Google Cloud Database adds more artificial intelligence capabilities
Google Cloud is beefing up its analytic and transactional databases, including BigQuery, AlloyDB and Spanner, in an effort to drive the development of its customers' generated artificial intelligence applications.

BigQuery is Google Cloud’s advanced database service designed to support analytics and artificial intelligence tasks. The service introduces several artificial intelligence enhancements. First, Google Cloud launched a preview version of the integration of BigQuery and Vertex AI, focusing on text and speech capabilities. This integration will enable users to extract valuable insights from unstructured data such as images and documents.
Gemini, the company’s most powerful artificial intelligence model, has been made available to BigQuery customers through Vertex AI. The model sparked some controversy last week after a less-than-stellar debut on the consumer market.
These AI features follow BigQuery’s earlier announcement of vector search capabilities. The vector search feature in preview is a key component of GenAI applications, supporting similarity search and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) using large language models.
Direct access to Vertex AI in BigQuery provides ease of use for Google Cloud AI customers in multiple ways, said Gerrit Kazmaier, general manager and vice president of data analytics at Google Cloud AI.
In the press conference, Kazmaier mentioned that as a data analysis practitioner, you can access all Vertex AI models, including Gemini models, through the SQL command line or the BigQuery embedded Python API. This makes it easier to access these models without relying on a data scientist or machine learning platform. You can access it directly in your field of work, using the data at hand. The emergence of this new technology brings more possibilities and flexibility to data analysis.
Kazmaier noted that a second advantage of integration is easier access to the data needed for AI models. Prior to integration, transferring data to AI models often required building and maintaining data pipelines to move the data. Now, he says, that's no longer necessary. "All the complicated procedures have been simplified."
In vertex, using the capabilities of text- and image-based artificial intelligence models, data analysts can gain more data analysis advantages through BigQuery to provide customers with bring more benefits.
"This opens a new stage of analyzing scenarios." He said that the summary, emotion extraction, classification, concentration, and translation of structured and unstructured data are a big deal. Roughly speaking, 90% of data is unstructured. This data is typically not used for enterprise data analytics because you can't process it in a meaningful way.
On the transactional (or operational) side, Google Cloud announced the general availability of AlloyDB AI, the AI-specific version of the hosted Postgres database the company announced at last year’s Next 23 conference. AlloyDB AI has the ability to store vector embeddings and perform vector search functions, which Google Cloud considers a core component of its customers' GenAI use cases.
Google Cloud also launched a new integration with LangChain, a popular open source framework that helps connect customer data into large language models (LLMs). Andi Gutmans, Google Cloud general manager and vice president of databases, said that all Google Cloud databases will be integrated with LangChain.
The new capabilities are in response to customer demand to find a way to get more GenAI value from their data, Gutmans said.
The company also announced that it will add vector search capabilities to other databases hosted on its cloud for customers, including Redis and MySQL. Cloud Spanner, Firestore and Bigtable will also gain vector capabilities, Gutmans said.
“What’s special about Spanner is it’s going to have nearest neighbor search capabilities, which is a slightly different variant,” Gutmans said. “What’s really exciting is the customers that have really, really big use cases. -- Trillions of vectors, for example, highly partitioned based on user. You could imagine some of Google's internal applications being partitioned by user -- they would be able to store and search vectors at trillions (vectors) scale."
"Our belief is that any database, any place that stores operational data that you might need to use in a GenAI use case, should also have vector capabilities," he said. "This is not the same as databases from 15 to 20 years ago. There is no difference when adding JSON support to both. We believe that good vector functionality should just keep the basic functionality of the database."
The above is the detailed content of Google Cloud Database adds more artificial intelligence capabilities. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What is Graph of Thought in Prompt EngineeringApr 13, 2025 am 11:53 AM
What is Graph of Thought in Prompt EngineeringApr 13, 2025 am 11:53 AMIntroduction In prompt engineering, “Graph of Thought” refers to a novel approach that uses graph theory to structure and guide AI’s reasoning process. Unlike traditional methods, which often involve linear s
 Optimize Your Organisation's Email Marketing with GenAI AgentsApr 13, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Optimize Your Organisation's Email Marketing with GenAI AgentsApr 13, 2025 am 11:44 AMIntroduction Congratulations! You run a successful business. Through your web pages, social media campaigns, webinars, conferences, free resources, and other sources, you collect 5000 email IDs daily. The next obvious step is
 Real-Time App Performance Monitoring with Apache PinotApr 13, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Real-Time App Performance Monitoring with Apache PinotApr 13, 2025 am 11:40 AMIntroduction In today’s fast-paced software development environment, ensuring optimal application performance is crucial. Monitoring real-time metrics such as response times, error rates, and resource utilization can help main
 ChatGPT Hits 1 Billion Users? 'Doubled In Just Weeks' Says OpenAI CEOApr 13, 2025 am 11:23 AM
ChatGPT Hits 1 Billion Users? 'Doubled In Just Weeks' Says OpenAI CEOApr 13, 2025 am 11:23 AM“How many users do you have?” he prodded. “I think the last time we said was 500 million weekly actives, and it is growing very rapidly,” replied Altman. “You told me that it like doubled in just a few weeks,” Anderson continued. “I said that priv
 Pixtral-12B: Mistral AI's First Multimodal Model - Analytics VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AM
Pixtral-12B: Mistral AI's First Multimodal Model - Analytics VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AMIntroduction Mistral has released its very first multimodal model, namely the Pixtral-12B-2409. This model is built upon Mistral’s 12 Billion parameter, Nemo 12B. What sets this model apart? It can now take both images and tex
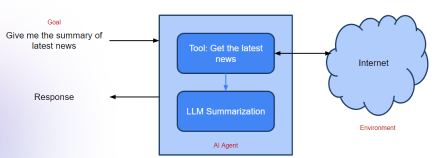 Agentic Frameworks for Generative AI Applications - Analytics VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Agentic Frameworks for Generative AI Applications - Analytics VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:13 AMImagine having an AI-powered assistant that not only responds to your queries but also autonomously gathers information, executes tasks, and even handles multiple types of data—text, images, and code. Sounds futuristic? In this a
 Applications of Generative AI in the Financial SectorApr 13, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Applications of Generative AI in the Financial SectorApr 13, 2025 am 11:12 AMIntroduction The finance industry is the cornerstone of any country’s development, as it drives economic growth by facilitating efficient transactions and credit availability. The ease with which transactions occur and credit
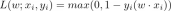 Guide to Online Learning and Passive-Aggressive AlgorithmsApr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Guide to Online Learning and Passive-Aggressive AlgorithmsApr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AMIntroduction Data is being generated at an unprecedented rate from sources such as social media, financial transactions, and e-commerce platforms. Handling this continuous stream of information is a challenge, but it offers an


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools





