JS has variable promotion. This design is actually poor, or it is a side effect of language implementation. It allows variables to be accessed without declaration, or declared later and used first. Newbies are confused by this, and even many veterans who have used JS for many years are confused. But after ES6 added let/const, the variable Hoisting no longer exists.
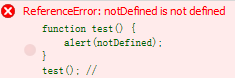
1. The variable is not declared, use it directly
function test() {
alert(notDefined);
}
test(); // ?
It is natural to report errors
2. Variable declaration at the end
function test() {
alert(declaredButNotAssigned); // undefined
var declaredButNotAssigned;
}
test();
Output undefined, the result is improved compared to the above example, no error is reported, the code can run, but the variable value may not be what the programmer expected.
3. Declare the variable at the end and assign a value to the variable at the same time
function test() {
alert(declaredAndAssigned); // undefined
var declaredAndAssigned = 1;
}
test();
The result is the same as two. Obviously, 1 will not be output just because of the assignment.
Both two and three have variable hoisting (Hoisting), simply defined
Variable promotion: In the specified scope, in terms of code order, variables are used first and then declared, but the "accessibility" of the variable at runtime is promoted to the top of the current scope, and its value is undefined, and there is no "availability" ".
The emphasis here is on “code order” and “running order” because most of the time the code we write is executed sequentially, that is, “code order” and “running order” are consistent. This is also consistent with the thinking process of the human brain. For example, programmers with experience in C language
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x = 1;
printf("%d, ", x); // 1
}
Two lines of code, first declare the integer type x, and then output it. The code sequence and running sequence are consistent, that is, normal operation.
If the order is reversed
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("%d, ", x); // error
int x = 1;
}
At this point, the compilation cannot pass. But it can be written in reverse in JS, see 2 and 3.
Therefore, programmers with experience in C-like languages know that variables need to be declared first and then used, otherwise an error will be reported. In JS, there is a phenomenon of variable promotion, which can be used first and then declared. The experience of C is used in JS, and confusion arises.
4. Function expressions also have variable promotion
function test() {
alert(func); // undefined
var func = function() {};
}
test();
But if you want to use this func, it’s not possible
function test() {
alert(func); // undefined
func(); // 报异常
var func = function() {};
}
test();
The result func is undefined, and calling func will report an exception. Accessibility and availability are mentioned in the above definition and correspond to the following statements.
Accessibility: alert(func), output undefined, can be run, func can be accessed.
Availability: func() reports an exception and func cannot be called normally, indicating no availability.
Second, third, and fourth are all variables declared using var. Function declarations in JS will also be improved, but this "variable" is special. It is a function type (can be used as a function, method or constructor). Its name (identifier) is also hoisted to the top of the current scope.
5. The name of the function declaration will also be promoted to the top of the current scope
function test() {
alert(f1); // function
f1(); // "called"
function f1() {
alert('called');
}
}
test();
We see that f1 is declared at the end of the code and f1 is used first. Both alert(f1) and f1() are executed normally, indicating that accessibility and usability are both present.
As mentioned before, variable hoisting is of no use. It is a poor design of the language. The good habit is to "declare first and then use". This feature will also appear in many interview questions of large companies
Question 1:
// 写出以下代码的运行结果
var a = 1;
function fn() {
if (!a) {
var a = 2;
}
alert(a); // ?
}
fn();
Question 2:
// 写出以下代码的运行结果
var a = 1;
function fn() {
a = 2;
return;
function a() {}
}
fn();
alert(a); // ?
But this all ended with the arrival of let/const in ES6. Except for global variables, everything else in ES uses let/const. After replacing var with let, variable promotion no longer exists.
function test() {
alert(declaredButNotAssigned1); // 报异常
alert(declaredButNotAssigned2); // 报异常
alert(func); // 报异常
let declaredButNotAssigned1;
let declaredButNotAssigned2 = true;
let func = function() {};
}
test();
This forces programmers to develop good habits. Variables need to be "declared first and then used", otherwise an error will be reported.
The following is excerpted from MDN’s description of variable promotion when let does not occur
In ECMAScript 6, let does not hoist the variable to the top of the block. If you reference a variable in a block before the let declaration for that variable is encountered, this results in a ReferenceError, because the variable is in a "temporal dead zone" from the start of the block until the declaration is processed.
After using let to declare variables, typeof is no longer safe
if (condition) {
alert(typeof num); // Error!
let num = 100;
}
In the past, you could use typeof == 'undefined' to determine whether a certain lib was introduced, such as jQuery
// 判断jQuery是否引入了
if (typeof $ !== 'undefined') {
// do something
}...
jQuery is not introduced and $ is not declared. This sentence will not report an error and affect the execution of the following code, but if it is declared by let, an error will be reported.
The above is the entire content of this article, I hope you all like it.
 es6数组怎么去掉重复并且重新排序May 05, 2022 pm 07:08 PM
es6数组怎么去掉重复并且重新排序May 05, 2022 pm 07:08 PM去掉重复并排序的方法:1、使用“Array.from(new Set(arr))”或者“[…new Set(arr)]”语句,去掉数组中的重复元素,返回去重后的新数组;2、利用sort()对去重数组进行排序,语法“去重数组.sort()”。
 JavaScript的Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表详解Jun 02, 2022 am 11:50 AM
JavaScript的Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表详解Jun 02, 2022 am 11:50 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表的相关问题,包括了Symbol类型的描述、Symbol不会隐式转字符串等问题,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 原来利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播!Jun 10, 2022 pm 01:00 PM
原来利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播!Jun 10, 2022 pm 01:00 PM怎么制作文字轮播与图片轮播?大家第一想到的是不是利用js,其实利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播,下面来看看实现方法,希望对大家有所帮助!
 JavaScript对象的构造函数和new操作符(实例详解)May 10, 2022 pm 06:16 PM
JavaScript对象的构造函数和new操作符(实例详解)May 10, 2022 pm 06:16 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于对象的构造函数和new操作符,构造函数是所有对象的成员方法中,最早被调用的那个,下面一起来看一下吧,希望对大家有帮助。
 JavaScript面向对象详细解析之属性描述符May 27, 2022 pm 05:29 PM
JavaScript面向对象详细解析之属性描述符May 27, 2022 pm 05:29 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于面向对象的相关问题,包括了属性描述符、数据描述符、存取描述符等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 javascript怎么移除元素点击事件Apr 11, 2022 pm 04:51 PM
javascript怎么移除元素点击事件Apr 11, 2022 pm 04:51 PM方法:1、利用“点击元素对象.unbind("click");”方法,该方法可以移除被选元素的事件处理程序;2、利用“点击元素对象.off("click");”方法,该方法可以移除通过on()方法添加的事件处理程序。
 整理总结JavaScript常见的BOM操作Jun 01, 2022 am 11:43 AM
整理总结JavaScript常见的BOM操作Jun 01, 2022 am 11:43 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于BOM操作的相关问题,包括了window对象的常见事件、JavaScript执行机制等等相关内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 foreach是es6里的吗May 05, 2022 pm 05:59 PM
foreach是es6里的吗May 05, 2022 pm 05:59 PMforeach不是es6的方法。foreach是es3中一个遍历数组的方法,可以调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传给回调函数进行处理,语法“array.forEach(function(当前元素,索引,数组){...})”;该方法不处理空数组。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






