 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Backbone.js 0.9.2 Source Code Comments Chinese Translation Version_Basic Knowledge
Backbone.js 0.9.2 Source Code Comments Chinese Translation Version_Basic Knowledge
// Backbone.js 0.9.2
// (c) 2010-2012 Jeremy Ashkenas, DocumentCloud Inc.
// Backbone may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
// For all details and documentation:
// http://backbonejs.org
(function() {
// Create a global object, represented as a window object in the browser and a global object in Node.js
var root = this;
// Save the value of the "Backbone" variable before it was overwritten
// If there is a naming conflict or considering the specification, you can use the Backbone.noConflict() method to restore the value of the variable before it was occupied by Backbone, and return the Backbone object for renaming
var previousBackbone = root.Backbone;
//Cache the slice and splice methods in Array.prototype to local variables for calling
var slice = Array.prototype.slice;
var splice = Array.prototype.splice;
var Backbone;
if( typeof exports !== 'undefined') {
Backbone = exports;
} else {
Backbone = root.Backbone = {};
}
//Define Backbone version
Backbone.VERSION = '0.9.2';
// Automatically import Underscore in the server environment. Some methods in Backbone depend on or inherit from Underscore.
var _ = root._;
if(!_ && ( typeof require !== 'undefined'))
_ = require('underscore');
// Define the third-party library as a unified variable "$", which is used to call methods in the library during view (View), event processing and synchronization with server data (sync)
// Supported libraries include jQuery, Zepto, etc. They have the same syntax, but Zepto is more suitable for mobile development. It is mainly aimed at Webkit core browsers.
// You can also customize a custom library with syntax similar to jQuery for use by Backbone (sometimes we may need a customized version that is lighter than jQuery or Zepto)
// The "$" defined here is a local variable, so it will not affect the normal use of third-party libraries outside the Backbone framework.
var $ = root.jQuery || root.Zepto || root.ender;
// Manually set up third-party libraries
// If you have not imported a third-party library before importing Backbone, you can set the "$" local variable through the setDomLibrary method
// The setDomLibrary method is also commonly used to dynamically import custom libraries in Backbone.
Backbone.setDomLibrary = function(lib) {
$ = lib;
};
//Abandon naming the framework after "Backbone" and return the Backbone object, generally used to avoid naming conflicts or standardize naming methods
// For example:
// var bk = Backbone.noConflict(); // Cancel the "Backbone" naming and store the Backbone object in the bk variable
// console.log(Backbone); // This variable can no longer access the Backbone object and is restored to the value before Backbone was defined.
// var MyBackbone = bk; // And bk stores the Backbone object, we rename it to MyBackbone
Backbone.noConflict = function() {
root.Backbone = previousBackbone;
return this;
};
// For browsers that do not support REST, you can set Backbone.emulateHTTP = true
// The server request will be sent in POST mode, and the _method parameter will be added to the data to identify the operation name, and the X-HTTP-Method-Override header information will also be sent.
Backbone.emulateHTTP = false;
// For browsers that do not support application/json encoding, you can set Backbone.emulateJSON = true;
//Set the request type to application/x-www-form-urlencoded, and place the data in the model parameter to achieve compatibility
Backbone.emulateJSON = false;
// Backbone.Events related to custom events
// ------------------
// eventSplitter specifies the parsing rules for event names when processing multiple events.
var eventSplitter = /s /;
// Custom event manager
// By binding Events related methods in the object, it is allowed to add, delete and trigger custom events to the object.
var Events = Backbone.Events = {
// Bind custom events and callback functions to the current object
//The context object in the callback function is the specified context. If the context is not set, the context object defaults to the object of the current bound event.
// This method is similar to the addEventListener method in DOM Level2
// events allows specifying multiple event names, separated by whitespace characters (such as spaces, tabs, etc.)
// When the event name is "all", when any event is triggered by calling the trigger method, all callback functions bound in the "all" event will be called.
on : function(events, callback, context) {
//Define local variables used in some functions
var calls, event, node, tail, list;
//The callback function must be set
if(!callback)
return this;
// Parse event names through eventSplitter, use split to split multiple event names into an array
// Generally use blank characters to specify multiple event names
events = events.split(eventSplitter);
// calls records the list of events and callback functions bound in the current object
calls = this._callbacks || (this._callbacks = {});
// Loop through the list of event names and store the event names in the event variable from beginning to end.
while( event = events.shift()) {
// Get the callback function that has been bound to the event event
// list stores the list of callback functions bound to a single event name
// The function list is not stored in an array, but is related sequentially through the next attributes of multiple objects.
/**数据格式如:
* {
* tail: {Object},
* next: {
* callback: {Function},
* context: {Object},
* next: {
* callback: {Function},
* context: {Object},
* next: {Object}
* }
* }
* }*/
// The next object at each level of the list stores information related to a callback event (function body, context and next callback event)
// The top level of the event list stores a tail object, which stores the identifier of the last bound callback event (the same object as the next of the last callback event)
// Through the tail identifier, you can know that the last callback function has been reached when traversing the callback list
list = calls[event];
// The node variable is used to record information related to this callback function.
//tail only stores the identifier of the last bound callback function
// Therefore, if the callback function has been bound before, assign the previous tail to node as an object, and then create a new object identifier for tail
// The reason why this callback event is added to the tail object of the previous callback is to arrange the object hierarchy of the callback function list in the binding order (the latest bound event will be placed at the bottom)
node = list ? list.tail : {};
node.next = tail = {};
//Record the function body and context information of this callback
node.context = context;
node.callback = callback;
//Reassemble the callback list of the current event, this callback event has been added to the list
calls[event] = {
tail: tail,
next : list ? list.next : node
};
}
// Return the current object to facilitate method chain calls
return this;
},
// Remove bound events or callback functions in the object. You can filter the events or callback functions that need to be deleted through events, callback and context.
// - If context is empty, remove all functions specified by callback
// - If callback is empty, remove all callback functions in the event
// - If events is empty, but callback or context is specified, remove the callback function specified by callback or context (event names are not distinguished)
// - If no parameters are passed, remove all events and callback functions bound in the object
off : function(events, callback, context) {
var event, calls, node, tail, cb, ctx;
// No events, or removing *all* events.
//The current object does not have any events bound to it
if(!( calls = this._callbacks))
return;
// If no parameters are specified, remove all events and callback functions (remove the _callbacks attribute)
if(!(events || callback || context)) {
delete this._callbacks;
return this;
}
// Parse the event list that needs to be removed
// - If events are specified, the event name is parsed according to eventSplitter
// - If events are not specified, parse the name list of all bound events
events = events ? events.split(eventSplitter) : _.keys(calls);
// Loop event name list
while( event = events.shift()) {
// Remove the current event object from the list and cache it in the node variable
node = calls[event];
delete calls[event];
// If the current event object does not exist (or no removal filter conditions are specified, it is considered that the current event and all callback functions will be removed), then terminate this operation (the event object has been removed in the previous step)
if(!node || !(callback || context))
continue;
// Create a new list, omitting the indicated callbacks.
// According to the callback function or context filter conditions, assemble a new event object and rebind it
tail = node.tail;
// Traverse all callback objects in the event
while(( node = node.next) !== tail) {
cb = node.callback;
ctx = node.context;
// Based on the callback function and context in the parameters, filter the callback function and rebind the callback function that does not meet the filtering conditions to the event (because all callback functions in the event have been removed above)
if((callback && cb !== callback) || (context && ctx !== context)) {
this.on(event, cb, ctx);
}
}
}
return this;
},
// Trigger one or more events that have been defined, and execute the bound callback function list in sequence
trigger : function(events) {
var event, node, calls, tail, args, all, rest;
//The current object does not have any events bound to it
if(!( calls = this._callbacks))
return this;
// Get the "all" event list bound in the callback function list
all = calls.all;
// Parse the event name that needs to be triggered into an array according to eventSplitter rules
events = events.split(eventSplitter);
// Record the parameters of trigger from the second to the rest variable, which will be passed to the callback function in turn.
rest = slice.call(arguments, 1);
// Loop through the list of events that need to be triggered
while( event = events.shift()) {
// The node variable here records a list of all callback functions of the current event
if( node = calls[event]) {
//The tail variable records the object ID of the last binding event
tail = node.tail;
//The value of the node variable is assigned to the bound single callback event object in sequence according to the binding order of the event.
// The next property of the last bound event refers to the same object as tail, which is used as the basis for judging whether the end of the list has been reached.
while(( node = node.next) !== tail) {
// Execute all bound events and pass the parameters when calling the trigger to the callback function
node.callback.apply(node.context || this, rest);
}
}
// The variable all records the "all" event during binding, that is, when any event is called, the callback function in the "all" event will be executed.
// - The callback functions in the "all" event, regardless of the binding order, will be executed sequentially after all the callback function lists of the current event have been executed.
// - The "all" event should be automatically called when a normal event is triggered. If the "all" event is forced to be triggered, the callback function in the event will be executed twice.
if(node = all) {
tail = node.tail;
//The difference from calling the callback function of a normal event is that the all event will pass the currently called event name as the first parameter to the callback function.
args = [event].concat(rest);
// Traverse and execute the callback function list in the "all" event
while(( node = node.next) !== tail) {
node.callback.apply(node.context || this, args);
}
}
}
return this;
}
};
// Aliases for binding events and release events, also for compatibility with previous versions of Backbone
Events.bind = Events.on;
Events.unbind = Events.off;
// Backbone.Model data object model
//-------------
// Model is the base class of all data object models in Backbone, used to create a data model
// @param {Object} attributes specifies the initialization data when creating the model
// @param {Object} options
/*** @format options
* {
* parse: {Boolean},
* collection: {Collection}
* }*/
var Model = Backbone.Model = function(attributes, options) {
// The defaults variable is used to store the default data of the model
var defaults;
// If the attributes parameter is not specified, set attributes to an empty object
attributes || ( attributes = {});
//Set the parsing method of attributes default data. For example, the default data is obtained from the server (or the original data is in XML format). In order to be compatible with the data format required by the set method, the parse method can be used for parsing.
if(options && options.parse)
attributes = this.parse(attributes);
if( defaults = getValue(this, 'defaults')) {
// If the Model sets defaults data when it is defined, the initialization data uses the data merged with the defaults and attributes parameters (the data in attributes will overwrite the data with the same name in defaults)
attributes = _.extend({}, defaults, attributes);
}
// Explicitly specify the Collection object to which the model belongs (when calling the add, push and other methods of Collection to add the model to the collection, the Collection object to which the model belongs will be automatically set)
if(options && options.collection)
this.collection = options.collection;
//The attributes attribute stores the JSON objectified data of the current model and is empty by default when creating the model.
this.attributes = {};
// Define _escapedAttributes cache object, which will cache data processed through the escape method
this._escapedAttributes = {};
// Configure a unique identifier for each model
this.cid = _.uniqueId('c');
//Define a series of objects used to record data status. Please refer to the comments when defining the object for specific meanings.
this.changed = {};
this._silent = {};
this._pending = {};
// Set initialization data when creating an instance. Use the silent parameter for the first time and the change event will not be triggered.
this.set(attributes, {
silent : true
});
// The initialization data has been set above. The status of changed, _silent, _pending objects may have changed. Re-initialize it here.
this.changed = {};
this._silent = {};
this._pending = {};
// The _previousAttributes variable stores a copy of the model data
// Used to obtain the state before the model data is changed in the change event. The data of the previous state can be obtained through the previous or previousAttributes method.
this._previousAttributes = _.clone(this.attributes);
//Call initialize initialization method
this.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
};
// Use the extend method to define a series of properties and methods for the Model prototype
_.extend(Model.prototype, Events, {
//The changed attribute records the key collection of changed data each time the set method is called.
changed: null,
// // When the silent attribute is specified, the change event will not be triggered, and the changed data will be recorded until the next change event is triggered.
// The _silent attribute is used to record the changed data when silent is used
_silent : null,
_pending : null,
// The unique identification attribute of each model (default is "id", the id attribute name can be customized by modifying idAttribute)
// If the id attribute is included when setting the data, the id will override the model's id.
// The id is used to find and identify the model in the Collection. When communicating with the backend interface, the id will also be used as the identifier of a record.
idAttribute: 'id',
// Model initialization method, automatically called after the model is constructed
initialize : function() {
},
// Return a copy of the data in the current model (JSON object format)
toJSON : function(options) {
return _.clone(this.attributes);
},
//According to the attr attribute name, get the data value in the model
get : function(attr) {
return this.attributes[attr];
},
//According to the attr attribute name, obtain the data value in the model. The HTML special characters contained in the data value will be converted into HTML entities, including & " '
// Implemented through _.escape method
escape : function(attr) {
varhtml;
// Find data from the _escapedAttributes cache object, and return directly if the data has been cached
if(html = this._escapedAttributes[attr])
return html;
// No data found in _escapedAttributes cache object
// Then get the data from the model first
var val = this.get(attr);
// Convert the HTML in the data into entities using the _.escape method, and cache it to the _escapedAttributes object for easy retrieval next time
return this._escapedAttributes[attr] = _.escape(val == null ? '' : '' val);
},
// Check whether a certain attribute exists in the model. When the value of the attribute is converted to Boolean type and the value is false, it is considered not to exist.
// If the value is false, null, undefined, 0, NaN, or an empty string, it will be converted to false
has : function(attr) {
return this.get(attr) != null;
},
//Set the data in the model. If the key value does not exist, it will be added to the model as a new attribute. If the key value already exists, it will be modified to the new value.
set : function(key, value, options) {
// Record the data objects that need to be set in the attrs variable
var attrs, attr, val;
// The parameter form allows key-value object form, or separate settings through key and value parameters.
// If key is an object, it is considered to be set in object form, and the second parameter will be regarded as the options parameter.
if(_.isObject(key) || key == null) {
attrs = key;
options = value;
} else {
// Set the two parameters of key and value separately, and put the data into the attrs object for unified processing.
attrs = {};
attrs[key] = value;
}
// The options configuration item must be an object. If options are not set, the default value is an empty object.
options || ( options = {});
// No action is performed when no parameters are set.
if(!attrs)
return this;
// If the data object being set belongs to an instance of the Model class, assign the attributes data object of the Model object to attrs
// Generally, this action will be performed when copying data from one Model object to another Model object.
if(attrs instanceof Model)
attrs = attrs.attributes;
// If the unset attribute is set in the options configuration object, reset all attributes in the attrs data object to undefined
// Generally, this operation is performed when copying data from one Model object to another Model object, but only the data in the Model needs to be copied without copying the value.
if(options.unset)
for(attr in attrs)
attrs[attr] =
void 0;
//Verify the current data, and stop execution if the verification fails
if(!this._validate(attrs, options))
return false;
// If the set id attribute name is included in the data collection, overwrite the id to the id attribute of the model
// This is to ensure that after customizing the id attribute name, the id can be accessed correctly when accessing the id attribute of the model.
if(this.idAttribute in attrs)
this.id = attrs[this.idAttribute];
var changes = options.changes = {};
// now records the data objects in the current model
var now = this.attributes;
// escaped records the data cached by escape in the current model
var escaped = this._escapedAttributes;
// prev records the value before the data in the model is changed
var prev = this._previousAttributes || {};
// Traverse the data objects that need to be set
for(attr in attrs) {
// attr stores the current attribute name, val stores the current attribute value
val = attrs[attr];
// If the current data does not exist in the model, or has changed, or the unset attribute deletion is specified in options, delete the data that was replaced by the data in _escapedAttributes.
if(!_.isEqual(now[attr], val) || (options.unset && _.has(now, attr))) {
// Only delete data cached through escape. This is to ensure that the data in the cache is synchronized with the real data in the model.
delete escaped[attr];
// If the silent attribute is specified, the change event will not be triggered by this set method call, so the changed data will be recorded in the _silent attribute so that the next time the change event is triggered, the event listening function will be notified that the data has changed.
// If the silent attribute is not specified, directly set the current data in the changes attribute to the changed state.
(options.silent ? this._silent : changes)[attr] = true;
}
// If unset is set in options, delete the data (including key) from the model
// If the unset attribute is not specified, it is considered that new or modified data will be added, and new data will be added to the model's data object.
options.unset?
delete now[attr] : now[attr] = val;
// If the data in the model is inconsistent with the new data, it means that the data has changed
if(!_.isEqual(prev[attr], val) || (_.has(now, attr) != _.has(prev, attr))) {
// Record the changed status of the current attribute in the changed attribute
this.changed[attr] = val;
if(!options.silent)
this._pending[attr] = true;
} else {
// If the data has not changed, remove the changed status from the changed attribute
delete this.changed[attr];
delete this._pending[attr];
}
}
// Call the change method, which will trigger the function bound to the change event
if(!options.silent)
this.change(options);
return this;
},
//Delete the specified data from the current model (attributes will also be deleted at the same time)
unset : function(attr, options) {
(options || ( options = {})).unset = true;
// Inform the set method to perform the deletion operation through the options.unset configuration item
return this.set(attr, null, options);
},
// Clear all data and attributes in the current model
clear : function(options) {
(options || ( options = {})).unset = true;
// Clone a copy of the properties of the current model, and tell the set method to perform the deletion operation through the options.unset configuration item
return this.set(_.clone(this.attributes), options);
},
// Obtain the default model data from the server. After obtaining the data, use the set method to fill the data into the model. Therefore, if the obtained data is inconsistent with the data in the current model, the change event will be triggered.
fetch : function(options) {
// Make sure options is a new object, and then change the properties in options
options = options ? _.clone(options) : {};
var model = this;
// In options, you can specify a custom callback function after the data is successfully obtained.
var success = options.success;
// When the data is obtained successfully, fill in the data and call the custom success callback function
options.success = function(resp, status, xhr) {
// Convert the data returned by the server through the parse method
// Fill the converted data into the model through the set method, so the change event may be triggered (when the data changes)
// If validation fails when filling data, the custom success callback function will not be called
if(!model.set(model.parse(resp, xhr), options))
return false;
//Call the custom success callback function
if(success)
success(model, resp);
};
// Handle the error event through wrapError when an error occurs in the request
options.error = Backbone.wrapError(options.error, model, options);
// Call the sync method to get data from the server
return (this.sync || Backbone.sync).call(this, 'read', this, options);
},
//Save the data in the model to the server
save : function(key, value, options) {
// attrs stores the data objects that need to be saved to the server
var attrs, current;
//Supports setting a single attribute key: value
// Support batch setting method in object form {key: value}
if(_.isObject(key) || key == null) {
// If key is an object, it is considered to be set through the object method
// At this time the second parameter is considered options
attrs = key;
options = value;
}else {
// If a single attribute is set in the form of key: value, set attrs directly
attrs = {};
attrs[key] = value;
}
// The configuration object must be a new object
options = options ? _.clone(options) : {};
// If the wait option is set in options, the changed data will be verified in advance, and when the server does not respond to the new data (or the response fails), the local data will be restored to the state before modification.
// If the wait option is not set, the local data will be modified to the latest status regardless of whether the server is set successfully.
if(options.wait) {
// Verify the data that needs to be saved in advance
if(!this._validate(attrs, options))
return false;
//Record the data in the current model, used to restore the data after sending it to the server
// If the server response fails or no data is returned, the state before modification can be maintained
current = _.clone(this.attributes);
}
// silentOptions adds silent to the options object (no data verification)
// Use the silentOptions configuration item when using the wait parameter, because the data has been verified above
// If the wait parameter is not set, the original options configuration items are still used
var silentOptions = _.extend({}, options, {
silent : true
});
// Save the latest modified data to the model, so that the model data can be obtained in the sync method and saved to the server.
if(attrs && !this.set(attrs, options.wait ? silentOptions : options)) {
return false;
}
var model = this;
// In options, you can specify a custom callback function after successfully saving the data.
var success = options.success;
//Execute success after the server responds successfully
options.success = function(resp, status, xhr) {
// Get the latest status data of the server's response
var serverAttrs = model.parse(resp, xhr);
// If the wait parameter is used, the modified data status will be set directly to the model first.
if(options.wait) {
delete options.wait;
serverAttrs = _.extend(attrs || {}, serverAttrs);
}
//Set the latest data status into the model
// If verification fails when calling the set method, the custom success callback function will not be called.
if(!model.set(serverAttrs, options))
return false;
if(success) {
//Call the customized success callback function after the response is successful
success(model, resp);
} else {
// If no custom callback is specified, the sync event is triggered by default
model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options);
}
};
// Handle the error event through wrapError when an error occurs in the request
options.error = Backbone.wrapError(options.error, model, options);
//Save the data in the model to the server
// If the current model is a newly created model (without id), use the create method (new), otherwise it is considered to be the update method (modified)
var method = this.isNew() ? 'create' : 'update';
var xhr = (this.sync || Backbone.sync).call(this, method, this, options);
// If options.wait is set, restore the data to the state before modification
// The saved request has not received a response at this time, so if the response fails, the model will remain in the state before modification. If the server responds successfully, the data in the model will be set to the latest state in success.
if(options.wait)
this.set(current, silentOptions);
return xhr;
},
//Delete the model, the model will be deleted from the Collection to which it belongs.
// If the model is created on the client, delete it directly from the client.
// If the model data exists on the server at the same time, the server-side data will be deleted at the same time.
destroy : function(options) {
// The configuration item must be a new object
options = options ? _.clone(options) : {};
var model = this;
// In options, you can specify a custom callback function after the data is successfully deleted.
var success = options.success;
// Called successfully to delete data, the destroy event is triggered. If the model exists in the Collection, the collection will listen to the destroy event and remove the model from the collection when triggered.
// When deleting a model, the data in the model has not been cleared, but the model has been removed from the collection, so when there is no reference to the model anywhere, it will be automatically released from memory.
// It is recommended to set the reference variable of the model object to null when deleting the model.
var triggerDestroy = function() {
model.trigger('destroy', model, model.collection, options);
};
// If the model is a model newly created by the client, directly call triggerDestroy to remove the model from the collection.
if(this.isNew()) {
triggerDestroy();
return false;
}// When deleting data from the server is successful
options.success = function(resp) {
// If the wait item is configured in the options object, it means that the model data in local memory will be deleted after the server data is successfully deleted.
// If the server response fails, the local data will not be deleted
if(options.wait)
triggerDestroy();
if(success) {
//Call the custom success callback function
success(model, resp);
} else {
// If there is no custom callback, the sync event is triggered by default
model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options);
}
};
// Handle the error event through wrapError when an error occurs in the request
options.error = Backbone.wrapError(options.error, model, options);
//Send a request to delete data through the sync method
var xhr = (this.sync || Backbone.sync).call(this, 'delete', this, options);
// If the wait item is not configured in the options object, the local data will be deleted first, and then a request will be sent to delete the server data.
// At this time, regardless of whether the server deletion is successful or not, the local model data has been deleted.
if(!options.wait)
triggerDestroy();
return xhr;
},
// Get the URL corresponding to the model in the server interface. When calling save, fetch, destroy and other methods to interact with the server, this method will be used to obtain the URL.
// The generated URL is similar to the "PATHINFO" mode. The server only has one URL for model operations. For modification and deletion operations, the model ID will be appended to the URL for easy identification.
// If urlRoot is defined in the model, the server interface should be in the form of [urlRoot/id]
// If the Collection to which the model belongs defines the url method or attribute, use the url form in the collection: [collection.url/id]
// When accessing the server url, the model id will be appended to the url to facilitate the server to identify a record, so the id in the model needs to correspond to the server record.
// If the url of the model or collection cannot be obtained, the urlError method will be called and an exception will be thrown.
// If the server interface is not organized according to "PATHINFO", you can achieve seamless interaction with the server by overloading the url method.
url : function() {
//Define the url path corresponding to the server
var base = getValue(this, 'urlRoot') || getValue(this.collection, 'url') || urlError();
// If the current model is a model newly created by the client, there is no id attribute, and the server url directly uses base.
if(this.isNew())
return base;
// If the current model has an id attribute, the save or destroy method may be called, and the model's id will be appended to the base.
//The following will determine whether the last character of base is "/", and the generated URL format is [base/id]
return base (base.charAt(base.length - 1) == '/' ? '' : '/') encodeURIComponent(this.id);
},
// The parse method is used to parse the data obtained from the server and return a model data that can be parsed by the set method.
// Generally, the parse method will be overloaded based on the data returned by the server in order to build a seamless connection with the server.
// When the data structure returned by the server is inconsistent with the data structure required by the set method (for example, when the server returns XML format data), the parse method can be used for conversion.
parse : function(resp, xhr) {
return resp;
},
// Create a new model with the same data as the current model
clone : function() {
return new this.constructor(this.attributes);
},
// Check whether the current model is a new model created by the client
// The checking method is based on whether the model has an id identifier. The new model created by the client does not have an id identifier.
// Therefore, the model data responded by the server must contain the id identifier. The attribute name of the identifier defaults to "id". You can also customize the identifier by modifying the idAttribute attribute.
isNew : function() {
return this.id == null;
},
// Function that triggers change event binding when data is updated
// When the set method is called, the change method will be called automatically. If the silent configuration is specified when the set method is called, the change method needs to be called manually.
change : function(options) {
// options must be an object
options || ( options = {});
// There are some problems with the logic related to this._changing
// this._changing is set to false at the end of the method, so the value of the changing variable above the method is always false (the first time is undefined)
// The author's original intention should be to use this variable to indicate whether the change method has been executed. It is meaningless for single-threaded scripts on the browser side because this method will block other scripts when executed.
// changing gets the status of the last execution. If the last script has not been executed, the value is true.
var changing = this._changing;
//Start executing the flag. The value is always true during execution. After execution, this._changing is modified to false.
this._changing = true;
//Add data status other than this change to the _pending object
for(var attr in this._silent)
this._pending[attr] = true;
// The changes object contains all the data that has been changed since the last time the change event was executed on the current data.
// If the change event was not triggered by using silent before, it will be placed in the changes object this time.
var changes = _.extend({}, options.changes, this._silent);
//Reset _silent object
this._silent = {};
// Traverse the changes object and trigger separate change events for each attribute.
for(var attr in changes) {
// Pass the Model object, attribute values, and configuration items as parameters to the event listening function
this.trigger('change:' attr, this, this.get(attr), options);
}
//If the method is executing, stop execution
if(changing)
return this;
// Trigger the change event. After any data is changed, the "change:property" event and "change" event will be triggered in sequence.
while(!_.isEmpty(this._pending)) {
this._pending = {};
// Trigger the change event, and pass the Model instance and configuration items as parameters to the listening function
this.trigger('change', this, options);
// Traverse the data in the changed object, and remove the status of the changed data from changed in turn
// After this, if you call hasChanged to check the data status, you will get false (unchanged)
for(var attr in this.changed) {
if(this._pending[attr] || this._silent[attr])
continue;
//Remove the status of the data in changed
delete this.changed[attr];
}
// After the change event is executed, the _previousAttributes attribute will record the latest data copy of the current model
// Therefore, if you need to get the previous state of the data, you can usually only get it through the previous or previousAttributes method in the triggered change event.
this._previousAttributes = _.clone(this.attributes);
}
//Execution completed flag
this._changing = false;
return this;
},
// Check whether a certain data has been changed since the last change event was executed
/*** Generally used in conjunction with the previous or previousAttributes method in the change event, such as:
* if(model.hasChanged('attr')) {
* var attrPrev = model.previous('attr');
* }*/
hasChanged : function(attr) {
if(!arguments.length)
return !_.isEmpty(this.changed);
return _.has(this.changed, attr);
},
// Get the data collection in the current model and the data that has changed in the last data
// (Generally, the change method is not called when using the silent attribute, so the data will be temporarily stored in the changed attribute. The last data can be obtained through the previousAttributes method)
// If a diff set is passed, the last model data will be compared with the data in the diff set, and an inconsistent data set will be returned.
// If there is no difference in the comparison result, return false
changedAttributes : function(diff) {
// If diff is not specified, the data collection of the current model that has changed from the previous state will be returned. These data have been stored in the changed attribute, so a copy of the changed collection is returned.
if(!diff)
return this.hasChanged() ? _.clone(this.changed) : false;
// The diff set that needs to be compared is specified, and the comparison result between the last data and the diff set will be returned.
//The old variable stores the model data of the previous state
var val, changed = false, old = this._previousAttributes;
// Traverse the diff collection and compare each item with the collection of previous states
for(var attr in diff) {
// Temporarily store data with inconsistent comparison results into the changed variable
if(_.isEqual(old[attr], ( val = diff[attr])))
continue;
(changed || (changed = {}))[attr] = val;
}
// Return the comparison result
return changed;
},
// In the change event triggered by the model, obtain the data of the previous state before an attribute was changed, which is generally used for data comparison or rollback.
// This method is generally called in the change event. After the change event is triggered, the _previousAttributes attribute stores the latest data.
previous : function(attr) {
// attr specifies the attribute name that needs to get the previous state
if(!arguments.length || !this._previousAttributes)
return null;
return this._previousAttributes[attr];
},
// When the model triggers the change event, obtain the data collection of the previous state of all attributes
// This method is similar to the previous() method. It is generally called in the change event and is used for data comparison or rollback.
previousAttributes : function() {
// Clone the data object of the previous state into a new object and return
return _.clone(this._previousAttributes);
},
// Check if the model is currently in a valid state. It's only possible to
// get into an *invalid* state if you're using silent changes.
// Verify whether the data in the current model can be verified by the validate method. Please make sure the validate method is defined before calling.
isValid : function() {
return !this.validate(this.attributes);
},
// Data verification method is automatically executed when calling set, save, add and other data update methods.
// Failure in verification will trigger the "error" event of the model object. If an error processing function is specified in options, only the options.error function will be executed.
// @param {Object} attrs attributes of the data model, which stores the objectized data of the model
// @param {Object} options configuration items
// @return {Boolean} Returns true if the verification passes, false if it fails.
_validate : function(attrs, options) {
// If the options.silent attribute is set when calling set, save, add and other data update methods, verification is ignored
// If the validate method is not added to the Model, validation is ignored
if(options.silent || !this.validate)
return true;
// Get all attribute values in the object and put them into the validate method for verification
//The validate method contains two parameters, which are the data collection and configuration object in the model. If the validation passes, no data will be returned (the default is undefined). If the validation fails, data with error information will be returned.
attrs = _.extend({}, this.attributes, attrs);
var error = this.validate(attrs, options);
//Verification passed
if(!error)
return true;
// Verification failed
// If the error error handling method is set in the configuration object, call this method and pass the error data and configuration object to this method
if(options && options.error) {
options.error(this, error, options);
} else {
// If an error event listener is bound to the model, the binding event will be triggered.
this.trigger('error', this, error, options);
}
//Return verification failed identification
return false;
}
});
// Backbone.Collection data model collection related
//------------------
// Collection stores a series of data models of the same class and provides related methods to operate the models
var Collection = Backbone.Collection = function(models, options) {
//Configuration object
options || ( options = {});
//Set the model class of the collection in the configuration parameters
if(options.model)
this.model = options.model;
// If the comparator attribute is set, the data in the collection will be sorted according to the sorting algorithm in the comparator method (it will be automatically called in the add method)
if(options.comparator)
this.comparator = options.comparator;
//Reset the internal state of the collection when instantiated (the first call can be understood as the definition state)
this._reset();
// Call the custom initialization method. If necessary, the initialize method will generally be overloaded.
this.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
// If models data is specified, call the reset method to add the data to the collection.
// The silent parameter is set when called for the first time, so the "reset" event will not be triggered.
if(models)
this.reset(models, {
silent : true,
parse : options.parse
});
};
// Define the collection class prototype method through the extend method
_.extend(Collection.prototype, Events, {
// Define the model class of the collection. The model class must be a subclass of Backbone.Model
// When using collection-related methods (such as add, create, etc.), data objects are allowed to be passed in. The collection method will automatically create the corresponding instance according to the defined model class.
//The data models stored in the collection should all be instances of the same model class
model : Model,
// Initialization method, this method is automatically called after the collection instance is created
// This method is generally overloaded when defining the collection class
initialize : function() {
},
// Return an array containing the data objects of each model in the collection
toJSON : function(options) {
// Use Undersocre's map method to form an array of toJSON results for each model in the collection, and return
return this.map(function(model) {
// Call the toJSON method of each model object in turn. This method will return the model's data object (copied copy) by default.
// If you need to return a string or other forms, you can overload the toJSON method
return model.toJSON(options);
});
},
//Add one or more model objects to the collection
// The "add" event will be triggered by default. If the silent attribute is set in options, this event triggering can be turned off.
// The models passed in can be one or a series of model objects (instances of the Model class). If the model attribute is set in the collection, data objects (such as {name: 'test'}) are allowed to be passed in directly. Automatically instantiate the data object into the model object pointed to by model
add : function(models, options) {
//Local variable definition
var i, index, length, model, cid, id, cids = {}, ids = {}, dups = [];
options || ( options = {});
// models must be an array, if only one model is passed in, convert it to an array
models = _.isArray(models) ? models.slice() : [models];
// Traverse the list of models that need to be added. During the traversal process, the following operations will be performed:
// - Convert data object to model object
// - Establish a reference between the model and the collection
// - Log invalid and duplicate models and filter them later
for( i = 0, length = models.length; i
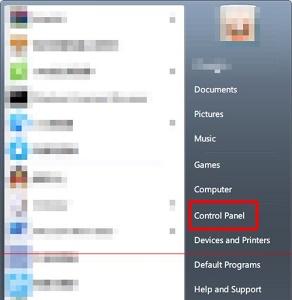 如何将windows 7的语言设置为中文Dec 21, 2023 pm 10:07 PM
如何将windows 7的语言设置为中文Dec 21, 2023 pm 10:07 PM有些朋友可能会在安装系统时不小心设置成了英文,结果所有界面都变成了英文,看都看不懂。其实我们可以在控制面板中设置语言,将语言更改为中文,下面就一起来看一下更改的方法吧。win7如何更改语言为中文1、首先点击屏幕左下角的按钮,然后选择“ControlPanel”2、找到“Clock,Language,andRegion”下的“Changedispalylanguage”3、点击下方“English”就可以在下拉菜单中选择简体中文了。4、确定之后点击“Logoffnow”注销并重启电脑。5、回来之后
 放弃中国市场?《万智牌》官宣:今后不再推出中文实体卡Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
放弃中国市场?《万智牌》官宣:今后不再推出中文实体卡Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:46 PM2月23日消息,官方威世智今日宣布,自《摩登新篇3》之后将不再生产葡萄牙语版产品,自《Bloomburrow》开始停止生产中文版实体卡牌产品。完整公告如下:万智牌实体卡牌产品语言调整通知万智牌作为一款全球知名游戏,一直深受全球玩家的喜爱。今年,我们遗憾地做出这个艰难的决定:在《摩登新篇3》之后将不再生产葡萄牙语版产品,自《Bloomburrow》开始停止生产中文版实体卡牌产品。我们深知这对热爱万智牌的中国和葡萄牙玩家是一次重大的变化,但这一决策并不是对玩家热情的否定。请大家相信,我们将继续在这两
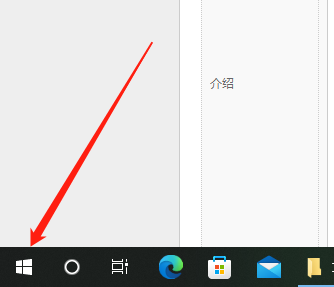 如何将Win10电脑的语言设置为汉语?Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
如何将Win10电脑的语言设置为汉语?Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:51 PM有时候我们再刚刚入手安装好电脑系统之后发现系统时英文的,遇到这种情况我们就需要把电脑的语言改成中文,那么win10系统里面该怎么把电脑的语言改成中文呢,现在就给大家带来具体的操作方法。win10电脑语言怎么改成中文1、打开电脑点击左下角的开始按键。2、点击左侧的设置选项。3、打开的页面选择“时间和语言”4、打开后,再点击左侧的“语言”5、在这里就可以设置你要的电脑语言。
 怎么将eclipse语言设置为中文Jan 04, 2023 pm 03:50 PM
怎么将eclipse语言设置为中文Jan 04, 2023 pm 03:50 PMeclipse语言设置为中文的方法:1、打开浏览器找到语言包下载地址,并将最新的安装包地址复制;2、打开eclipse,点击“help”,然后点击安装新的插件;3、点击“Add”,在Location中粘帖网址;4、在下拉菜单中找到简体中文包,进行勾选,点击Next等待安装;5、重启eclipse即可。
 Win11系统语言如何改成中文Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Win11系统语言如何改成中文Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:15 PMWin11系统语言如何改成中文?近期有用户刚给电脑安装了最新的Win11系统,但是在使用中发现系统语言为英文,自己使用起来很吃力,为此有没有什么方法可以将系统语言改成中文呢?方法很简单,下面我们来看看这篇Win11系统语言设置为中文的方法吧。 Win11系统语言设置为中文的步骤 1、首先我们进入齿轮按钮的settings,然后找到其中的Time打开时间和语言。 2、在时间和语言中点击左边栏的Language选项,然后在右侧点击Addalanguage。 3、接着在上方搜索框输入chi
 正确在matplotlib中显示中文字符的方法Jan 13, 2024 am 11:03 AM
正确在matplotlib中显示中文字符的方法Jan 13, 2024 am 11:03 AM在matplotlib中正确地显示中文字符,是很多中文用户常常遇到的问题。默认情况下,matplotlib使用的是英文字体,无法正确显示中文字符。为了解决这个问题,我们需要设置正确的中文字体,并将其应用到matplotlib中。下面是一些具体的代码示例,帮助你正确地在matplotlib中显示中文字符。首先,我们需要导入需要的库:importmatplot
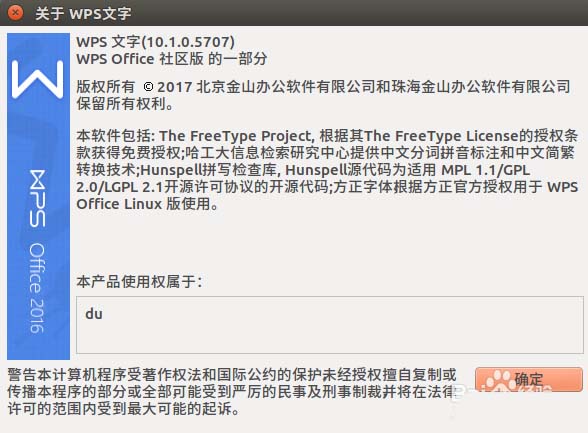 解决Ubuntu系统中WPS无法输入中文的问题该做什么?Dec 30, 2023 pm 12:55 PM
解决Ubuntu系统中WPS无法输入中文的问题该做什么?Dec 30, 2023 pm 12:55 PM虽然Linux有LibreOffice,但是对微软的office兼容不是很好,有些排版会出现问题。而几年前,金山也开发了Linux版的WPS,不过在Ubuntu上使用,无法直接输入中文,这咋弄才可以让WPS正常输入中文呢1、打开WPS的文档,右上角的输入法已经是中文了,但是实际输入的时候,只能输入英文字母,出不了中文2、在终端输入:sudogedit/usr/bin/wps3、从第二行加上:exportXMODIFIERS="@im=fcitx"exportQT_IM_MODULE=&
 解决中文乱码问题的matplotlib方法Jan 13, 2024 pm 02:49 PM
解决中文乱码问题的matplotlib方法Jan 13, 2024 pm 02:49 PM解决matplotlib中文乱码问题的方法,需要具体代码示例Matplotlib是一个常用的用于数据可视化的Python库,可以生成各种图表和图形。然而,对于中文用户来说,经常会遇到一个问题,就是生成的图表中的中文字符显示乱码。这个问题可以通过一些简单的方法来解决。本文将介绍一些常见的解决方法,并附上相关的代码示例,帮助读者解决这个烦人的问题。方法一:设置字


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software





