
Working with files in the Linux operating system requires the use of various commands and techniques that enable developers to efficiently create and execute files, code, programs, scripts, and other things. In the Linux environment, files with the extension ".a" have great importance as static libraries. These libraries play an important role in software development, allowing developers to efficiently manage and share common functionality across multiple programs.
For effective software development in a Linux environment, it is crucial to understand how to create and run ".a" files. This article will introduce how to comprehensively install and configure the Linux ".a" file. Let's explore the definition, purpose, structure, and methods of creating and executing the Linux ".a" file.
What is a ".a" file in Linux?
The ".a" file in Linux is an archive file used to store code and data, often called a static library. These files are linked into the calling code at compile time and become an essential part of the application. They provide a precompiled base contribution to the application, and in contrast to ".so" dynamic library files, linking does not occur at runtime.
Suppose a developer creates three different programs with shared functionality between them. In order to better organize and reuse these common functions, the developers decided to encapsulate them in a library file called "common_functions.a". This library file becomes a reusable collection of code and data in Linux, and other developers can easily reference and use these shared functions in their projects. This approach helps improve the maintainability and reusability of the code, as well as speed up the development process, making it easier to share and utilize code resources between different projects.
prerequisites:
Before learning how to create and run a file named "a" in a Linux system, it is crucial to understand some basic knowledge. Before performing any operation in Linux, it is very important to ensure the following points. Specifically:
- Ubuntu 20.04 or any latest version
- Access command line or terminal window
- User accounts for various files and directories, especially sudo permissions
How to create and run Linux ".a" files?
Creating and running a Linux ".a" file involves a series of steps: creation, compilation, and execution. There are different ways to perform these operations, and we'll explore each one separately. let's start.
You need a GCC compiler to run and execute the following examples. The compiler is used to run all commands that create and run Linux ".a" files:
The following are the steps explained through various commands and techniques.
Step 1: Compile C source files
First, use the GCC compiler to create a C source file, compile the C source file (.c) into an object file (.o), use the following command:
$gcc—Wall—c *. c
The "-wall" flag enables all warnings, and the "-c" flag tells GCC to only compile, not link, at this point.
Step 2: Create Library Archive
The next step is to create the library file. The "ar" command creates a static library archive (.a) from an object file. Therefore, we use the following command:
$ar-cvq libfile.a*.o
This command creates a static archive file named "libfile.a" by combining various object files with the ".o" extension using the "ar" (archive) command in the Linux operating system. There are three things to note about this command: "c", "v" and "q". Let's break down the components and understand what each flag and parameter is used for in the context of this command:
AR: It executes the archive command in Linux systems. The basic functions of the "ar" command are to create, modify and extract archives.
-c: This flag instructs to create a new archive if it has not been created or does not yet exist. If an archive file with the given name exists, the "-c" flag will ensure that the file is recreated, replacing any previous contents.
—v: Verbose flag displays detailed information about the archiving process. It provides feedback on which files have been added to the archive.
—q: "q" stands for "quick append". It requires the "ar" flag to quickly append the specified files to the archive without checking for duplicate symbols or time-consuming operations.
libfile.a: The command to create or modify requires a filename. Here, we give a file name "libfile" with a ".a" extension, which indicates that it is a static library archive.
* . o: The "*" at the end of the command represents each file in the selected directory, with the extension ". o", which refers to the object file. An object file is the result of compilation of source code and contains machine code that has not yet been linked to any final executable file.
Step 3: View library contents
Now that we have created the library archive, we can view it using the "ar --t" command. The "ar --t" command lists everything that exists in the library.
$ar—t libfile.a
The "ar -t libfile.a" command lists all object files contained in the static library archive named "libfile.a" using the "ar" command in the Linux operating system. Let’s analyze each flag and its function:
ar: As mentioned before, this is the archive command in Linux systems.
—t: The "-t" flag is used to display the directory of the archive and the name of the object file stored in "libfile. a".
A: To read the data, we need to know the name of the archive file.
Step 4: Use the library in another program
Now let’s see how to use the newly developed Linux “.a” files in different programs. Since we created a library, now it can be used anywhere and in any program simply by adding the library to the compile command. We can accomplish it with the help of subsequent commands. It includes all necessary headers and links for the library.
$gcc—o MyProgramMain.c—L path/to/libdir—lfile
In this command, "-L" specifies the library path, "-lfile" links to the "library.a" libfile, and deletes the "lib" prefix and ". a" suffix.
Step 5: Run a ".a" Linux file
Finally, we can run the ".a" file. After running the following script in your terminal, the results will be displayed to you immediately:
$./MyProgramMain
This command utilizes the functions provided in the source file and the linked static library to execute the file.
in conclusion
Creating and running ".a" files in Linux requires compilation and execution of various commands for file creation, compilation and linking. Understanding these steps and what each command does enables developers to organize their code, use external libraries, and develop scalable programs. Whether you need to work with basic commands like Nano and GCC, or work with more advanced static library techniques, mastering these skills will help with practical Linux-based development.
The above is the detailed content of Create and run Linux ".a" files. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
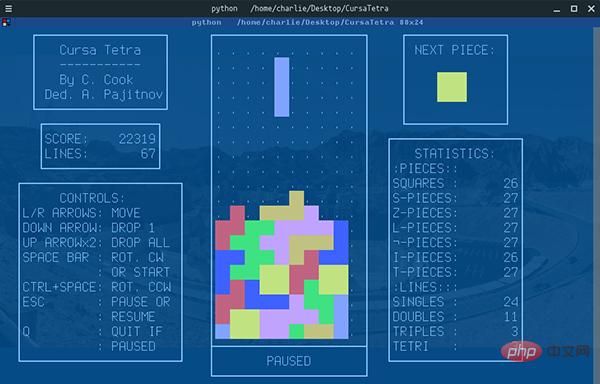 Python 文本终端 GUI 框架,太酷了Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:52 PM
Python 文本终端 GUI 框架,太酷了Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:52 PMCurses首先出场的是 Curses[1]。CurseCurses 是一个能提供基于文本终端窗口功能的动态库,它可以: 使用整个屏幕 创建和管理一个窗口 使用 8 种不同的彩色 为程序提供鼠标支持 使用键盘上的功能键Curses 可以在任何遵循 ANSI/POSIX 标准的 Unix/Linux 系统上运行。Windows 上也可以运行,不过需要额外安装 windows-curses 库:pip install windows-curses 上面图片,就是一哥们用 Curses 写的 俄罗斯
 五个方便好用的Python自动化脚本Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
五个方便好用的Python自动化脚本Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:31 PM相比大家都听过自动化生产线、自动化办公等词汇,在没有人工干预的情况下,机器可以自己完成各项任务,这大大提升了工作效率。编程世界里有各种各样的自动化脚本,来完成不同的任务。尤其Python非常适合编写自动化脚本,因为它语法简洁易懂,而且有丰富的第三方工具库。这次我们使用Python来实现几个自动化场景,或许可以用到你的工作中。1、自动化阅读网页新闻这个脚本能够实现从网页中抓取文本,然后自动化语音朗读,当你想听新闻的时候,这是个不错的选择。代码分为两大部分,第一通过爬虫抓取网页文本呢,第二通过阅读工
 用Python写了个小工具,再复杂的文件夹,分分钟帮你整理!Apr 11, 2023 pm 08:19 PM
用Python写了个小工具,再复杂的文件夹,分分钟帮你整理!Apr 11, 2023 pm 08:19 PM糟透了我承认我不是一个爱整理桌面的人,因为我觉得乱糟糟的桌面,反而容易找到文件。哈哈,可是最近桌面实在是太乱了,自己都看不下去了,几乎占满了整个屏幕。虽然一键整理桌面的软件很多,但是对于其他路径下的文件,我同样需要整理,于是我想到使用Python,完成这个需求。效果展示我一共为将文件分为9个大类,分别是图片、视频、音频、文档、压缩文件、常用格式、程序脚本、可执行程序和字体文件。# 不同文件组成的嵌套字典 file_dict = { '图片': ['jpg','png','gif','webp
 用 WebAssembly 在浏览器中运行 PythonApr 11, 2023 pm 09:43 PM
用 WebAssembly 在浏览器中运行 PythonApr 11, 2023 pm 09:43 PM长期以来,Python 社区一直在讨论如何使 Python 成为网页浏览器中流行的编程语言。然而网络浏览器实际上只支持一种编程语言:JavaScript。随着网络技术的发展,我们已经把越来越多的程序应用在网络上,如游戏、数据科学可视化以及音频和视频编辑软件。这意味着我们已经把繁重的计算带到了网络上——这并不是JavaScript的设计初衷。所有这些挑战提出了对新编程语言的需求,这种语言可以提供快速、可移植、紧凑和安全的代码执行。因此,主要的浏览器供应商致力于实现这个想法,并在2017年向世界推出
 一文读懂层次聚类(Python代码)Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:13 PM
一文读懂层次聚类(Python代码)Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:13 PM首先要说,聚类属于机器学习的无监督学习,而且也分很多种方法,比如大家熟知的有K-means。层次聚类也是聚类中的一种,也很常用。下面我先简单回顾一下K-means的基本原理,然后慢慢引出层次聚类的定义和分层步骤,这样更有助于大家理解。层次聚类和K-means有什么不同?K-means 工作原理可以简要概述为: 决定簇数(k) 从数据中随机选取 k 个点作为质心 将所有点分配到最近的聚类质心 计算新形成的簇的质心 重复步骤 3 和 4这是一个迭代过程,直到新形成的簇的质心不变,或者达到最大迭代次数
 从头开始构建,DeepMind新论文用伪代码详解TransformerApr 09, 2023 pm 08:31 PM
从头开始构建,DeepMind新论文用伪代码详解TransformerApr 09, 2023 pm 08:31 PM2017 年 Transformer 横空出世,由谷歌在论文《Attention is all you need》中引入。这篇论文抛弃了以往深度学习任务里面使用到的 CNN 和 RNN。这一开创性的研究颠覆了以往序列建模和 RNN 划等号的思路,如今被广泛用于 NLP。大热的 GPT、BERT 等都是基于 Transformer 构建的。Transformer 自推出以来,研究者已经提出了许多变体。但大家对 Transformer 的描述似乎都是以口头形式、图形解释等方式介绍该架构。关于 Tra
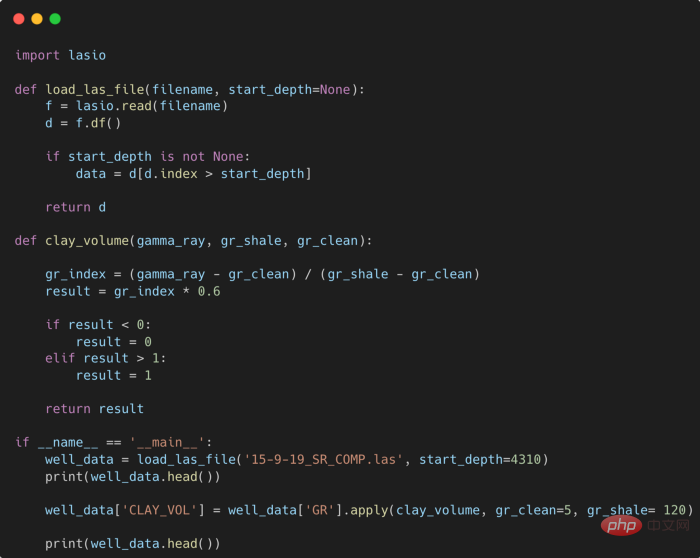 提高Python代码可读性的五个基本技巧Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM
提高Python代码可读性的五个基本技巧Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM译者 | 赵青窕审校 | 孙淑娟你是否经常回头看看6个月前写的代码,想知道这段代码底是怎么回事?或者从别人手上接手项目,并且不知道从哪里开始?这样的情况对开发者来说是比较常见的。Python中有许多方法可以帮助我们理解代码的内部工作方式,因此当您从头来看代码或者写代码时,应该会更容易地从停止的地方继续下去。在此我给大家举个例子,我们可能会得到如下图所示的代码。这还不是最糟糕的,但有一些事情需要我们去确认,例如:在load_las_file函数中f和d代表什么?为什么我们要在clay函数中检查结果
 用 Python 实现导弹自动追踪,超燃!Apr 12, 2023 am 08:04 AM
用 Python 实现导弹自动追踪,超燃!Apr 12, 2023 am 08:04 AM大家好,我是J哥。这个没有点数学基础是很难算出来的。但是我们有了计算机就不一样了,依靠计算机极快速的运算速度,我们利用微分的思想,加上一点简单的三角学知识,就可以实现它。好,话不多说,我们来看看它的算法原理,看图:由于待会要用pygame演示,它的坐标系是y轴向下,所以这里我们也用y向下的坐标系。算法总的思想就是根据上图,把时间t分割成足够小的片段(比如1/1000,这个时间片越小越精确),每一个片段分别构造如上三角形,计算出导弹下一个时间片走的方向(即∠a)和走的路程(即vt=|AC|),这时


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor






