With the continuous popularity of artificial intelligence technology (AI), various algorithms play an important role in promoting the development of this field. From linear regression algorithms used to predict house prices to neural networks powering self-driving cars, these algorithms quietly power and operate countless applications. As the amount of data increases and computing power improves, the performance and efficiency of artificial intelligence algorithms are also constantly improving. The applications of these algorithms are becoming more and more widespread, covering medical diagnosis, financial risk assessment, natural language processing, etc.

Today, we will take you Take a look at these popular artificial intelligence algorithms (linear regression, logistic regression, decision tree, naive Bayes, support vector machine (SVM), ensemble learning, K nearest neighbor algorithm, K-means algorithm, neural network, reinforcement learning Deep Q-Networks ) to explore their working principles, application scenarios, and real-world impact.
1. Linear regression:
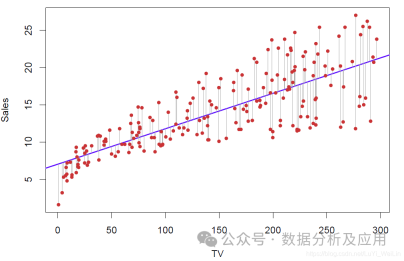
The principle of linear regression is to find an optimal straight line to fit the distribution of data points to the greatest extent .
Model training is the use of known input and output data to optimize the model, usually by minimizing the difference between predicted values and actual values.
Advantages: simple and easy to understand, high calculation efficiency.
Disadvantages: Limited ability to handle non-linear relationships.
Usage scenarios: Suitable for problems of predicting continuous values, such as predicting housing prices, stock prices, etc.
Sample code (build a simple linear regression model using Python’s Scikit-learn library):
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.datasets import make_regression# 生成模拟数据集X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=0.1)# 创建线性回归模型对象lr = LinearRegression()# 训练模型lr.fit(X, y)# 进行预测predictions = lr.predict(X)
2. Logistic regression:
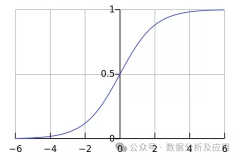
Model principle: Logistic regression is a machine learning algorithm used to solve binary classification problems. It maps continuous input to discrete output ( usually binary). It uses a logistic function to map the results of linear regression to the range (0,1) to obtain the probability of classification.
Model training: Use sample data of known classifications to train a logistic regression model, and optimize the parameters of the model to minimize the cross-entropy loss between the predicted probability and the actual classification.
Advantages: Simple and easy to understand, better for two-classification problems.
Disadvantages: Limited ability to handle non-linear relationships.
Usage scenarios: Suitable for binary classification problems, such as spam filtering, disease prediction, etc.
Sample code (build a simple logistic regression model using Python’s Scikit-learn library):
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.datasets import make_classification# 生成模拟数据集X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, random_state=42)# 创建逻辑回归模型对象lr = LogisticRegression()# 训练模型lr.fit(X, y)# 进行预测predictions = lr.predict(X)
3. Decision tree:
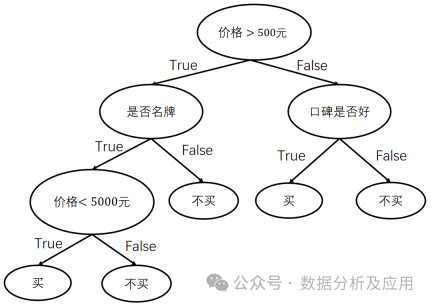
Model principle: Decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm that recursively divides the data set into smaller sub-trees. set to construct decision boundaries. Each internal node represents a judgment condition on a feature attribute, each branch represents a possible attribute value, and each leaf node represents a category.
Model training: Build a decision tree by selecting the best partitioning attributes, and use pruning techniques to prevent overfitting.
Advantages: Easy to understand and explain, able to handle classification and regression problems.
Disadvantages: easy to overfit, sensitive to noise and outliers.
Usage scenarios: Suitable for classification and regression problems, such as credit card fraud detection, weather forecast, etc.
Sample code (using Python’s Scikit-learn library to build a simple decision tree model):
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 加载数据集iris = load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.target# 划分训练集和测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 创建决策树模型对象dt = DecisionTreeClassifier()# 训练模型dt.fit(X_train, y_train)# 进行预测predictions = dt.predict(X_test)
4. Naive Bayess:
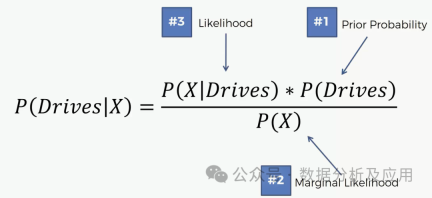
Model principle: Naive Bayes is a classification based on Bayes theorem and the assumption of feature condition independence method. It performs probabilistic modeling of the attribute values of samples in each category, and then predicts the category to which new samples belong based on these probabilities.
Model training: Build a Naive Bayes classifier by using sample data with known classes and attributes to estimate the prior probability of each class and the conditional probability of each attribute .
Advantages: Simple, efficient, especially effective for large categories and small data sets.
Disadvantages: Poor modeling of dependencies between features.
Usage scenarios: Suitable for text classification, spam filtering and other scenarios.
Example code (building a simple naive Bayes classifier using Python’s Scikit-learn library):
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNBfrom sklearn.datasets import load_iris# 加载数据集iris = load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.target# 创建朴素贝叶斯分类器对象gnb = GaussianNB()# 训练模型gnb.fit(X, y)# 进行预测predictions = gnb.predict(X)
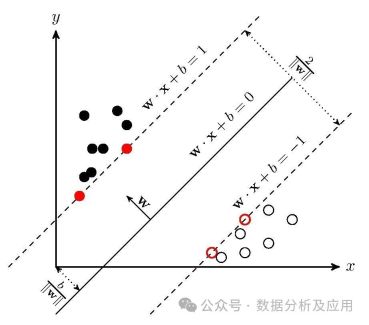
5、支持向量机(SVM):
模型原理:支持向量机是一种监督学习算法,用于分类和回归问题。它试图找到一个超平面,使得该超平面能够将不同类别的样本分隔开。SVM使用核函数来处理非线性问题。
模型训练:通过优化一个约束条件下的二次损失函数来训练SVM,以找到最佳的超平面。
优点:对高维数据和非线性问题表现良好,能够处理多分类问题。
缺点:对于大规模数据集计算复杂度高,对参数和核函数的选择敏感。
使用场景:适用于分类和回归问题,如图像识别、文本分类等。
示例代码(使用Python的Scikit-learn库构建一个简单的SVM分类器):
from sklearn import svmfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 加载数据集iris = load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.target# 划分训练集和测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 创建SVM分类器对象,使用径向基核函数(RBF)clf = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf')# 训练模型clf.fit(X_train, y_train)# 进行预测predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
6、集成学习:
模型原理:集成学习是一种通过构建多个基本模型并将它们的预测结果组合起来以提高预测性能的方法。集成学习策略有投票法、平均法、堆叠法和梯度提升等。常见集成学习模型有XGBoost、随机森林、Adaboost等
模型训练:首先使用训练数据集训练多个基本模型,然后通过某种方式将它们的预测结果组合起来,形成最终的预测结果。
优点:可以提高模型的泛化能力,降低过拟合的风险。
缺点:计算复杂度高,需要更多的存储空间和计算资源。
使用场景:适用于解决分类和回归问题,尤其适用于大数据集和复杂的任务。
示例代码(使用Python的Scikit-learn库构建一个简单的投票集成分类器):
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifierfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 加载数据集iris = load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.target# 划分训练集和测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 创建基本模型对象和集成分类器对象lr = LogisticRegression()dt = DecisionTreeClassifier()vc = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lr', lr), ('dt', dt)], voting='hard')# 训练集成分类器vc.fit(X_train, y_train)# 进行预测predictions = vc.predict(X_test)7、K近邻算法:
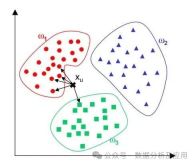
模型原理:K近邻算法是一种基于实例的学习,通过将新的样本与已知样本进行比较,找到与新样本最接近的K个样本,并根据这些样本的类别进行投票来预测新样本的类别。
模型训练:不需要训练阶段,通过计算新样本与已知样本之间的距离或相似度来找到最近的邻居。
优点:简单、易于理解,不需要训练阶段。
缺点:对于大规模数据集计算复杂度高,对参数K的选择敏感。
使用场景:适用于解决分类和回归问题,适用于相似度度量和分类任务。
示例代码(使用Python的Scikit-learn库构建一个简单的K近邻分类器):
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifierfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 加载数据集iris = load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.target# 划分训练集和测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 创建K近邻分类器对象,K=3knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)# 训练模型knn.fit(X_train, y_train)# 进行预测predictions = knn.predict(X_test)
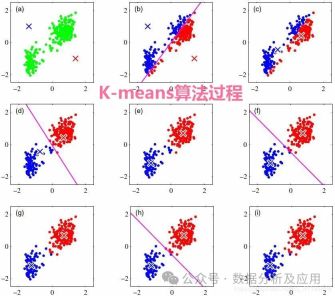
8、K-means算法:
模型原理:K-means算法是一种无监督学习算法,用于聚类问题。它将n个点(可以是样本数据点)划分为k个聚类,使得每个点属于最近的均值(聚类中心)对应的聚类。
模型训练:通过迭代更新聚类中心和分配每个点到最近的聚类中心来实现聚类。
优点:简单、快速,对于大规模数据集也能较好地运行。
缺点:对初始聚类中心敏感,可能会陷入局部最优解。
使用场景:适用于聚类问题,如市场细分、异常值检测等。
示例代码(使用Python的Scikit-learn库构建一个简单的K-means聚类器):
from sklearn.cluster import KMeansfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 生成模拟数据集X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=300, centers=4, cluster_std=0.60, random_state=0)# 创建K-means聚类器对象,K=4kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=4)# 训练模型kmeans.fit(X)# 进行预测并获取聚类标签labels = kmeans.predict(X)# 可视化结果plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=labels, cmap='viridis')plt.show()
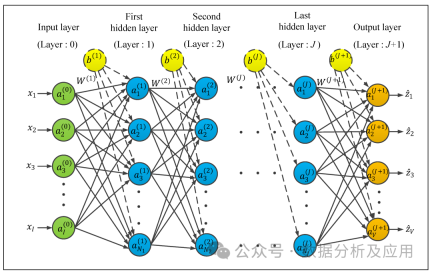
9、神经网络:
模型原理:神经网络是一种模拟人脑神经元结构的计算模型,通过模拟神经元的输入、输出和权重调整机制来实现复杂的模式识别和分类等功能。神经网络由多层神经元组成,输入层接收外界信号,经过各层神经元的处理后,最终输出层输出结果。
模型训练:神经网络的训练是通过反向传播算法实现的。在训练过程中,根据输出结果与实际结果的误差,逐层反向传播误差,并更新神经元的权重和偏置项,以减小误差。
优点:能够处理非线性问题,具有强大的模式识别能力,能够从大量数据中学习复杂的模式。
缺点:容易陷入局部最优解,过拟合问题严重,训练时间长,需要大量的数据和计算资源。
使用场景:适用于图像识别、语音识别、自然语言处理、推荐系统等场景。
示例代码(使用Python的TensorFlow库构建一个简单的神经网络分类器):
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras import layers, modelsfrom tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist# 加载MNIST数据集(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()# 归一化处理输入数据x_train = x_train / 255.0x_test = x_test / 255.0# 构建神经网络模型model = models.Sequential()model.add(layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)))model.add(layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))# 编译模型并设置损失函数和优化器等参数model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])# 训练模型model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)# 进行预测predictions = model.predict(x_test)
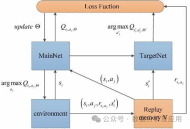
10.深度强化学习(DQN):
模型原理:Deep Q-Networks (DQN) 是一种结合了深度学习与Q-learning的强化学习算法。它的核心思想是使用神经网络来逼近Q函数,即状态-动作值函数,从而为智能体在给定状态下选择最优的动作提供依据。
模型训练:DQN的训练过程包括两个阶段:离线阶段和在线阶段。在离线阶段,智能体通过与环境的交互收集数据并训练神经网络。在线阶段,智能体使用神经网络进行动作选择和更新。为了解决过度估计问题,DQN引入了目标网络的概念,通过使目标网络在一段时间内保持稳定来提高稳定性。
优点:能够处理高维度的状态和动作空间,适用于连续动作空间的问题,具有较好的稳定性和泛化能力。
缺点:容易陷入局部最优解,需要大量的数据和计算资源,对参数的选择敏感。
使用场景:适用于游戏、机器人控制等场景。
示例代码(使用Python的TensorFlow库构建一个简单的DQN强化学习模型):
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequentialfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flattenfrom tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adamfrom tensorflow.keras import backend as Kclass DQN:def __init__(self, state_size, action_size):self.state_size = state_sizeself.action_size = action_sizeself.memory = deque(maxlen=2000)self.gamma = 0.85self.epsilon = 1.0self.epsilon_min = 0.01self.epsilon_decay = 0.995self.learning_rate = 0.005self.model = self.create_model()self.target_model = self.create_model()self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())def create_model(self):model = Sequential()model.add(Flatten(input_shape=(self.state_size,)))model.add(Dense(24, activation='relu'))model.add(Dense(24, activation='relu'))model.add(Dense(self.action_size, activation='linear'))return modeldef remember(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):self.memory.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))def act(self, state):if len(self.memory) > 1000:self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decayif self.epsilon
The above is the detailed content of Top 10 Must-Know Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
![Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174717025174979.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AM
Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AMChatGPT is not accessible? This article provides a variety of practical solutions! Many users may encounter problems such as inaccessibility or slow response when using ChatGPT on a daily basis. This article will guide you to solve these problems step by step based on different situations. Causes of ChatGPT's inaccessibility and preliminary troubleshooting First, we need to determine whether the problem lies in the OpenAI server side, or the user's own network or device problems. Please follow the steps below to troubleshoot: Step 1: Check the official status of OpenAI Visit the OpenAI Status page (status.openai.com) to see if the ChatGPT service is running normally. If a red or yellow alarm is displayed, it means Open
 Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AM
Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AMOn 10 May 2025, MIT physicist Max Tegmark told The Guardian that AI labs should emulate Oppenheimer’s Trinity-test calculus before releasing Artificial Super-Intelligence. “My assessment is that the 'Compton constant', the probability that a race to
 An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AMAI music creation technology is changing with each passing day. This article will use AI models such as ChatGPT as an example to explain in detail how to use AI to assist music creation, and explain it with actual cases. We will introduce how to create music through SunoAI, AI jukebox on Hugging Face, and Python's Music21 library. Through these technologies, everyone can easily create original music. However, it should be noted that the copyright issue of AI-generated content cannot be ignored, and you must be cautious when using it. Let’s explore the infinite possibilities of AI in the music field together! OpenAI's latest AI agent "OpenAI Deep Research" introduces: [ChatGPT]Ope
 What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AM
What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AMThe emergence of ChatGPT-4 has greatly expanded the possibility of AI applications. Compared with GPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4 has significantly improved. It has powerful context comprehension capabilities and can also recognize and generate images. It is a universal AI assistant. It has shown great potential in many fields such as improving business efficiency and assisting creation. However, at the same time, we must also pay attention to the precautions in its use. This article will explain the characteristics of ChatGPT-4 in detail and introduce effective usage methods for different scenarios. The article contains skills to make full use of the latest AI technologies, please refer to it. OpenAI's latest AI agent, please click the link below for details of "OpenAI Deep Research"
 Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AM
Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AMChatGPT App: Unleash your creativity with the AI assistant! Beginner's Guide The ChatGPT app is an innovative AI assistant that handles a wide range of tasks, including writing, translation, and question answering. It is a tool with endless possibilities that is useful for creative activities and information gathering. In this article, we will explain in an easy-to-understand way for beginners, from how to install the ChatGPT smartphone app, to the features unique to apps such as voice input functions and plugins, as well as the points to keep in mind when using the app. We'll also be taking a closer look at plugin restrictions and device-to-device configuration synchronization
 How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AM
How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AMChatGPT Chinese version: Unlock new experience of Chinese AI dialogue ChatGPT is popular all over the world, did you know it also offers a Chinese version? This powerful AI tool not only supports daily conversations, but also handles professional content and is compatible with Simplified and Traditional Chinese. Whether it is a user in China or a friend who is learning Chinese, you can benefit from it. This article will introduce in detail how to use ChatGPT Chinese version, including account settings, Chinese prompt word input, filter use, and selection of different packages, and analyze potential risks and response strategies. In addition, we will also compare ChatGPT Chinese version with other Chinese AI tools to help you better understand its advantages and application scenarios. OpenAI's latest AI intelligence
 5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AM
5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AMThese can be thought of as the next leap forward in the field of generative AI, which gave us ChatGPT and other large-language-model chatbots. Rather than simply answering questions or generating information, they can take action on our behalf, inter
 An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AMEfficient multiple account management techniques using ChatGPT | A thorough explanation of how to use business and private life! ChatGPT is used in a variety of situations, but some people may be worried about managing multiple accounts. This article will explain in detail how to create multiple accounts for ChatGPT, what to do when using it, and how to operate it safely and efficiently. We also cover important points such as the difference in business and private use, and complying with OpenAI's terms of use, and provide a guide to help you safely utilize multiple accounts. OpenAI


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







