 web3.0
web3.0 Monad raised US$225 million to kick off the 'parallel EVM' hype again. What other projects are worth paying attention to?
Monad raised US$225 million to kick off the 'parallel EVM' hype again. What other projects are worth paying attention to?Author: Xiyou, ChainCatcher
Editor: Marco, ChainCatcher
April 9, Layer1 network Monad developer Monad Labs It completed US$225 million in financing at a valuation of US$3 billion. This round of financing was led by Paradigm, with participation from well-known institutions such as Electric CapitalAmber Group, Animoca Ventures, Bankless Ventures, Coinbase Ventures, and Wintermute Ventures.
The recent financing raised by Monad is the largest cryptocurrency financing so far in 2024. More than 50 institutions and investors participated in the investment, making it another king worth paying attention to in the crypto community. The project has also set off a boom in "parallel EVM" hype.
Monad is a high-performance Layer1 network that focuses on the concept of "Parallel EVM". It hopes to improve and enhance the execution efficiency of EVM in the Layer1 network by introducing "parallel processing" in the execution layer.
However, Monad’s mainnet will not be deployed until the end of this year, and the testnet is not open to the public. Currently, users can only participate by joining its Discord community. But its main concept of "parallel EVM" has become popular again with Monad's large financing.
"Parallel EVM": optimize EVM execution efficiency, "horizontal expansion" blockchain performance
"Parallel EVM" can be regarded as "parallel EVM compatible" II The technology integration of the two is an optimization of the existing EVM network execution layer. It is essentially a special optimization of the performance of each component of EVM to increase the number of transactions (TPS) or computing tasks processed by the network per unit time. Solve the current EVM inefficiency problem caused by transaction sequence execution.
In traditional EVM environments, such as Ethereum, each transaction on the chain is executed in sequence, that is, when a user submits multiple transactions. When a transaction is submitted, it needs to be queued and processed in the order of submission time. Only after the transaction submitted first is confirmed, the transaction submitted later will start to be processed. Most high-performance Layer 1 such as Solana, Aptos, Sui, etc. , in fact, they are essentially designing their own optimization solutions based on the inability to process transactions in parallel on the Ethereum chain. However, everyone pays more attention to the innovation of the consensus algorithm and ignores the technical innovation of the execution layer. But they want to get one. For a high-performance public chain, the consensus algorithm and execution layer need to cooperate with each other. The consensus algorithm can ensure node collaboration and maintain network security. The execution layer needs to improve the efficiency of processing transactions and executing smart contracts. Parallel EVM. It is hoped that by partitioning or grouping all the transactions to be executed, and then relying on the scheduling algorithm to effectively manage the synchronization processing of each zone or each group of transactions, the ultimate goal is to allow multiple independent transactions to be executed in parallel at the same time, thereby improving Layer1 Transaction execution efficiency of the overall network. For example, Ethereum’s EVM is like a one-way street. Cars, electric vehicles, bicycles, people, etc. all gather on the same street, in order of queuing. Driving one after another is very congested and chaotic; but parallel EVM technology can divide this one-way road into multiple lanes such as motor lanes, non-motorized lanes, cycling lanes, and sidewalks to move forward simultaneously, which improves efficiency and alleviates congestion. Parallel execution in the blockchain is to process unrelated transactions at the same time, such as partitioning or grouping transactions on the chain such as DEX, NFT, GameFi, etc., so that they can execute transactions independently in parallel. This It also means that different transactions can be executed on different processing units at the same time, instead of being queued in chronological order, which greatly improves efficiency. Solana's SVM and Aptos' STM, which are famous for their high performance, are all used. ## Regarding the improvement of blockchain performance by "parallel EVM", community user Liu said:
## Regarding the improvement of blockchain performance by "parallel EVM", community user Liu said:
In fact, the "Parallel EVM" narrative is not a new concept. As early as 2022, Polygon PoS announced that it had completed a parallel EVM upgrade and doubled its network speed. BSC also It has already cooperated with NodeReal to develop parallel EVM technology.
It’s just that at that time, everyone didn’t pay much attention to the “parallel EVM” technology. They paid more attention to the consensus algorithm of the blockchain network and the Rollup expansion method.
Until the end of 2023, Paradigm CTO Georgios Konstantopoulos, Dragonfly Capital partner Haseeb Qureshi, Polygon former founder Jaynti Kanani (JD) and others all said when looking forward to industry trends in 2024: "2024 will be The Year of Parallel EVM".
Among them, JD, the former founder of Polygon, said that in 2024, every L2 will be labeled as "Parallel EVM" and rebranded.
The public support of leading VCs has sparked a wave of EVM-compatible Layer 1s that use parallel execution technology, such as Sei, Monad, Polygon, etc., and has also made the concept of "parallel EVM" a new hot spot pursued by the encryption community.
In March this year, the news that "Solana EVM solution Eclipse received US$30 million in financing" caused dissatisfaction from Sei founder Jay, questioning its excessive hype and difficulty in implementing ecological development. It also triggered a heated public debate on the topic of "EVM parallel expansion" among Eclipse founder Neel Somani, Fantom founder AC, etc., making the "parallel EVM" narrative once again become the focus of the community.
What are the representative projects of parallel EVM network?
Data from the encrypted data platform Rootdata shows that there are 7 "parallel EVM" concept projects that have been included, including Monad, Sei, Canto, Artela, Neon, Eclipse, Cipherem, etc.

Developer Pignard said: "A major premise of 'parallel EVM' is that EVM is compatible with the network. Although networks such as Solana, Aptos, Fuel, and Sui use parallel execution, due to It is a non-EVM network, so it is not included in the 'Parallel EVM' project category. "
Currently, existing parallel EVM networks can be divided into three categories:
First: Originally, EVM that did not use parallel execution technology was compatible with Layer 1. Later, parallel EVM upgrades were completed through technical iterations, and all EVM networks can essentially undergo parallel EVM upgrades. For example, Polygon has completed the parallel EVM upgrade in 2022; Fantom's Fantom Sonic upgrade network, which will be launched in April, also introduces parallel execution technology;
The second is: EVM using parallel execution technology Compatible with Layer1, such as Monand, Sei V2 and Artela;
The third is: Layer2 network using non-EVM Layer1 parallel execution technology, such as expanded layer2 EVM compatible chain represented by Solana Neon, Eclipse, Lumio, etc. They abstract EVM into a pluggable execution module, and can select the best "VM execution layer" according to needs, thereby realizing parallel capabilities. For example, the Lumio settlement layer is in Ethereum, and the execution layer can choose to use Solana VM, Move VM, EVM etc.
Parallel EVM track representative project
1、Parallel EVM leader Monad
Monad is A Layer 1 network area dedicated to solving the scalability problem of traditional EVM, aiming to improve network transaction processing speed by optimizing EVM such as introducing parallel execution and pipeline architecture, so that its TPS can reach 10,000.
On April 9, Monad completed a US$225 million financing led by Paradigm at a valuation of US$3 billion. In February last year, it also raised US$19 million in the seed round, bringing the total financing to US$244 million. It is currently the parallel EVM project with the highest financing and valuation.
Monad’s team background also attracts attention. The founding team members come from the market-making giant Jump Trading. One of the founders, Keone Hon, was the head of research at Jump Trading and has worked in the company for 8 years. Another co-founder, James Hunsaker, is a senior software engineer at Jump Trading and a core maintainer of Pyth Network.
In September last year, Monad revealed the network token MON in the project technical document released, but then the introduction to MON in the document was deleted.
Monad has launched an internal test network in March. It is reported that the test network will be open to the public in a few months.
2, Sei will launch the parallel EVM network Sei V2 in the first half of the year
Sei was originally a Layer1 network dedicated to transactions. Provide advanced infrastructure for various trading applications such as DeFi, DEX, games, etc.
In November last year, Sei announced that it would comprehensively upgrade its network and launch Sei V2, becoming the first high-performance parallel EVM, increasing its TPS to 12,500.
The Sei v2 parallel EVM test network was launched in February this year. Applications that support EVM deployment can be migrated to the network with one click. It is reported that its parallel EVM network can handle thousands of transactions per second. The main network It is expected to be launched in the first half of this year.
In March, Sei announced the launch of the Parallel Stack open source framework, which supports the use of parallel processing technology in Layer2 and Rollup networks.
3, Artela launches EVM dual virtual machines to improve execution layer performance
Artela hopes to expand the EVM to unlock the scalability of the Layer 1 network and support EVM parallelism implement. It aims to unlock the performance of the EVM blockchain and improve network execution efficiency by building EVM, that is, EVM WASM. The core members of the team come from Ant Chain.
The public test network is now online. It is reported that the Artela ecological incentive plan Renaissance Plan will be launched in April.
4, Canto plans to introduce parallel EVM technology
Canto is an EVM-compatible Layer1 network built based on the Cosmos SDK, specially designed for DeFi applications.
In March this year, Canto announced a Cyclone Stack development plan, aiming to introduce parallel execution EVM technology to improve its network performance.
5, Neon: Solana EVM compatible solution
Neon EVM is a parallel EVM built based on the Solana network, and is also the first Solana EVM compatible solution , allowing Solidity and Vyper EVM developers to deploy their DApps to the Solana network with one click and enjoy Solana’s high throughput and low gas fees.
The specific process is that Neon EVM can package transactions similar to the EVM network into Solana transactions for operation, and then send them to the Solana network, and then process and execute transaction data in a parallel manner in the network , to improve transaction speed, the network TPS is now as high as 2000.
Simply put, Neon EVM has built a software environment for Solana. Through this network, EVM developers can migrate applications to Solana with one click, and transactions are executed in parallel with Solana.
6, Eclipse aims to introduce SVM to Ethereum
Eclipse is a Rollup Layer2 modular universal solution supported by Solana virtual machine SVM , that is, the transaction data of the Eclipse network is settled in Ethereum, and ETH is used as gas fee on the chain, but the execution layer runs in the SVM environment.
Facing the problem of insufficient performance caused by the sequential execution of EVM, contrary to Neon’s idea of introducing EVM into Solana, Eclipse’s strategy is to introduce SVM into Ethereum.
In short, the logic of Eclipse product operation is: transaction execution is in Solana's SVM, and transaction settlement is still on Ethereum.
On March 11, Eclipse announced the completion of a $50 million Series A financing led by Hack VC and others. Currently, Eclipse is in the testnet stage. On April 9, an official document stated that the mainnet will be open to developers soon.
7, Lumio: Modular VM Layer2
Lumio is a modular VM Layer2 network built based on OP Stack, because it is an Optimism super chain One of them, called SuperLumio, aims to introduce high-performance VMs such as Aptos VM, Move VM, and Solana VM into the existing major Ethereum and Bitcoin Layer 2.
The product design logic is similar to the Eclipse product. Simply put, Lumio supports the use of Ethereum or Bitcoin as its settlement layer, and the execution layer can use virtual machines such as Aptos VM and Solana VM for parallel execution.
Lumio is the mainnet that was launched in February this year
The above is the detailed content of Monad raised US$225 million to kick off the 'parallel EVM' hype again. What other projects are worth paying attention to?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM
区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM不是。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript、Go都可以实现区块链的开发;区块链技术涉及的面很广,而编程语言只是一种手段,把设计理念用代码呈现出来,做成产品服务用户。
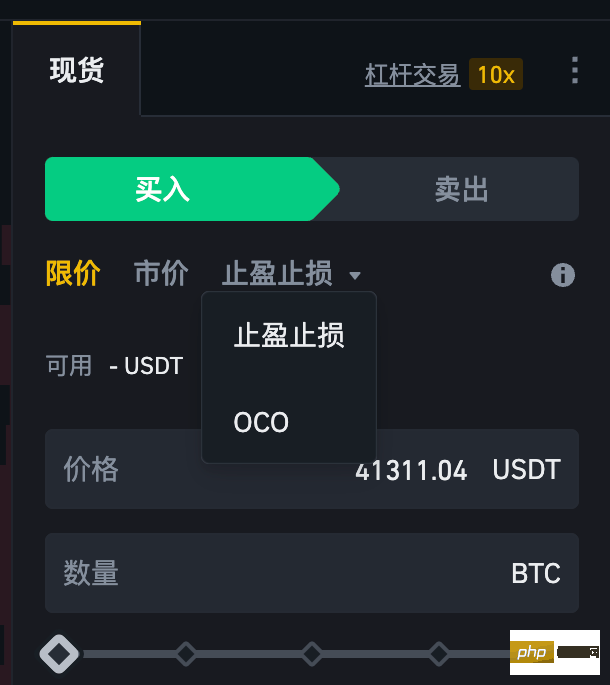 什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM
什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM二选一订单(OneCancelstheOther,简称OCO)可让您同时下达两个订单。它结合了限价单和限价止损单,但只能执行其中一个。换句话说,只要其中的限价单被部分或全部成交、止盈止损单被触发,另一个订单将自动取消。请注意,取消其中一个订单也会同时取消另一个订单。在币安交易平台进行交易时,您可以将二选一订单作为交易自动化的基本形式。这个功能可让您选择同时下达两个限价单,从而有助于止盈和最大程度减少潜在损失。如何使用二选一订单?登录您的币安帐户之后,请前往基本交易界面,找到下图所示的交易区域。点
 为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM
为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM原因:1、Go语言具有部署简单、性能优秀、并行执行性能好、良好语言设计、内置大量库、团队牛逼等优势。2、以太坊和超级账本都选择使用Go作为开发语言;这两大超级区块链的影响力很大,不仅在生态中占据了大的坑位,事实上还隐性的制定了区块链的标准。
 go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM可以开发。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如go语言、Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript都可以实现区块链的开发。Go语言是为了解决分布式计算,而区块链是典型的分布式数据存储系统,因此go语言能开发区块链。且Go易学易用,能很好的满足区块链行开发需要的“执行效率高、高并发、跨平台,网络开发要求高”等特点。
 深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM区块链技术的出现,使得数字货币的应用成为可能,也在许多领域得到了广泛应用。随着区块链技术领域的扩大,开发人员对于更好的应用程序编写方式的需求也高涨起来。于是,一个叫做Go语言(简称Golang)的编程语言悄悄兴起,成为了区块链开发人员的最爱。Go语言是谷歌公司开发的一种系统级编程语言,自诞生以来,一直着重强调程序设计的简捷和高效。Go语言的优点包括:静态类型
 打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM
打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM随着区块链技术的发展和应用越来越广泛,有越来越多的人开始参与到区块链技术的开发中来。而要想打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,选择合适的开发语言和工具是非常重要的。Go语言正是一个很好的选择,因为它的性能很高,同时还有很多优秀的开源工具和库,能够大大提高开发效率。下面就来介绍一下如何打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,使用Go语言进行开发。一、选择Go语言在选择开发语言
 Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AM
Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AMJava是一种广泛使用的编程语言,它被许多公司和组织用作开发各种应用程序的工具。最近几年来,区块链和加密货币技术在全球范围内引起了大量的关注。Java的灵活性和多功能性使得它成为开发区块链和加密货币应用程序的优秀选择。区块链技术是一种安全的、去中心化的数据库,它可以存储和共享交易记录,而无需任何中央机构的干涉。Java提供了许多区块链开发框架,例如H
 如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识Jun 04, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识Jun 04, 2023 pm 03:51 PM区块链是一种去中心化的分布式账本技术,随着其应用领域的不断扩展,如何保障区块链参与者的身份安全问题也逐渐成为热门话题。本文将介绍如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识。一、为什么需要区块链身份标识在现有的互联网世界中,身份验证是一个非常重要的问题。通过用户名和密码等方式,用户可以登录到我门的网站上,从而使用我们的服务。但是,在互联网上,身份验证存在着

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






