 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials System Installation
System Installation U disk format selection guide: Differences and application scenarios of FAT32, NTFS and exFAT
U disk format selection guide: Differences and application scenarios of FAT32, NTFS and exFATphp editor Xiaoxin will analyze the U disk format selection guide for you: the differences and application scenarios of FAT32, NTFS and exFAT. FAT32 is suitable for various operating systems, NTFS supports large file storage and higher security, and exFAT is suitable for large-capacity file transfer and cross-platform use. When choosing a USB flash drive format, you need to make a reasonable choice based on specific needs and usage scenarios to obtain the best results.

Tool materials:
System version: Windows 11 Professional Edition (21H2)
Brand model: Kingston DataTraveler Exodia DTX 32GB
Software version: Windows Explorer (Windows 11 built-in)
1. FAT32 format
FAT32 is one of the most common U disk formats at present, and its advantage is compatibility Very good, almost all operating systems support it. However, the FAT32 format has an obvious disadvantage, that is, the size of a single file cannot exceed 4GB. If you need to store large files, such as high-definition movies or game installation packages, the FAT32 format is not suitable.
FAT32 format U disk is suitable for the following scenarios:
1. Need to share files between different operating systems, such as Windows, Mac and Linux;
2. Storage The files are relatively small, no more than 4GB;
3. The U disk capacity is small, such as less than 32GB.
2. NTFS Format
NTFS is the default file system of Windows operating system. Its biggest advantage is that it supports large file storage and can theoretically store files of 16EB (1EB=1024PB). In addition, NTFS also supports advanced functions such as file encryption and access control, making it more secure. However, the compatibility of NTFS formatted USB flash drives on other operating systems is not as good as FAT32, especially on Mac and Linux systems, and additional software may need to be installed to read and write.
NTFS format U disk is suitable for the following scenarios:
1. Need to store large files, such as high-definition movies, game installation packages, etc.;
2. File security The requirements are high and require encryption or access control;
3. Only use USB flash drives on Windows systems.
3. exFAT format
exFAT is a new file system launched by Microsoft, aiming to replace the FAT32 format. It combines the advantages of FAT32 and NTFS, not only supports large file storage (up to 16EB), but also has good compatibility and can be directly read and written on Windows, Mac and Linux systems. However, since exFAT is a relatively new format, some older devices may not support it.
ExFAT format U disk is suitable for the following scenarios:
1. Large files need to be shared between different operating systems;
2. The U disk has a large capacity, such as 64GB or more;
3. You need to use a USB flash drive on a newer device.
Content extension:
1. How to format a USB flash drive in Windows system?
Formatting a USB flash drive in Windows is very simple. Just right-click the USB flash drive in the explorer, select "Format", and then select the desired file system (FAT32, NTFS or exFAT). Finally click "Start". However, it should be noted that formatting will clear all data in the USB flash drive, so please back up important files in advance.
2. How to read and write NTFS formatted USB flash drive on Mac system?
In Mac systems, NTFS formatted USB drives can only be read by default, but cannot be written to. If you need to write an NTFS formatted USB flash drive in a Mac system, you can use third-party software, such as Paragon NTFS for Mac, Tuxera NTFS for Mac, etc. These software allow Mac systems to natively support reading and writing in NTFS format.
3. How to read and write NTFS formatted U disk in Linux system?
In Linux systems, NTFS-formatted U disks can only be read by default, but cannot be written to. If you need to write an NTFS-formatted USB flash drive in a Linux system, you can install the ntfs-3g software package. ntfs-3g is an open source NTFS file system driver. After installation, you can freely read and write NTFS-formatted U disks in the Linux system.
Summary:
Choosing the appropriate U disk format is very important for our daily use and file transfer. The FAT32 format has the best compatibility, but does not support large files above 4GB; the NTFS format supports large file storage, but is not as compatible as FAT32; the exFAT format has the advantages of both, but may not be supported by some older devices. We should choose the most appropriate U disk format based on actual needs and usage environment. At the same time, you should also pay attention to the support of different operating systems for different formats. If necessary, you can install third-party software to expand functions.
The above is the detailed content of U disk format selection guide: Differences and application scenarios of FAT32, NTFS and exFAT. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 昂达主板如何升级BIOS?Feb 14, 2024 am 10:30 AM
昂达主板如何升级BIOS?Feb 14, 2024 am 10:30 AM昂达主板如何升级BIOS?按照下面的步骤进行:1.下载正确版本的BIOS更新文件。在昂达官方网站或其他可信网站,下载正确型号、版本和日期的BIOS更新文件,注意选择所需的操作系统和编程语言版本。2.准备U盘。选择一个可以存储更新文件的U盘,格式化为FAT32文件系统。3.将BIOS文件复制到U盘。将下载的BIOS更新文件复制到U盘根目录中。4.进入BIOS设置。开机时,在昂达主板启动屏幕出现后,按下对应按键进入BIOS设置,通常是DEL或F2。5.进入Q-Flash。在BIOS设置中,找到Q-F
 mac复制文件损坏(mac复制文件损坏怎么解决)Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
mac复制文件损坏(mac复制文件损坏怎么解决)Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:00 PM本文将为大家介绍mac复制文件损坏的相关内容,希望能给大家提供帮助。请继续阅读。苹果电脑不能拷贝写入复制文件到硬盘/U盘怎么办根据向导提示,重启电脑后,打开Mac的“偏好设置”,即可双击图标打开该软件。如果你的文件容量大于硬盘容量,无法将文件复制或拷贝到移动硬盘或U盘。此时,你可以考虑更换硬盘。首先,将硬盘或U盘插入电脑。接着,按下【+空格】快捷键,打开【磁盘工具】窗口。根据下图箭头所指的位置,选择相应的磁盘。进行格式化设置,可选择FAT或ExFAT格式。点击确定后,右键菜单将出现复制选项,可方
 Win10格式化U盘没有FAT32选项怎么办?win10把u盘格式化为fat32的方法Feb 12, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
Win10格式化U盘没有FAT32选项怎么办?win10把u盘格式化为fat32的方法Feb 12, 2024 pm 09:39 PM我们在使用u盘的时候会遇到故障或者是损坏等等问题,这个时候格式化u盘就可以让我们的u盘恢复正常的工作,很多不熟悉电脑的用户们会在格式化的时候遇到U盘没有FAT32选项,这要怎么办?下面就让本站来为用户们来分享win10把u盘格式化为fat32的方法吧。win10把u盘格式化为fat32的方法方法一:1、首先将U盘插入到电脑USB口,在我的电脑可以查看到U盘,小编这里的是H盘。2、鼠标右键H盘,在弹出的菜单中选择“格式化”。3、点击文件系统选项,改变格式化文件系统,您可以根据自己的需
 mac不小心抹走硬盘(macbook把磁盘抹掉了系统还在吗)Feb 08, 2024 am 10:12 AM
mac不小心抹走硬盘(macbook把磁盘抹掉了系统还在吗)Feb 08, 2024 am 10:12 AM前言:本篇文章本站来给大家介绍有关mac不小心抹走硬盘的相关内容,希望对大家有所帮助,一起来看看吧。把mac磁盘抹掉了,怎么恢复系统首先,将MacOSXInstallDVD插入光盘驱动器,并重新启动电脑。在电脑启动时,按住Option键。然后,在出现的启动选项中,选择“MacOSXInstallDVD”,然后点击下方的箭头,以从DVD安装光盘启动。无论您选择执行哪种抹除选项,您都可以尝试使用TimeMachine进行恢复。首先,连接您的TimeMachine备份硬盘。然后打开Finder,并导航
 技嘉主板怎么进入BIOS?Feb 06, 2024 pm 01:48 PM
技嘉主板怎么进入BIOS?Feb 06, 2024 pm 01:48 PM技嘉主板怎么进入BIOS?1.在电脑开机的一瞬间并跳出技嘉的标志界面,立即按“F12”键,即可进入技嘉主板BIOS界面中2.进入到了技嘉主板BIOS设置中,主要分为上部菜单栏、左侧使用栏、右侧提醒栏等。主界面中显示了主机信息设置,下方我们还可以设置处理器、内存及电压相关参数。技嘉主板bios损坏怎么修复?如果技嘉主板的BIOS损坏,可以按照以下步骤尝试修复:1.准备一个U盘,将U盘格式化为FAT32格式;2.访问技嘉主板官方网站,下载主板的最新BIOS程序,并将其解压缩,将解压后的文件复制到U盘
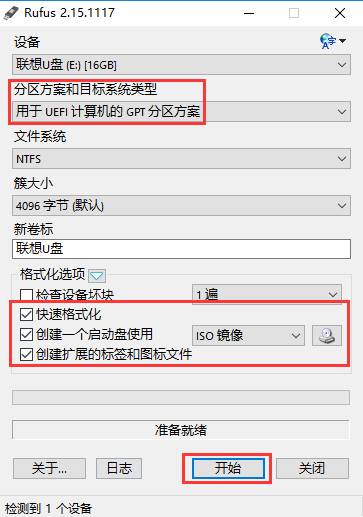 uefiu盘歌格式Feb 12, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
uefiu盘歌格式Feb 12, 2024 pm 10:18 PM随着win10系统的不断更新,其原版安装镜像也越来越大,给喜欢使用U盘进行UEFI启动方式安装的同学带来了困扰,大家都知道,使用EFI方式安装系统,直接将微软原版镜像解压缩后,复制到fat32或fat16格式的U盘根目录,然后直接设置主板U盘启动就可以安装了,但是最近有很多小伙伴反映事与愿违,U盘使用fat格式有个限制,那就是单个文件最大不能超过4G,不然就会出现无法写入的情况,但是随着win10镜像的增大,其安装包里的install.wim文件也越来越大,已经超过了4G,这就导致了无法直接使用
 手机u盘在手机上怎么使用「详细讲解:华为手机连接U盘方法」Feb 07, 2024 am 09:09 AM
手机u盘在手机上怎么使用「详细讲解:华为手机连接U盘方法」Feb 07, 2024 am 09:09 AM大家在生活中使用手机时可能会遇到一些小问题,难免会遇到手机需要和U盘互连获取某些文件,可是手里拿着手机和U盘,却不能正常连接,一个充电口,一个USB口,完全不匹配啊,这个时候怎么办呢,不要着急哦,也许你只是缺少了一样东西。接下来以华为Mate30Pro为例,为大家详细解读如何正确连接手机和U盘。一,华为自用手机二,任意型号的U盘(可USB,可T-Y)三,最重要的配件(转接口)一般数码店或者电脑店都有的,褚杰华这个是买U盘送的首先,我们要做的呢就是将U盘与转接口相连接转接口与U盘连接然后用前面这个
 u盘制作启动盘还能存东西吗Feb 11, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
u盘制作启动盘还能存东西吗Feb 11, 2024 pm 05:30 PM制作u盘启动盘教程,我们今天讲一下如何制作一个pe启动盘,并且用它来安装系统准备八g以上的存储设备,最好16g或32g,因为现代系统镜像较大,容量稍大会更好。然后就去搜索一个pe的制作工具,我这里用的是u深度然后直接下载安装就可以了,下载安装完以后,打开软件选择我们插入的u盘在制作过程中,点击一键制作即可开始制作。请注意,如果你安装了360等软件,需要先退出,因为它们可能会占用U盘,导致制作失败。我们制作完了以后呢,就把镜像考到这个u盘启动盘里面,我这里已经考好了使用U盘重装系统或解决其他问题非


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






