Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >Linux operating file commands
Linux operating file commands
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2024-03-06 11:34:19531browse
ls command is mainly used to display and print out the files or directories in the directory. Commonly used parameters are as follows:
-a: Output all files together with hidden files. -l: Completely display file information, including permissions and attributes. -d: Only display the directory itself, not the files in the directory.
Display user home directory information:
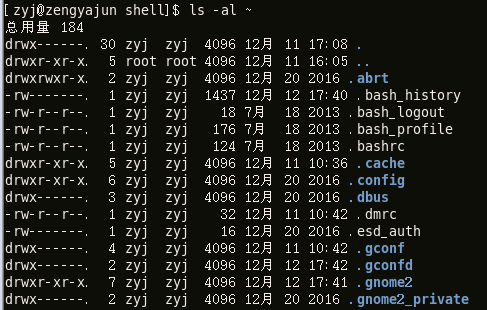
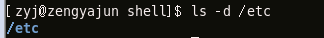
Display the directory itself:
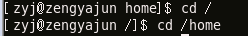
The cd command is mainly used to change directories
The pwd command is used to display the path and directory where the user is currently located
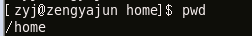
Because we used the cd command to enter the /home directory above, we use the pwd command to display our current directory
This command is used to create a new directory, as follows
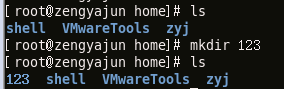
We created a new directory named 123 in the /home directory
This command is used to delete an empty directory. When there is data in the directory, this command cannot be deleted. The data in the directory must be deleted before the directory can be deleted.
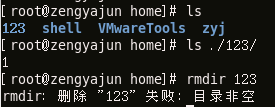
This command is used to delete directories and files. This command is very powerful. We usually use this command to delete files
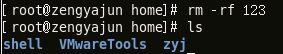
Adding the -rf parameter to this command can delete files, but be careful when using this command, because it will be very troublesome if you accidentally delete important files
This command is used to copy files to other directories
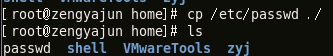
Copy the /etc/passwd file to the current directory and view it
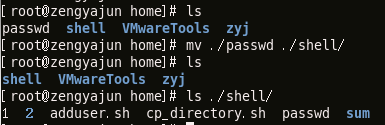
This command is used to move files to other directories, which is equivalent to cutting
Move passwd to the shell directory under the current directory
The above is the detailed content of Linux operating file commands. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

