Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >How to run terminal commands efficiently in Linux
How to run terminal commands efficiently in Linux
- PHPzforward
- 2024-02-15 13:00:18892browse
Linux Terminal is a powerful tool that allows you to perform various system operations using commands. File operations, program management, and service automation are all operations that can be performed efficiently using shell commands.
However, when multiple operations need to be performed, running commands one by one is not efficient. A faster way is to chain multiple commands in one line. Not only does this speed up the process, it also saves you time.
Let’s explore all the ways to run multiple commands at once in Linux.
Run multiple Linux commands at once
Linux uses three operators to help you execute multiple commands in one line:
-
Semicolon (;) Operator
-
Logical OR (||) operator
-
logic
AND (&&) operator
All these operators can run two or more shell commands simultaneously. However, knowing which operators to use and when can help you create commands more efficiently. The following sections discuss the purpose and syntax of using these operators correctly:
1. Use the semicolon (;) operator
Using semicolons to segment command chains is the most common practice for running multiple commands in a Linux terminal. Part of this is due to the way the operator is executed: it runs all commands in the sequence regardless of whether the previous command ran successfully.
For example, if there are two commands: command A and command B, using the semicolon operator between them ensures that the two commands are executed in order regardless of the output of the first command.
command A ; command B
So if you need to run two or more unrelated terminal commands simultaneously so that the output status of the first command does not affect the execution of the latter, the semicolon operator is the way to go.
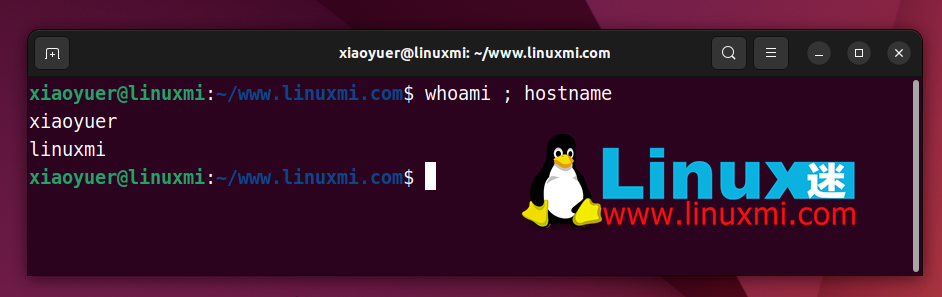
Example use case: If you want to view the name of the current user and the system host name, you can use:
xiaoyuer@linuxmi: ~/www.linuxmi.com$ whoami ; hostnamexiaoyuerlinuxmi
Remember that the shell executes these commands in the exact order you mention them. The output looks like this:
2. Use the OR (||) operator
The definition of the word "or" is a giveaway here: when you run two commands using the OR operator, you tell the shell to execute only one of the two commands.
Suppose you use the OR operator with two commands: Command A and Command B. Here's what the concatenated command looks like using the OR operator:
command A || command B
Here, command B is executed only when command A fails, i.e. when command A returns an error. Likewise, if command A runs successfully, command B will not execute.
Talking about its use case, when you need to run two related commands at the same time, you can use the OR operator so that the shell only executes the next command if the previous command fails.
Example use case: Suppose you want to create a new file, say Document.txt, but before doing so, you need to make sure that the file does not already exist in the current directory. In this case, you can run the commands in the following order:
xiaoyuer@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ find . -name linuxmi.txt || touch linuxmi.txtxiaoyuer@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$
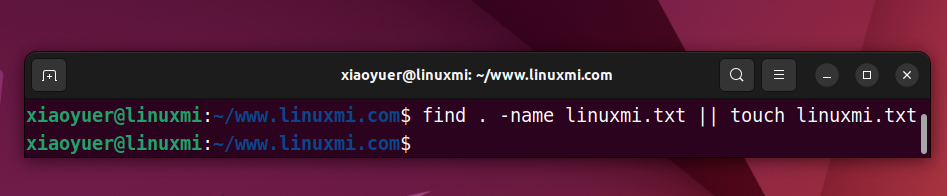
Here, the find command will find the current working directory for the linux.txt file. If the file is found, command progress will stop and the second command will not run.
On the other hand, if the file is not found, the command on the right will be executed and a new file named linux.txt will be created in the current working directory.
3. Use the AND (&&) operator
As you may have guessed, the AND operator allows you to run multiple commands sequentially, i.e. it only executes the next command in the sequence if the previous command ran successfully.
为了更好地理解这一点,请考虑这样一个场景:您希望运行两个相关命令,以便仅当第一个命令返回有效输出时才运行第二个命令。在这种情况下,您可以使用 AND 运算符(称为 &&)将命令绑定在一起,以获得所需的结果。
示例用例:在 Linux 中,AND 运算符最常见的用例之一是创建一个新目录并立即进入该目录。这样,您就不必分别运行这两个命令来执行操作。
在本指南中,假设您要创建一个名为“linuxmi”的新目录,并立即将当前工作目录更改为该目录。这是你可以做到的:
xiaoyuer@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ mkdir linuxmi && cd linuxmixiaoyuer@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com/linuxmi$
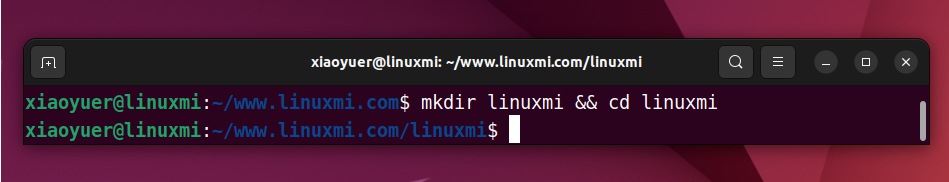
在这里,mkdir 命令将在当前工作目录中创建一个名为 linuxmi 的新目录。如果成功,它将允许执行 cd 命令。
组合多个运算符以满足您的执行标准
除了在命令中单独使用运算符外,还可以对多个运算符进行分组以满足执行条件。当您想要执行满足多个条件的命令时,这会派上用场。
例如,假设您希望仅在命令 A 失败时才执行两个命令(命令 B 和命令 C)。为此,您需要使用运算符,如下面的符号所示:
command A || command B && command C
示例用例:假设您要确定当前工作目录中是否存在文件夹(名为 linuxmi),如果不存在,则创建该文件夹。
在这种情况下,您可以一起使用 OR 和 AND 运算符来有效地执行整个操作,而不是运行单独的命令来查找目录并创建新目录。
就是这样子:
find . -name linuxmi1 || echo "目录未找到" && mkdir linuxmi
在此命令中,find 要求 shell 在当前工作目录中搜索名为 Document 的文件夹。如果该目录不存在,终端会将流传输到 echo 和 mkdir 命令,这些命令分别打印指定的字符串并创建新文件夹。
使用 shell 脚本一次运行多个命令
shell 脚本是一个程序,可让您一次自动执行一系列命令。它消除了在 Linux 终端中键入多个命令的需要,并节省了时间和精力。
只需创建一个脚本,其中包含频繁运行所需的所有命令,并将其转换为可执行文件。然后,在您需要执行这些命令时运行它,它将为您完成所有操作。
首先创建一个新文件,然后键入要立即执行的命令。使用适当的名称保存文件,并在末尾添加“.sh”扩展名。
现在,打开终端并导航到保存脚本的文件夹。运行以下命令以使文件可执行:
chmod +x linuxmi.sh
完成后,下次需要再次执行这些命令时,请转到终端中包含脚本文件的文件夹并像这样执行它:
./linuxmi.sh
您可以使用它的一个应用程序是系统更新。与其在每次要更新系统时在终端中手动键入和执行 sudo apt update 和 sudo apt upgrade 命令,不如创建一个脚本来自动为您运行命令。
只需使用以下命令创建一个脚本文件,然后按照上面演示的其余步骤操作:
#!/bin/bash sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
在 Linux 中高效运行终端命令
如您所见,在命令中使用运算符可以简化大多数命令行操作。
如果您希望通过终端在计算机上执行不同的系统操作,了解如何使用这些运算符将非常有帮助,并帮助您有效地运行 Linux 命令。
同样,如果您刚刚开始(或者不太熟悉)Linux,那么学习不同的终端命令是掌握命令行界面的又一步。
The above is the detailed content of How to run terminal commands efficiently in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

