
CPython Architecture
Cpython is a stack-based virtual machine that uses interpreter mode to parse and execute Python code. The interpreter compiles the source code into an intermediate representation (IR) called bytecode, which consists of a series of opcodes that specify the operations to be performed. When the interpreter executes bytecodes, it pushes them onto the stack and pops operands from the stack during execution.
Bytecode
Bytecode is a compact and efficient representation that converts Python source code into a form more suitable for execution by the interpreter. Bytecode includes various opcodes, such as loading values onto the stack, performing arithmetic operations, and calling functions.
Sample code:
# Python 源代码 x = 5 y = 10 print(x + y)
# 相应的字节码: LOAD_FAST0 (x) LOAD_CONST 1 (10) BINARY_OP0 (+) PRINT_ITEM RETURN_VALUE
Memory Management
Python uses reference counting to manage memory. Every object has a reference counter that tracks the number of references pointing to that object. When the reference counter reaches zero, the object will be released by the garbage collector. CPython also uses a mark-and-sweep algorithm to reclaim unreachable objects.
Optimization TechnologyIn order to improve performance, CPython uses a variety of
optimizationtechniques, including:
- JIT Compilation:
- Just-In-Time compiler compiles bytecode into machine code, thereby increasing execution speed. Bytecode caching:
- Compiled bytecode is cached to avoid repeated compilation on subsequent executions. Type annotations:
- Type annotations provide information about the types of variables and functions, which helps the interpreter make more optimal decisions. Multi-threading support:
- CPython supports multi-threading, allowing multiple Python tasks to be executed simultaneously.
The advantages of CPython include:
- Widely used:
- It is the most popular Python implementation with a large user base and rich library support. Multi-platform support:
- CPython can run across multiple platforms, including windows, MacOS and linux. Extensibility:
- CPython can be extended through extension modules to provide support for specific domains and applications. Disadvantages of CPython include:
- Overhead:
- The interpreter will incur certain overhead when interpreting bytecode, which may result in slightly lower performance than compiled languages. GIL:
- CPython uses a global interpreter lock (GIL) to ensure safety for multiple threads, which may limit Parallel operations.
CPython is a powerful and efficient implementation of the Python language. With a deep understanding of its internals, including its
architecture, memory management, and optimization techniques, you can use Python more effectively and write high-performance code. Although CPython has some shortcomings, this does not prevent it from becoming a popular choice for Python application development.
The above is the detailed content of Demystifying Python CPython. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何在 Windows 11 中增加虚拟内存(页面文件)May 13, 2023 pm 04:37 PM
如何在 Windows 11 中增加虚拟内存(页面文件)May 13, 2023 pm 04:37 PM如果您在运行高端应用程序或游戏时注意到一定的延迟,则可能是RAM/内存通常运行已满。这是增加Windows11中的虚拟内存或页面文件大小的地方。虚拟内存或页面文件是最容易被误解的概念之一,围绕它有很多神话。无论其他人说什么或做什么,都必须彻底了解如何从您的计算机中获得最佳性能。在以下部分中,我们将引导您完成在Windows11中增加虚拟内存的步骤,帮助您了解其重要性以及最佳虚拟内存大小。为什么需要虚拟内存?页面文件或虚拟内存基本上是用作RAM的硬盘的一部分。当内存已满且无法存储更多数据时
 如何在 Windows 11 中重置虚拟内存(页面文件)?Apr 13, 2023 pm 11:28 PM
如何在 Windows 11 中重置虚拟内存(页面文件)?Apr 13, 2023 pm 11:28 PM如果您的计算机没有足够的 RAM 或总是满的,您可以依靠虚拟内存从物理内存中卸载非活动文件。但是,如果这不太顺利,您可能需要在 Windows 11 中重置虚拟内存。我们经常看到我们的计算机滞后,最可能的情况是Windows 11 中的高 RAM 使用率。有很多方法可以降低 RAM 消耗,但这可能会影响您的体验。而且,这就是虚拟内存可以提供帮助的地方。有时需要在 Windows 11 中重置虚拟内存,因此,必须正确理解该概念和过程,我们在以下部分中进行了讨论。虚拟内存是如何工作的,为什么我需要重
 Windows 11 停止代码内存管理:7 个修复May 04, 2023 pm 11:34 PM
Windows 11 停止代码内存管理:7 个修复May 04, 2023 pm 11:34 PM如果您的PC出现内存管理错误,您需要查看这些Windows11停止代码内存管理修复程序。如果您的系统崩溃并出现蓝屏或BSOD,您可能已经看到了Windows11停止代码内存管理错误。它将在屏幕上显示MEMORY_MANAGEMENT,表明系统内存管理存在问题。例如,它可能(或可能不)伴随着停止代码,如0x0000001A。有时您可以通过基本重启来解决错误,但它通常涉及额外的故障排除步骤。如果您在Windows11PC上遇到错误,请应用以下修复程序并运行扫描以使您的系统重新启动并运
 揭秘Golang的字节码:探寻其编程语言的本质Feb 26, 2024 pm 02:36 PM
揭秘Golang的字节码:探寻其编程语言的本质Feb 26, 2024 pm 02:36 PMGolang(又称Go语言)是一种由Google开发的开源编程语言,于2007年首次发布,旨在提升工程师的生产力和开发效率。Golang旨在简化编程语言的复杂性,提供高效的执行速度,同时兼顾易用性。本文将深入探讨Golang的特点,解析它的字节码机制,并通过具体代码示例揭秘其工作原理。一、Golang的特点及优势简洁高效:Golang拥有简洁的语法结构和丰富
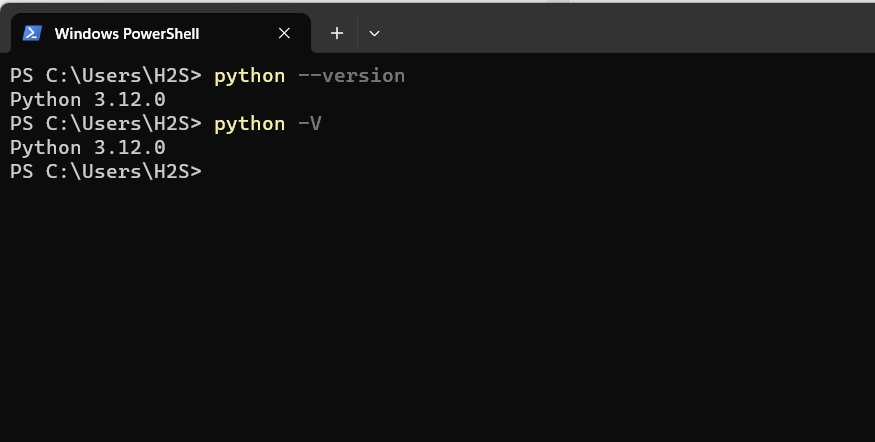 验证 Python 安装的多种方法 Windows 11Nov 18, 2023 am 11:05 AM
验证 Python 安装的多种方法 Windows 11Nov 18, 2023 am 11:05 AM检查Python是否安装在Windows11中的不同方法如果您的系统上还没有安装Python,那么可以查看我们的文章,其中显示了在Windows11上获取Python和PIP包管理器的单个命令。1.使用命令提示符第一种方法是使用命令行,为此,我们使用Windows的CMD。这是找出笔记本电脑或PC上安装的Python版本的最佳方法。python--version2.PowerShell的与命令提示符类似,PowerShell是Microsoft的命令行shell和脚本工具,可在Windows平台
 PHP中的内存管理和垃圾回收技术May 11, 2023 am 08:33 AM
PHP中的内存管理和垃圾回收技术May 11, 2023 am 08:33 AMPHP作为一种广泛使用的脚本语言,为了在运行时保证高效执行,具有独特的内存管理和垃圾回收技术。本文将简单介绍PHP内存管理和垃圾回收的原理和实现方式。一、PHP内存管理的原理PHP的内存管理采用了引用计数(ReferenceCounting)来实现,这种方式是现代化的语言中比较常见的内存管理方式之一。当一个变量被使用时,PHP会为其分配一段内存,并将这段内
 解密PyCharm解释器添加的技巧Feb 21, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
解密PyCharm解释器添加的技巧Feb 21, 2024 pm 03:33 PM解密PyCharm解释器添加的技巧PyCharm是许多Python开发者首选的集成开发环境(IDE),它提供了许多强大的功能来提高开发效率。其中,解释器的设置是PyCharm中一个重要的环节,正确设置解释器可以帮助开发者顺利运行代码并调试程序。本文将介绍一些解密PyCharm解释器添加的技巧,并结合具体代码示例来展示如何正确配置解释器。添加和选择解释器在Py
 理解PHP7底层开发原理:从字节码到机器码的转换过程Sep 08, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
理解PHP7底层开发原理:从字节码到机器码的转换过程Sep 08, 2023 pm 04:13 PM理解PHP7底层开发原理:从字节码到机器码的转换过程随着互联网的快速发展,PHP作为一种高效、可扩展性强的开发语言,受到了广大开发者的青睐。PHP语言的升级更新一直都是开发者们关注的焦点,而PHP7作为目前最新版本,不仅在性能方面有了大幅提升,还引入了底层开发原理的改变。本文将从字节码到机器码的转换过程入手,来深入理解PHP7底层开发原理。在PHP7之前的版


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






