The main virtual currencies in China are: Bitcoin (BTC) Ethereum (ETH) Tether (USDT) Other popular virtual currencies include: Ripple (XRP) Litecoin (LTC) Dogecoin (DOGE) Binance Coin (BNB) ) Cardano (ADA) Polkadot (DOT) Solana (SOL)

What virtual currencies are there in China?
Main virtual currency
- Bitcoin (BTC): The world’s first and most famous virtual currency, Known for its decentralization and security mechanisms.
- Ethereum (ETH): The second largest virtual currency after Bitcoin, it is known for its smart contract platform that allows the development of distributed applications.
- Tether (USDT): A stable currency whose value is pegged to the U.S. dollar and is used for trading and stabilizing the value of other virtual currencies.
Other popular virtual currencies
- Ripple (XRP): A currency designed for cross-border payments and settlements virtual currency, recognized for its fast and low-cost transactions.
- Litecoin (LTC): A Bitcoin offshoot virtual currency with faster transaction speeds, often referred to as "Bitcoin Silver".
- Dogecoin (DOGE): A virtual currency originally created as a joke but gained popularity due to its active community and low transaction costs.
- Binance Coin (BNB): The native virtual currency of the Binance exchange, used to pay trading fees and access features on its platform.
- Cardano (ADA): A smart contract platform focused on scalability, security and governance.
- Polkadot (DOT): A multi-chain platform that allows different blockchains to connect and interact with each other.
- Solana (SOL): A blockchain platform focused on high transaction throughput and low transaction costs.
It is worth noting that virtual currency transactions are strictly regulated in China, so participating in virtual currency transactions requires careful operation and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
The above is the detailed content of What are the domestic virtual currencies?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM
区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM不是。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript、Go都可以实现区块链的开发;区块链技术涉及的面很广,而编程语言只是一种手段,把设计理念用代码呈现出来,做成产品服务用户。
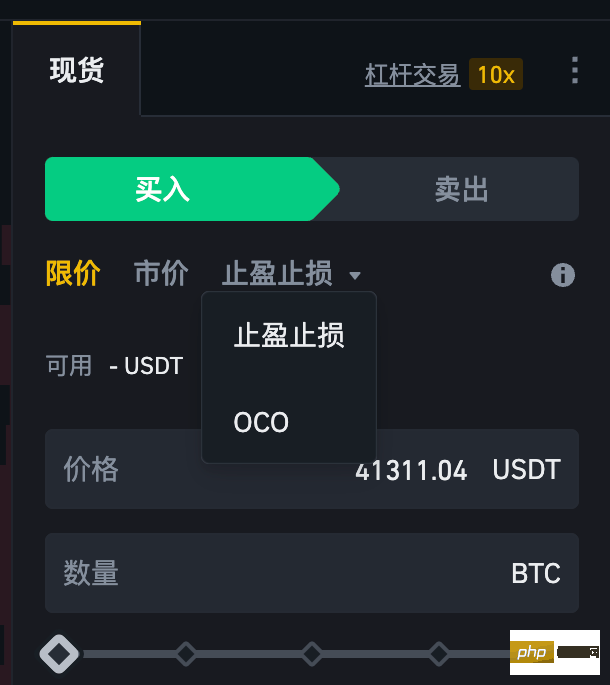 什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM
什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM二选一订单(OneCancelstheOther,简称OCO)可让您同时下达两个订单。它结合了限价单和限价止损单,但只能执行其中一个。换句话说,只要其中的限价单被部分或全部成交、止盈止损单被触发,另一个订单将自动取消。请注意,取消其中一个订单也会同时取消另一个订单。在币安交易平台进行交易时,您可以将二选一订单作为交易自动化的基本形式。这个功能可让您选择同时下达两个限价单,从而有助于止盈和最大程度减少潜在损失。如何使用二选一订单?登录您的币安帐户之后,请前往基本交易界面,找到下图所示的交易区域。点
 为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM
为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM原因:1、Go语言具有部署简单、性能优秀、并行执行性能好、良好语言设计、内置大量库、团队牛逼等优势。2、以太坊和超级账本都选择使用Go作为开发语言;这两大超级区块链的影响力很大,不仅在生态中占据了大的坑位,事实上还隐性的制定了区块链的标准。
 go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM可以开发。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如go语言、Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript都可以实现区块链的开发。Go语言是为了解决分布式计算,而区块链是典型的分布式数据存储系统,因此go语言能开发区块链。且Go易学易用,能很好的满足区块链行开发需要的“执行效率高、高并发、跨平台,网络开发要求高”等特点。
 深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM区块链技术的出现,使得数字货币的应用成为可能,也在许多领域得到了广泛应用。随着区块链技术领域的扩大,开发人员对于更好的应用程序编写方式的需求也高涨起来。于是,一个叫做Go语言(简称Golang)的编程语言悄悄兴起,成为了区块链开发人员的最爱。Go语言是谷歌公司开发的一种系统级编程语言,自诞生以来,一直着重强调程序设计的简捷和高效。Go语言的优点包括:静态类型
 Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AM
Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AMJava是一种广泛使用的编程语言,它被许多公司和组织用作开发各种应用程序的工具。最近几年来,区块链和加密货币技术在全球范围内引起了大量的关注。Java的灵活性和多功能性使得它成为开发区块链和加密货币应用程序的优秀选择。区块链技术是一种安全的、去中心化的数据库,它可以存储和共享交易记录,而无需任何中央机构的干涉。Java提供了许多区块链开发框架,例如H
 打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM
打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM随着区块链技术的发展和应用越来越广泛,有越来越多的人开始参与到区块链技术的开发中来。而要想打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,选择合适的开发语言和工具是非常重要的。Go语言正是一个很好的选择,因为它的性能很高,同时还有很多优秀的开源工具和库,能够大大提高开发效率。下面就来介绍一下如何打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,使用Go语言进行开发。一、选择Go语言在选择开发语言
 如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识Jun 04, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识Jun 04, 2023 pm 03:51 PM区块链是一种去中心化的分布式账本技术,随着其应用领域的不断扩展,如何保障区块链参与者的身份安全问题也逐渐成为热门话题。本文将介绍如何利用Go语言实现全球唯一的区块链身份标识。一、为什么需要区块链身份标识在现有的互联网世界中,身份验证是一个非常重要的问题。通过用户名和密码等方式,用户可以登录到我门的网站上,从而使用我们的服务。但是,在互联网上,身份验证存在着

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






