In social activities, large language models can be either your partners or your mentors.
In human social activities, in order to communicate with others more effectively in work and life, certain social skills are required, such as conflict resolution . #However, environments in which social skills can be practiced are often out of reach for most people. Training these skills, especially by experts, is often time-consuming, costly, and of limited availability. Existing practice and feedback mechanisms rely heavily on expert supervision, making training difficult to scale. Additionally, there is a shortage of professionally trained coaches, and most coaches who can provide customized feedback fail to help large numbers of people in need. Recently, in the paper "Social Skill Training with Large Language Models" co-authored by Stanford Assistant Professor Yang Diyi, researchers believe that with the help of large language models, we can Makes social skills training easier, safer, more engaging, and provides tailored feedback in real and virtual practice spaces. 
Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.04204.pdfSpecifically, Researchers have proposed the following two social skills training frameworks. The first training framework is AI Partner, which provides a scalable solution for experiential training through simulation exercises. Previous research has shown that human role-playing can effectively teach communication, collaboration and leadership skills. Simulation allows learners to take on fewer risks and opportunity costs than on-the-job training. And through simulation, AI Partner will reduce socioeconomic barriers to entry into the professional world. The second complementary training framework is AI Mentor, which will provide personalized feedback based on domain expertise and factual knowledge. Both training frameworks (collectively known as APAM) combine experiential learning with real-world practice and customized feedback. Researchers call for interdisciplinary innovation to address the broad impacts of APAM. Yang Diyi, the author of the paper, said: "Learning social skills is out of reach for most people. How can we make social skills training more accessible? ?Based on this, we launched APAM, which uses LLM to conduct social skills training through real-life practice and tailored feedback!" 
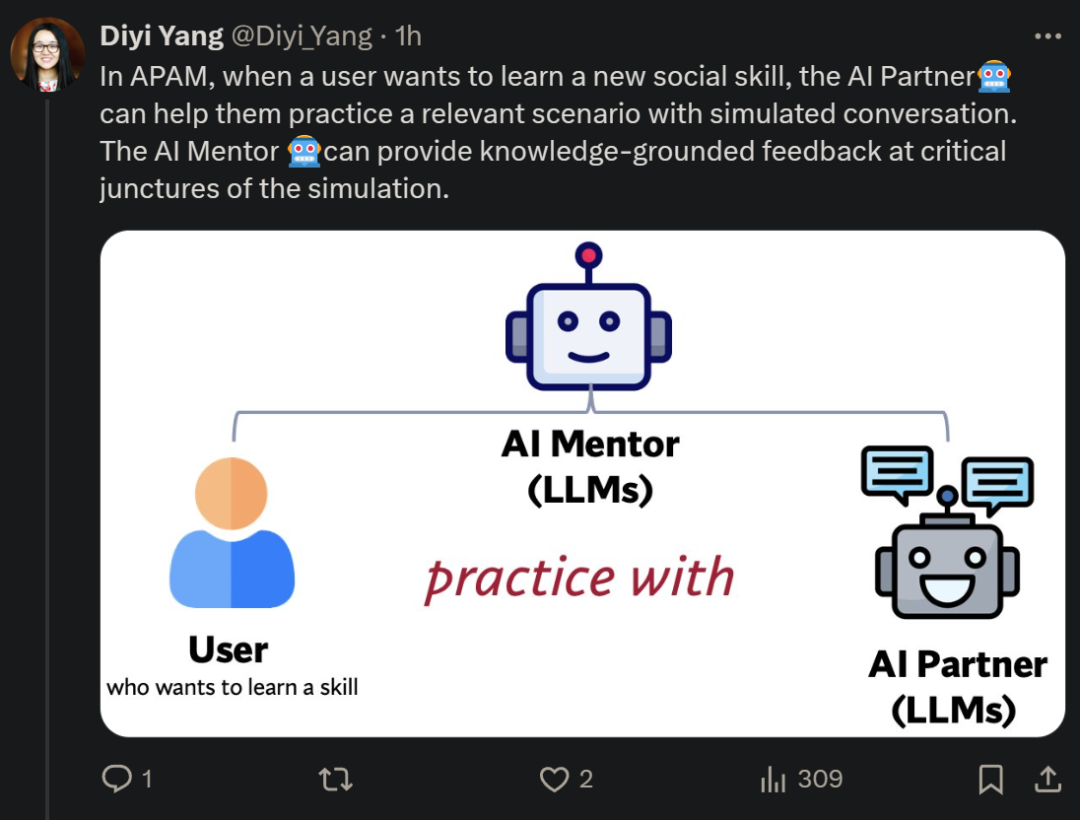
She continued: "In APAM, When users want to learn a new social skill, AI Partner can help them practice relevant scenarios through simulated conversations. AI Mentor can provide knowledge-based feedback at critical moments in the simulation." 
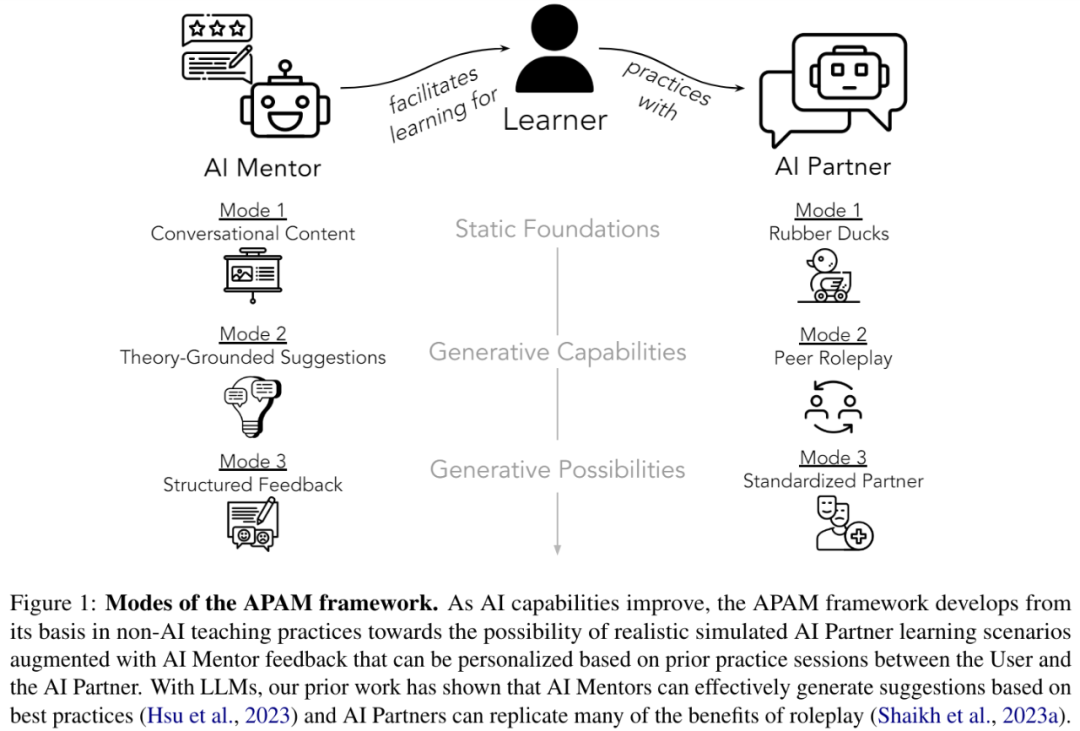
APAM Architecture OverviewThis study proposes a general framework specifically for social skills training, which includes AI Partner and AI Mentor (both referred to as APAM), and these two are crucial. When users want to learn a new social skill, AI Partner can help them practice relevant scenarios through simulated conversations. AI Mentor can provide knowledge-based feedback at critical moments in the simulation. 
However, building and deploying an AI Partner is not easy. For example, it is difficult to maintain consistency in the style, behavior, and emotional characteristics of the simulated characters. The development of AI Mentor relies heavily on factors such as domain expertise, situational awareness, and feedback efficiency. In order to solve the above problems, the researchers proposed a general method for social skills training through LLM, which is completed in four steps:
- Understand how to solve problem skills (e.g., resolve conflicts);
- Design an AI partner to simulate a conversation so that learners (i.e. users) Get in touch with the target process and practice;
- Create an AI mentor to provide feedback;
- Integrate these two agents into the simulation environment , so that users can learn.
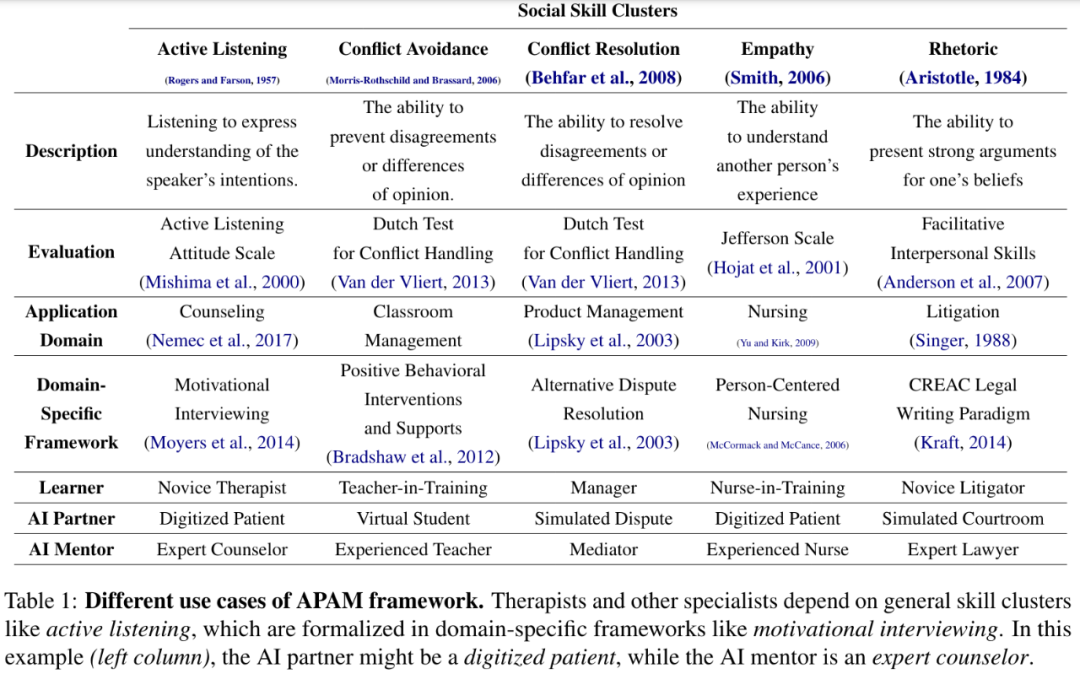
The ideal audience for the APAM framework is beginners, but experienced people can also use the APAM system to refresh their knowledge, the researchers said. APAM can improve learners’ skills in many areas. Table 1 lists some application scenarios, such as how to listen, mental health counseling, etc. However, the APAM framework is not limited to these typical examples, and there is more introduction in Section 6 of the paper. 
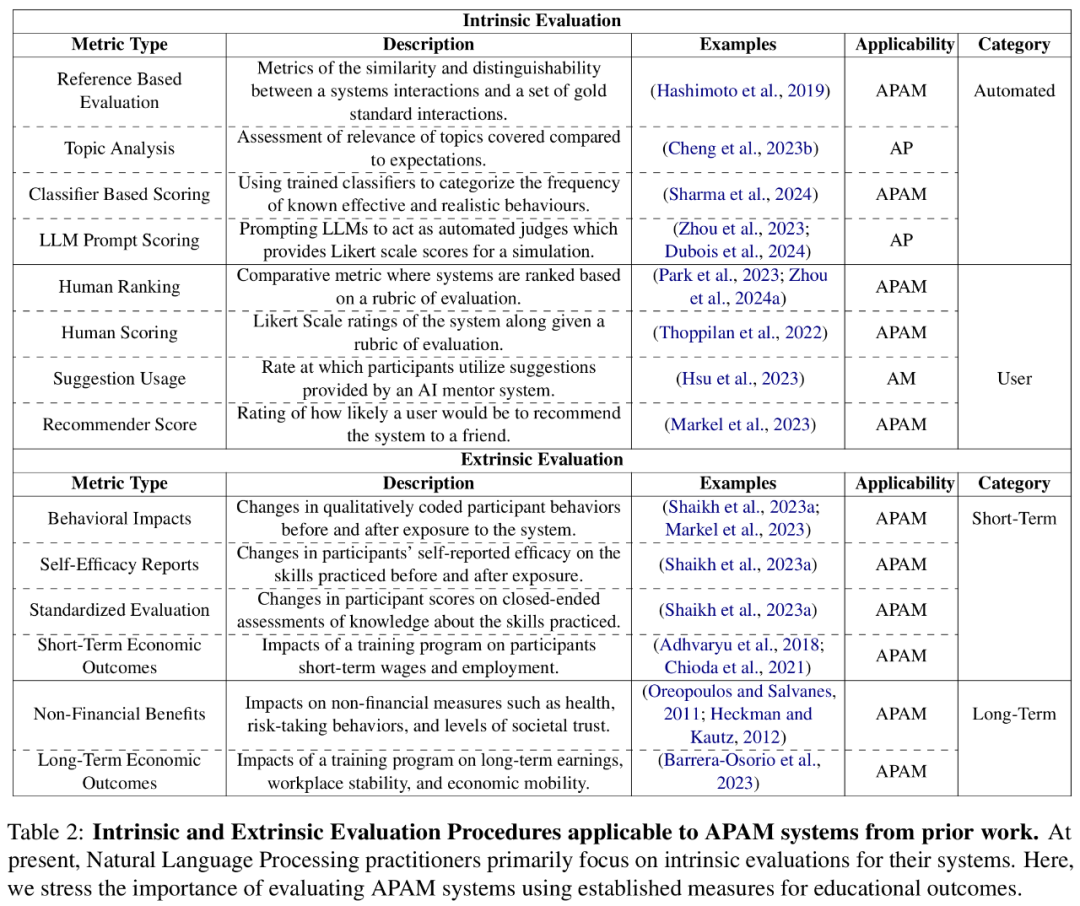
While LLMs have great potential as social skills training tools because they can generate coherent and natural text. However, this flexibility often comes with limited controllability. For security reasons, the APAM framework provides a series of measures for how to apply AI. They break down the use process into a continuum: AI Partner continuum and AI Mentor continuum. body, each continuum is completed by three models (as shown in Figure 1). The evaluation of AI partner and AI mentor is a major challenge. APAM-based tools involve complex computing systems and interaction with users with different needs and backgrounds. In order to develop these training tools as a field, evaluation measures need to go beyond traditional metrics in natural language processing and instead employ data from multiple related fields and stakeholders. plan. Incorporating a multidisciplinary perspective will help assess the empirical performance, usability from a user perspective, and long-term impact on users and communities of such systems. Currently, research on text generation mainly focuses on intrinsic evaluation, that is, evaluating the quality of the output through predefined rules or interactions. In Table 2 below, researchers are mainly divided into fully automatic evaluation and user-driven evaluation. Reference-based metrics such as perplexity or Kullback-Leibler divergence are often used for automated system quality assessment, as they are both simple and allow a rich definition of the desired behavior through demonstration. #Table 2 details the intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation procedures applied to APAM systems in previous work. Currently, natural language processing practitioners are primarily concerned with intrinsic evaluation of systems. In this article, researchers emphasize the importance of using established measures of educational outcomes to evaluate APAM systems. 
Please refer to the original paper for more details. The above is the detailed content of Yang Diyi's new work: The society may be saved. AI large models chat one-on-one and help i people become e people.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!