
Configuration Practice Guide for Spring Boot and MyBatis
Introduction:
Spring Boot is a rapid development framework used to simplify the startup and deployment process of Spring applications . And MyBatis is a popular persistence framework that can easily interact with various relational databases. This article will introduce how to configure and use MyBatis in a Spring Boot project and provide specific code examples.
1. Project configuration
1.Introduce dependencies
In the pom.xml file, add the following dependencies:
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MyBatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库驱动(例如,MySQL)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.Configure database connection
Inapplication.properties file, configure database connection information. For example, if you use a MySQL database, you can add the following configuration:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2. Create the entity class
1. Create the entity class
in the com.example.demo.entity package , create an entity class named User:
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
// 省略 getters 和 setters
}2. Create Mapper interface
In the com.example.demo.mapper package, create An interface named UserMapper:
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> getAllUsers();
User getUserById(int id);
void addUser(User user);
void updateUser(User user);
void deleteUser(int id);
} 3. Create Mapper XML file
Create UserMapper corresponding Mapper XML file UserMapper.xml, and configure the corresponding SQL operations:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.demo.entity.User">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAllUsers" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id=#{id}
</select>
<insert id="addUser">
INSERT INTO user(name, email) VALUES (#{name}, #{email})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser">
UPDATE user SET name=#{name}, email=#{email} WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser">
DELETE FROM user WHERE id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>4. Configure MyBatis
1. Create a configuration class
In the com.example.demo.config package, create a Configuration class named MyBatisConfig:
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.example.demo.mapper")
public class MyBatisConfig {
}2. Complete the configuration
In the application.properties file, add the following configuration:
# MyBatis mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath*:com/example/demo/mapper/*.xml
So far, we have completed the configuration and preparation of the project. Next, we will learn how to use MyBatis in a Spring Boot project.
5. Using MyBatis
1. Write business logic
In the com.example.demo.service package, create a service named UserService Class:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userMapper.getAllUsers();
}
public User getUserById(int id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
public void addUser(User user) {
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
userMapper.updateUser(user);
}
public void deleteUser(int id) {
userMapper.deleteUser(id);
}
}2. Create a controller
In the com.example.demo.controller package, create a controller class named UserController:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("")
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable int id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@PostMapping("")
public void addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
userService.addUser(user);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public void updateUser(@PathVariable int id, @RequestBody User user) {
user.setId(id);
userService.updateUser(user);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable int id) {
userService.deleteUser(id);
}
}3. Test API
Start the Spring Boot application, visit the following URL in the browser, test the API:
- Get all users: http://localhost:8080 /users
- Get a single user: http://localhost:8080/users/{id}
- Add a user: POST http://localhost:8080/users, the request body is in JSON format User object
- Update user: PUT http://localhost:8080/users/{id}, the request body is a user object in JSON format
- Delete user: DELETE http://localhost :8080/users/{id}
Summary:
This article introduces the configuration practice method of using MyBatis in the Spring Boot project and provides specific code examples. I hope this article can help readers quickly understand and use the combination of Spring Boot and MyBatis to develop Spring applications more efficiently.
The above is the detailed content of Spring Boot and MyBatis Configuration Tips Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Java之Mybatis的二级缓存怎么使用May 24, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
Java之Mybatis的二级缓存怎么使用May 24, 2023 pm 06:16 PM缓存的概述和分类概述缓存就是一块内存空间.保存临时数据为什么使用缓存将数据源(数据库或者文件)中的数据读取出来存放到缓存中,再次获取的时候,直接从缓存中获取,可以减少和数据库交互的次数,这样可以提升程序的性能!缓存的适用情况适用于缓存的:经常查询但不经常修改的(eg:省市,类别数据),数据的正确与否对最终结果影响不大的不适用缓存的:经常改变的数据,敏感数据(例如:股市的牌价,银行的汇率,银行卡里面的钱)等等MyBatis缓存类别一级缓存:它是sqlSession对象的缓存,自带的(不需要配置)不
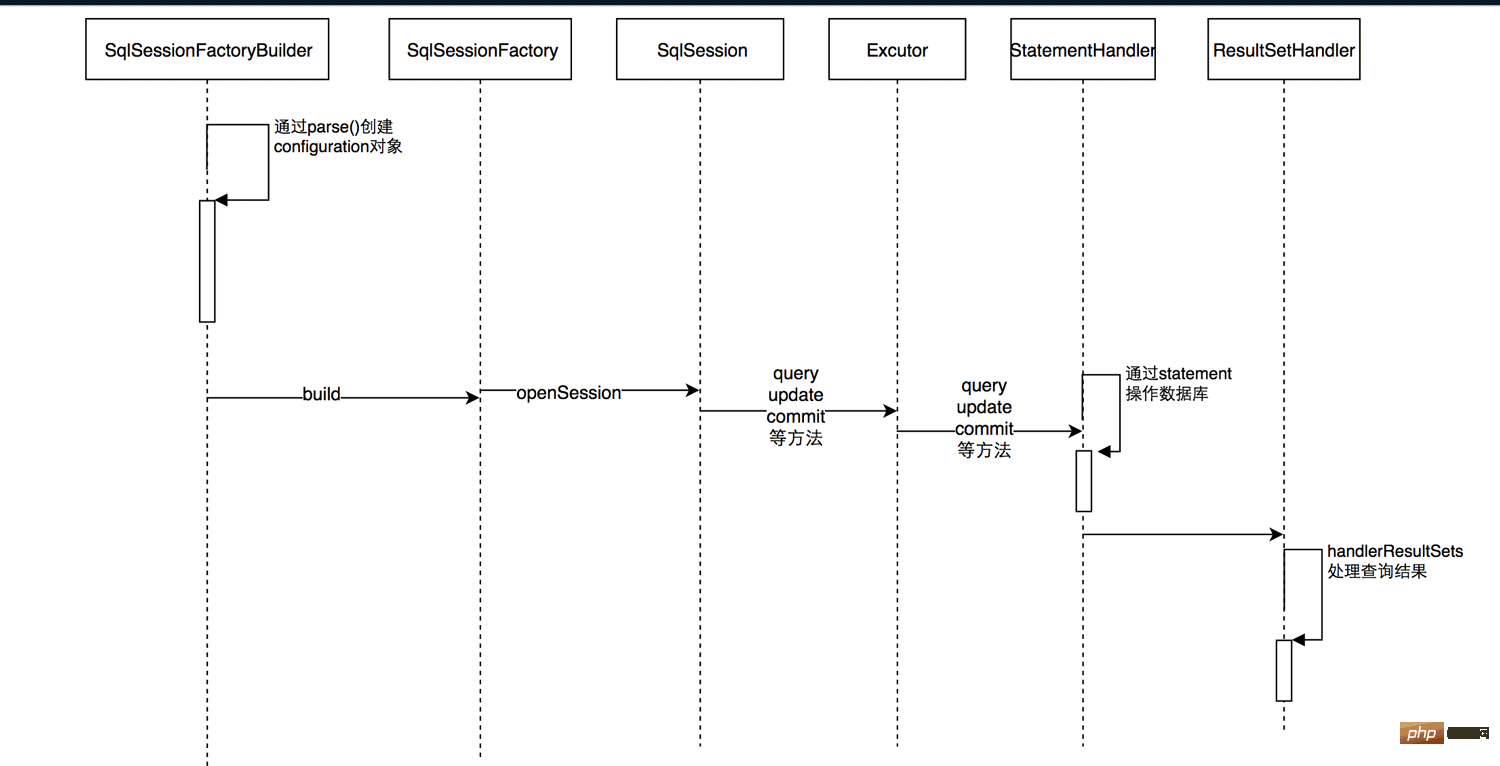 怎么使用springboot+mybatis拦截器实现水平分表May 14, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
怎么使用springboot+mybatis拦截器实现水平分表May 14, 2023 pm 06:43 PMMyBatis允许使用插件来拦截的方法Executor(update,query,flushStatements,commit,rollback,getTransaction,close,isClosed)ParameterHandler(getParameterObject,setParameters)ResultSetHandler(handleResultSets,handleOutputParameters)StatementHandler(prepare,parameterize,ba
 mybatis分页的几种方式Jan 04, 2023 pm 04:23 PM
mybatis分页的几种方式Jan 04, 2023 pm 04:23 PMmybatis分页的方式:1、借助数组进行分页,首先查询出全部数据,然后再list中截取需要的部分。2、借助Sql语句进行分页,在sql语句后面添加limit分页语句即可。3、利用拦截器分页,通过拦截器给sql语句末尾加上limit语句来分页查询。4、利用RowBounds实现分页,需要一次获取所有符合条件的数据,然后在内存中对大数据进行操作即可实现分页效果。
 怎么用springboot+mybatis plus实现树形结构查询May 21, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
怎么用springboot+mybatis plus实现树形结构查询May 21, 2023 pm 05:01 PM背景实际开发过程中经常需要查询节点树,根据指定节点获取子节点列表,以下记录了获取节点树的操作,以备不时之需。使用场景可以用于系统部门组织机构、商品分类、城市关系等带有层级关系的数据结构;设计思路递归模型即根节点、枝干节点、叶子节点,数据模型如下:idcodenameparent_code110000电脑0220000手机0310001联想笔记本10000410002惠普笔记本1000051000101联想拯救者1000161000102联想小新系列10001实现代码表结构CREATETABLE`
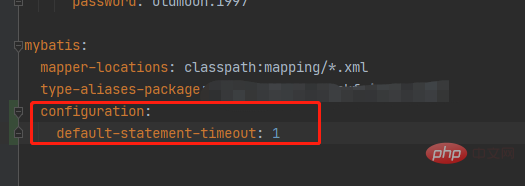 springboot配置mybatis的sql执行超时时间怎么解决May 15, 2023 pm 06:10 PM
springboot配置mybatis的sql执行超时时间怎么解决May 15, 2023 pm 06:10 PM当某些sql因为不知名原因堵塞时,为了不影响后台服务运行,想要给sql增加执行时间限制,超时后就抛异常,保证后台线程不会因为sql堵塞而堵塞。一、yml全局配置单数据源可以,多数据源时会失效二、java配置类配置成功抛出超时异常。importcom.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;importcom.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;importorg.apache.
 springboot怎么整合mybatis分页拦截器May 13, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
springboot怎么整合mybatis分页拦截器May 13, 2023 pm 04:31 PM简介今天开发时想将自己写好的代码拿来优化,因为不想在开发服弄,怕搞坏了到时候GIT到生产服一大堆问题,然后把它分离到我轮子(工具)项目上,最后运行后发现我获取List的时候很卡至少10秒,我惊了平时也就我的正常版本是800ms左右(不要看它很久,因为数据量很大,也很正常。),前提是我也知道很慢,就等的确需要优化时,我在放出我优化的plus版本,回到10秒哪里,最开始我刚刚接到这个app项目时,在我用PageHelper.startPage(page,num);(分页),还没等查到的数据封装(Pa
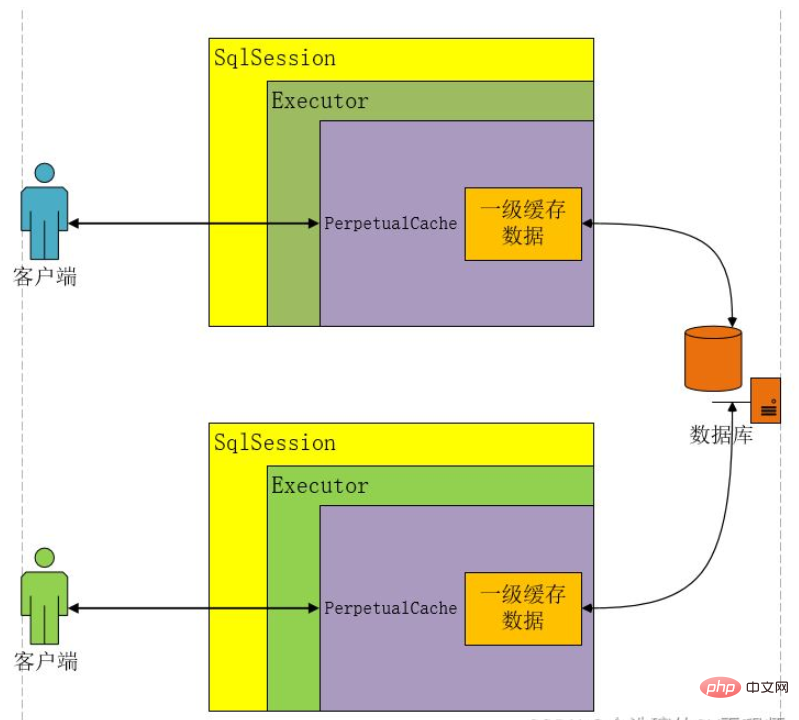 Java Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存是什么Apr 25, 2023 pm 02:10 PM
Java Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存是什么Apr 25, 2023 pm 02:10 PM一、什么是缓存缓存是内存当中一块存储数据的区域,目的是提高查询效率。MyBatis会将查询结果存储在缓存当中,当下次执行相同的SQL时不访问数据库,而是直接从缓存中获取结果,从而减少服务器的压力。什么是缓存?存在于内存中的一块数据。缓存有什么作用?减少程序和数据库的交互,提高查询效率,降低服务器和数据库的压力。什么样的数据使用缓存?经常查询但不常改变的,改变后对结果影响不大的数据。MyBatis缓存分为哪几类?一级缓存和二级缓存如何判断两次Sql是相同的?查询的Sql语句相同传递的参数值相同对结
 PageHelper在springboot+mybatis框架中如何使用May 12, 2023 pm 03:55 PM
PageHelper在springboot+mybatis框架中如何使用May 12, 2023 pm 03:55 PM一、思路将分页所需的内容都放到一个实体类中分页数据所需要的实体类!内包含页码,页大小,总条数,总页数,起始行pagehelpr提供了这个类pageInfo,不需要我们自己创建二、主要逻辑select*from表名limit起始行,展示几条数据#第n页每页展示五条数据select*from表名limit(n-1)*5,5#每页展示多少条pageSize3#总共有多少条totalselectcount(*)from表名#总页数pagespages=total%pagesSize==0?total/p


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools






