 web3.0
web3.0 Basic knowledge of Solana: What are the SOL chain network parameters? Detailed introduction to SOL chain network configuration
Basic knowledge of Solana: What are the SOL chain network parameters? Detailed introduction to SOL chain network configurationThe SOL chain has gradually recovered from the impact of the FTX thunderstorm, and its ecology is still prosperous, especially the application of PoH, which makes the SOL chain lead high-performance public chains and basically touches the TPS bottleneck that non-sharded public chains can maintain for a long time. . In addition, the SOL chain has also launched a series of technical updates, providing targeted repair solutions for some security issues, showing good security awareness, developmental technical capabilities and strong sustainability. Various signs indicate that SOL The chain has begun to reach its peak again. Today we will introduce what are the network parameters of the SOL chain? The editor will take you to understand the SOL chain network configuration.

#What are the SOL chain network parameters?
SOL chain is a high-performance blockchain network whose network parameters cover consensus algorithm, block time, transaction confirmation time, block rewards, and network participants. These network parameters are described in detail next.
Solana’s core innovation lies in its Proof of History technology. This technology provides a globally available, permissionless timestamp. It is not a change to the consensus mechanism. Solana still uses the POS mechanism and PBFT consensus algorithm. The main function of Proof of History is to solve the problem of on-chain transaction timestamp confirmation under high throughput conditions.
A key feature of the Turbine protocol is to allow the Leader to split the transaction sequence into fragments and publish them. However, this segmentation needs to ensure that the transaction sequence can be easily reassembled and restored. This is where Proof of History (PoH) comes in, providing a convenient mechanism to sequence events and be able to easily re-piece them back into the original sequence. This design makes it more reliable and easier to implement efficient transaction processing and data verification in distributed systems.
Solana is able to achieve ultra-high throughput mainly due to its fast and reliable synchronization mechanism. Solana uses a historically proven PoH algorithm, and the leader node proves the time interval since the last confirmation by carrying an encrypted timestamp to ensure that data is generated at the correct time point. This mechanism ensures that all hashed data has occurred before it is proven, thereby enhancing the reliability of the data. The leader node then shares the new block with the validator nodes, who can verify the evidence to ensure the validity of the new block. This efficient synchronization and verification mechanism enables Solana to achieve efficient data processing and block generation, thereby achieving the advantage of high throughput. This design of Solana makes the entire network more stable and reliable, providing users with a better experience.
Blocks can be transmitted to validator nodes in any order, even with a delay of several years. Solana leverages this reliable synchronization mechanism by splitting blocks into smaller batches of transactions, called entries. These entries are transmitted to validating nodes in real time, ensuring they are always in sync until consensus is reached.
From a technical point of view, Solana never sends a block, but uses this term to describe the verification nodes voting on the entries and finally obtaining confirmation. In this way, Solana's confirmation time can reach 800 milliseconds. In this mode, if consensus cannot be reached on an event, nodes simply roll back their state.
On the blockchain, validators are important participants in the network. They maintain the security of the network by verifying transactions and generating new blocks. As a reward, validators receive SOL tokens, an incentive that helps attract more people to participate in network verification efforts. In addition to validators, the SOL chain's network also includes various roles such as full nodes, developers, and users. Full nodes are responsible for storing copies of the entire blockchain, ensuring the reliability and stability of the network. Developers and users can use the SOL chain to build and use various decentralized applications and contribute to the development of the blockchain ecosystem. The collaboration and participation of these different roles jointly promote the development of blockchain technology and the expansion of its application scope.
What does solana mean?
Solana is a powerful open source project that implements a new, permissionless, high-speed layer-1 blockchain. Founded in 2017 by former Qualcomm executive Anatoly Yakovenko, Solana aims to scale throughput beyond what popular blockchains typically achieve while keeping costs low. Solana implements an innovative hybrid consensus model that combines a unique Proof of History (PoH) algorithm with a lightning-fast synchronization engine (aka another version of Proof of Stake, PoS). Therefore, the Solana network can theoretically handle over 710,000 transactions per second (TPS) without the need for any scaling solutions.
Solana’s third-generation blockchain architecture is designed to facilitate the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). The project supports a range of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms as well as non-fungible token (NFT) markets.
Solana Blockchain was launched in 2017 during the blockchain boom. The project's internal testnet was released in 2018, and subsequently went through multiple testnet stages before officially launching the mainnet in 2020.
The above is the detailed content of Basic knowledge of Solana: What are the SOL chain network parameters? Detailed introduction to SOL chain network configuration. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM
区块链只能用go语言吗Dec 27, 2022 pm 05:25 PM不是。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript、Go都可以实现区块链的开发;区块链技术涉及的面很广,而编程语言只是一种手段,把设计理念用代码呈现出来,做成产品服务用户。
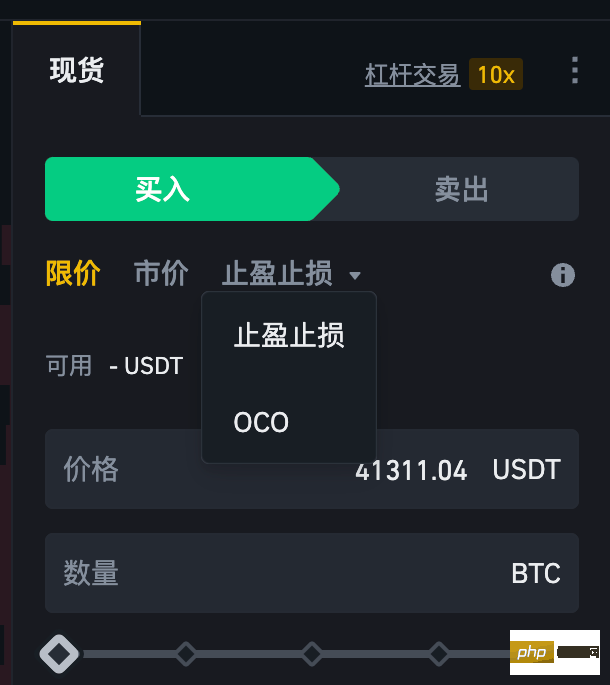 什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM
什么是OCO订单?Apr 25, 2023 am 11:26 AM二选一订单(OneCancelstheOther,简称OCO)可让您同时下达两个订单。它结合了限价单和限价止损单,但只能执行其中一个。换句话说,只要其中的限价单被部分或全部成交、止盈止损单被触发,另一个订单将自动取消。请注意,取消其中一个订单也会同时取消另一个订单。在币安交易平台进行交易时,您可以将二选一订单作为交易自动化的基本形式。这个功能可让您选择同时下达两个限价单,从而有助于止盈和最大程度减少潜在损失。如何使用二选一订单?登录您的币安帐户之后,请前往基本交易界面,找到下图所示的交易区域。点
 为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM
为什么用go语言写区块链Mar 04, 2021 pm 03:42 PM原因:1、Go语言具有部署简单、性能优秀、并行执行性能好、良好语言设计、内置大量库、团队牛逼等优势。2、以太坊和超级账本都选择使用Go作为开发语言;这两大超级区块链的影响力很大,不仅在生态中占据了大的坑位,事实上还隐性的制定了区块链的标准。
 Solana基础知识:SOL链网络参数是什么?SOL链网络配置具体介绍Mar 14, 2024 pm 05:19 PM
Solana基础知识:SOL链网络参数是什么?SOL链网络配置具体介绍Mar 14, 2024 pm 05:19 PMSOL链已经从FTX暴雷影响中逐步回温,其生态仍然繁荣,尤其是PoH的应用,让SOL链领跑高性能公链,基本触及了无分片公链可长期维持的TPS瓶颈。另外,SOL链还推出了一系列技术更新,对部分安全问题提供了针对性的修复方案,显示出良好的安全意识、发展性的技术能力和较强的可持续性,从种种迹象表明,SOL链已经开始重走巅峰,今天就再来介绍下SOL链网络参数是什么?小编带大家一起了解一下SOL链网络配置。SOL链网络参数是什么?SOL链是一个高性能的区块链网络,其网络参数涵盖了共识算法、区块时间、交易确
 go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
go语言能开发区块链吗Jan 03, 2023 pm 01:41 PM可以开发。区块链是一种编程思想,原则上使用任何一种编程语言都可以实现,比如go语言、Solidity、C++、C#、Java、javascript都可以实现区块链的开发。Go语言是为了解决分布式计算,而区块链是典型的分布式数据存储系统,因此go语言能开发区块链。且Go易学易用,能很好的满足区块链行开发需要的“执行效率高、高并发、跨平台,网络开发要求高”等特点。
 深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
深入学习区块链的Go语言开发框架Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM区块链技术的出现,使得数字货币的应用成为可能,也在许多领域得到了广泛应用。随着区块链技术领域的扩大,开发人员对于更好的应用程序编写方式的需求也高涨起来。于是,一个叫做Go语言(简称Golang)的编程语言悄悄兴起,成为了区块链开发人员的最爱。Go语言是谷歌公司开发的一种系统级编程语言,自诞生以来,一直着重强调程序设计的简捷和高效。Go语言的优点包括:静态类型
 打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM
打造高效的区块链技术开发环境(使用Go语言)Jun 05, 2023 am 08:21 AM随着区块链技术的发展和应用越来越广泛,有越来越多的人开始参与到区块链技术的开发中来。而要想打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,选择合适的开发语言和工具是非常重要的。Go语言正是一个很好的选择,因为它的性能很高,同时还有很多优秀的开源工具和库,能够大大提高开发效率。下面就来介绍一下如何打造高效的区块链技术开发环境,使用Go语言进行开发。一、选择Go语言在选择开发语言
 Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AM
Java 中的区块链和加密货币技术Jun 09, 2023 am 09:56 AMJava是一种广泛使用的编程语言,它被许多公司和组织用作开发各种应用程序的工具。最近几年来,区块链和加密货币技术在全球范围内引起了大量的关注。Java的灵活性和多功能性使得它成为开发区块链和加密货币应用程序的优秀选择。区块链技术是一种安全的、去中心化的数据库,它可以存储和共享交易记录,而无需任何中央机构的干涉。Java提供了许多区块链开发框架,例如H

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






