine can write to shared resources at the same time.
var rwmu sync.RWMutex
func someFunction() {
rwmu.RLock()
// 读取共享资源
rwmu.RUnlock()
}
func anotherFunction() {
rwmu.Lock()
// 写入共享资源
rwmu.Unlock()
}Condition variable (Cond)
Condition variable is used to coordinate waiting and notification between Goroutines. A Goroutine can wait on a condition variable until another Goroutine notifies it.
var cond sync.Cond
func someFunction() {
cond.L.Lock()
// 等待条件变量被通知
cond.Wait(&cond.L)
// 执行被通知后的代码
cond.L.Unlock()
}
func anotherFunction() {
cond.L.Lock()
// 通知正在等待条件变量的 Goroutine
cond.Signal()
cond.L.Unlock()
}WaitGroup
WaitGroup is used to wait for a group of Goroutines to complete. It ensures that certain operations are not performed until all Goroutines have completed.
var wg sync.WaitGroup
func someFunction() {
wg.Add(1)
// Goroutine 执行一些任务
wg.Done()
}
func main() {
wg.Add(5)
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
go someFunction()
}
// 等待所有 Goroutine 完成
wg.Wait()
// 主 Goroutine 执行一些操作
}Practical case
Take a shared buffer as an example. Multiple Goroutines read and write data from the buffer. We can use a mutex to ensure concurrent access to the buffer:
var mu sync.Mutex
type Buffer struct {
data []int
}
func (b *Buffer) Read() []int {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
return b.data
}
func (b *Buffer) Write(data []int) {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
b.data = data
}By using a mutex, we ensure that at any given time, only one Goroutine can access the shared buffer, thus avoiding data damage.
The above is the detailed content of What are the synchronization mechanisms between golang functions and goroutine?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Linux环境编程必须搞懂的几个概念Feb 15, 2024 am 08:03 AM
Linux环境编程必须搞懂的几个概念Feb 15, 2024 am 08:03 AM对于初学者来说,要想在Linux环境下编程,必须深入理解一些重要概念才能更好地编写代码,实现业务功能。下面我们将介绍几个重要且常用的知识点。掌握这些概念可以避免在将来的编码中出现混淆。系统调用“❝所有操作系统的内核中都有一些内置函数,这些函数可以用来完成一些系统级别的功能。在Linux系统中,这些函数被称为“系统调用”(systemcall)。它们代表了从用户空间到内核空间的一种转换。❞”已收到消息.对于初学者来说,要想在Linux环境下编程,必须深入理解一些重要概念才能更好地编写代码,实现业务
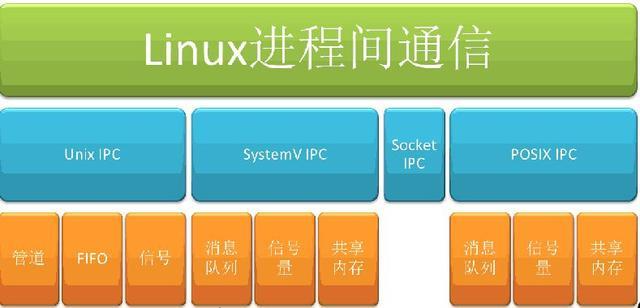 Linux 进程间通信的方法和技巧:如何让进程之间互相交流和协作Feb 11, 2024 pm 02:09 PM
Linux 进程间通信的方法和技巧:如何让进程之间互相交流和协作Feb 11, 2024 pm 02:09 PM进程间通信是指在Linux系统中,不同的进程之间进行数据的传递和共享,以实现进程之间的交流和协作。进程间通信的目的是提高系统的并发性和效率,以完成一些复杂的任务和功能。进程间通信的方法有很多种,如管道、消息队列、信号、共享内存、信号量、套接字等,它们各有各的特点和优缺点,适用于不同的场景和需求。但是,你真的了解Linux进程间通信的方法吗?你知道如何在Linux下使用和选择合适的进程间通信方法吗?你知道如何在Linux下优化和提高进程间通信的效果吗?本文将为你详细介绍Linux进程间通信的相关知
 作为嵌入式开发工程师,关于Linux kernel同步机制你不得不知道Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:50 PM
作为嵌入式开发工程师,关于Linux kernel同步机制你不得不知道Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:50 PM前言同步是进程之间,以及进程与系统资源之间的交互。由于Linux内核采用多任务,因此在多个进程之间必须有同步机制来保证协调。Linux内核中有许多种同步机制。今天我们将重点介绍kernel中的异步和同步机制,其中着重介绍kernel中的异步机制。kernel中的异步机制分为两种:一种是应用层的同步机制,即应用层线程之间的通信;另一种是内核的同步机制。当一个线程进入内核态后,它可以直接与内核沟通。kernel中有两个线程是这样的:一个是线程A,它进入内核态后会直接与内核沟通,告诉它要做什么,完成后
 Golang中同步机制对于游戏开发性能的提升Sep 27, 2023 am 09:25 AM
Golang中同步机制对于游戏开发性能的提升Sep 27, 2023 am 09:25 AMGolang中同步机制对于游戏开发性能的提升,需要具体代码示例引言:游戏开发是一个对性能高要求的领域,在处理实时交互的同时,还要保持游戏的流畅性和稳定性。而Go语言(Golang)则提供了一种高效的编程语言和并发模型,使得其在游戏开发中有着广泛应用的潜力。本文将重点探讨Golang中同步机制对于游戏开发性能的提升,并通过具体代码示例来加深理解。一、Golan
 Linux多线程互斥量:一种保证线程安全的同步机制Feb 13, 2024 pm 01:40 PM
Linux多线程互斥量:一种保证线程安全的同步机制Feb 13, 2024 pm 01:40 PMLinux系统是一种支持多任务并发执行的操作系统,它可以同时运行多个进程,从而提高系统的利用率和效率。但是,如果一个进程中有多个线程,而这些线程需要共享一些数据或资源,就可能出现数据不一致或资源竞争的问题,导致系统的错误或异常。为了解决这个问题,就需要使用一些同步机制,例如信号量、条件变量、互斥量等。其中,互斥量是一种比较简单而有效的同步机制,它可以让一个线程在访问共享数据或资源时,锁定它们,防止其他线程同时访问,从而保证线程安全。本文将介绍Linux系统中多线程互斥量的互斥的方法,包括互斥量的
 详解Linux内核中的RCU机制Feb 10, 2024 pm 09:09 PM
详解Linux内核中的RCU机制Feb 10, 2024 pm 09:09 PMLinux内核是一个复杂的系统,它需要处理多种多样的并发问题,如进程调度、内存管理、设备驱动、网络协议等。为了保证数据的一致性和正确性,Linux内核提供了多种同步机制,如自旋锁、信号量、读写锁等。但是,这些同步机制都有一些缺点,比如:自旋锁会导致CPU浪费时间在忙等待上,而且不能在抢占式内核中使用;信号量会导致进程睡眠和唤醒,增加了上下文切换的开销;读写锁会导致写者饥饿或者读者饥饿,而且在读者多写者少的情况下,写者还要获取锁的开销。那么,有没有一种更好的同步机制呢?答案是有的,那就是RCU(R
 深入探讨Java多线程:同步和死锁的原理解析Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:01 PM
深入探讨Java多线程:同步和死锁的原理解析Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:01 PMJava多线程原理剖析:线程同步与死锁问题分析摘要:本文将深入探讨Java多线程编程中的线程同步和死锁问题。通过详细解释线程的原理和Java提供的同步机制,我们将讨论如何正确地使用同步机制来避免线程冲突和数据不一致的问题。同时,我们还将分析死锁问题以及如何避免和解决这些问题。1.引言随着计算机硬件的发展,多核处理器已经成为现代计算机系统的标配。而多线程编程
 了解Java中volatile的作用:保证多线程间数据的可见性和有序性Jan 30, 2024 am 08:53 AM
了解Java中volatile的作用:保证多线程间数据的可见性和有序性Jan 30, 2024 am 08:53 AM了解Java中volatile的作用:保证多线程间数据的可见性和有序性,需要具体代码示例在Java多线程编程中,为了确保多个线程之间的数据同步,我们常常需要使用volatile关键字。volatile关键字可以保证可见性和有序性,确保多个线程对某个变量的读写操作是正确的。一、可见性在多线程环境下,如果一个线程对某个共享变量进行修改,那么其他线程是否能够立即看


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),





