What types of cryptocurrencies are there?

Encrypted digital currency type
Cryptocurrency, also known as cryptocurrency, is a digital asset that uses cryptography to protect transactions and control the creation of new units. They differ from traditional fiat currencies in that they are not regulated by a central bank or government.
The main types of encrypted digital currencies include:
1. Bitcoin (BTC)
- The first cryptocurrency
- The highest market value and liquidity
- Mainly used for value storage and investment
2. Ethereum (ETH)
- Programmable Blockchain Platform
- Allows the development of decentralized applications (dApps)
- Mainly used for smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi)
3. Litecoin (LTC)
- Bitcoin’s fork
- Transactions are faster and fees are lower
- Mainly used for payments and remittances
4. Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
- Fork of Bitcoin
- Block capacity is larger, allowing more transactions
- Mainly used for payments and remittances
5. Ripple (XRP)
- Cryptocurrency designed for cross-border payments
- Fast transaction speeds and extremely low fees
- Mainly used for remittances between banks and financial institutions
6. Dogecoin (DOGE)
- Meme coin with Shiba Inu as the mascot
- Started as a joke coin, but later gained popularity
- Mainly used for micropayments and rewards
7. Shiba Inu Coin (SHIB)
- Derivatives of Dogecoin
- Have huge community support
- Mainly used for speculation and trading
8. Carl Dano (ADA)
- Blockchain platform developed using scientific methods
- Focus on scalability, security and governance
- Mainly used for smart contracts and dApps
9. Solana (SOL)
- Extremely fast blockchain platform
- Uses a unique consensus mechanism to achieve high transaction throughput
- Mainly used for dApps, DeFi and games
10. Polkadot (DOT)
- Multi-chain blockchain network
- Allows different blockchains to operate with each other
- Mainly used for cross-chain asset transfer and dApp development
The above is the detailed content of What types of cryptocurrencies are there?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 FloppyPepe (FPPE) Price Could Explode As Bitcoin (BTC) Price Rallies Towards $450,000May 09, 2025 am 11:54 AM
FloppyPepe (FPPE) Price Could Explode As Bitcoin (BTC) Price Rallies Towards $450,000May 09, 2025 am 11:54 AMAccording to a leading finance CEO, the Bitcoin price could be set for a move to $450,000. This Bitcoin price projection comes after a resurgence of good performances, signaling that the bear market may end.
 Pi Network Confirms May 14 Launch—Qubetics and OKB Surge as Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term in 2025May 09, 2025 am 11:52 AM
Pi Network Confirms May 14 Launch—Qubetics and OKB Surge as Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term in 2025May 09, 2025 am 11:52 AMExplore why Qubetics, Pi Network, and OKB rank among the Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term. Get updated presale stats, features, and key real-world use cases.
 Sun Life Financial Inc. (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) Declares a Dividend of $0.88 Per ShareMay 09, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Sun Life Financial Inc. (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) Declares a Dividend of $0.88 Per ShareMay 09, 2025 am 11:50 AMTORONTO, May 8, 2025 /CNW/ - The Board of Directors (the "Board") of Sun Life Financial Inc. (the "Company") (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) today announced that a dividend of $0.88 per share on the common shares of the Company has been de
 Sun Life Announces Intended Renewal of Normal Course Issuer BidMay 09, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Sun Life Announces Intended Renewal of Normal Course Issuer BidMay 09, 2025 am 11:48 AMMay 7, 2025, the Company had purchased on the TSX, other Canadian stock exchanges and/or alternative Canadian trading platforms
 The Bitcoin price has hit $100k for the first time since February, trading at $101.3k at press time.May 09, 2025 am 11:46 AM
The Bitcoin price has hit $100k for the first time since February, trading at $101.3k at press time.May 09, 2025 am 11:46 AMBTC's strong correlation with the Global M2 money supply is playing out once again, with the largest cryptocurrency now poised for new all-time highs.
 Coinbase (COIN) Q1 CY2025 Highlights: Revenue Falls Short of Expectations, but Sales Rose 24.2% YoY to $2.03BMay 09, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Coinbase (COIN) Q1 CY2025 Highlights: Revenue Falls Short of Expectations, but Sales Rose 24.2% YoY to $2.03BMay 09, 2025 am 11:44 AMBlockchain infrastructure company Coinbase (NASDAQ: COIN) fell short of the market’s revenue expectations in Q1 CY2025, but sales rose 24.2% year
 Ripple Labs and the SEC Have Officially Reached a Settlement AgreementMay 09, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Ripple Labs and the SEC Have Officially Reached a Settlement AgreementMay 09, 2025 am 11:42 AMRipple Labs and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have officially reached a deal that, if approved by a judge, will bring their years-long legal battle to a close.
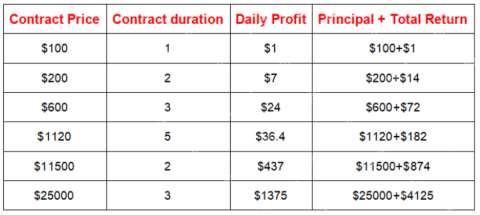 JA Mining Helps Global Users Share the Benefits of the Bitcoin Bull MarketMay 09, 2025 am 11:40 AM
JA Mining Helps Global Users Share the Benefits of the Bitcoin Bull MarketMay 09, 2025 am 11:40 AMBy lowering the threshold for mining and providing compliance protection, JA Mining helps global users share the benefits of the Bitcoin bull market.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools






