CentOS installation G and CentOS installation GaussDB
php editor Xigua brings you detailed tutorials on installing G on CentOS and installing GaussDB on CentOS. CentOS is a popular Linux operating system, and GaussDB is a powerful relational database management system. This article will introduce how to install G software and GaussDB on CentOS systems, and provide detailed steps and operation guides. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced user, you can easily complete the installation process by following this guide. Let’s take a look!

CentOS installation G
G is a keyword representing various software and tools that can be installed on CentOS. Installing G on CentOS can help users Quickly get the software and tools you need to improve work efficiency. Here are the steps to install G on CentOS:
1. Open a terminal and log in as the root user.
2. Enter the following command to install the G package manager:
sudo yum install epel-release3. Install the main components of G:
sudo yum install G4. After the installation is complete, you can use G to search and install various software and tools. To install a software named example, you can use the following command:
sudo G install exampleCentOS installation GaussDB
GaussDB is a popular database management system that can be installed and used on CentOS. The following are the steps to install GaussDB on CentOS:
2. Enter the following command to install the GaussDB dependencies:
sudo yum install -y libaio3. Download the GaussDB installation package, you can download it from the GaussDB official website or other available Download the installation package from the source of the letter.
4. Unzip the installation package:
tar -zxvf gaussdb.tar.gz5. Enter the decompressed directory:
cd gaussdb6. Run the installation program:
./install.sh7. The installation program will guide you through the installation process and follow the prompts to make the necessary configuration and settings.
8. After the installation is complete, you can use GaussDB to create and manage databases.
Shared for you
Among the Linux operating systems, CentOS is a very powerful and stable distribution. It not only provides a wide range of software and tools, but also has good compatibility and Performance, by installing G and GaussDB, you can further expand the functionality and application scope of CentOS. I hope this article will help you install G and GaussDB on CentOS.
The above is the detailed content of CentOS installation G and CentOS installation GaussDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
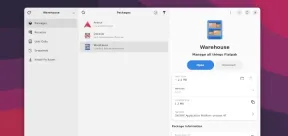 Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AM
Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AMA GUI for Effortless Flatpak Management: Introducing Warehouse Managing a growing collection of Flatpak applications can be cumbersome using only the command line. Enter Warehouse, a user-friendly graphical interface designed to streamline Flatpak a
 8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AM
8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AMThis article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying and resolving hard drive bottlenecks in Linux systems. Experienced server administrators will find this particularly useful. Slow disk operations can severely impact application performance,
 4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AM
4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AMEfficient QR code generation tool under Linux system In today's digital world, QR codes have become a way to quickly and conveniently share information, simplifying data access from URLs, texts, contacts, Wi-Fi credentials, and even payment information. Linux users can use a variety of tools to create QR codes efficiently. Let's take a look at some popular QR code generators that can be used directly on Linux systems. QRencode QRencode is a lightweight command line tool for generating QR codes on Linux. It is well-received for its simplicity and efficiency and is popular with Linux users who prefer direct methods. Using QRencode, you can use the URL,
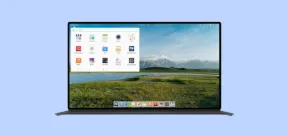 elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AM
elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AMElementary OS 8 Circe: A Smooth and Stylish Linux Experience Elementary OS, a Ubuntu-based Linux distribution, has evolved from a simple theme pack into a fully-fledged, independent operating system. Known for its user-friendly interface, elegant de
 40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AM
40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AMMastering Linux is crucial for any machine learning (ML) engineer. Its command-line interface offers unparalleled flexibility and control, streamlining workflows and boosting productivity. This article outlines essential Linux commands, explained fo
 Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AMArch Linux: A Beginner's Command-Line Cheat Sheet Arch Linux offers unparalleled control but can feel daunting for newcomers. This cheat sheet provides essential commands to confidently manage your system. System Information & Updates These com
 How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AM
How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AMThis guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of installing and using the Scikit-learn machine learning library on Linux systems. Scikit-learn (sklearn) is a powerful, open-source Python library offering a wide array of tools for various machine l
 How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AM
How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AMThis guide explains how to leverage Docker for accessing Kali Linux tools, a safer and more efficient alternative to outdated methods like Katoolin. Katoolin is no longer actively maintained and may cause compatibility problems on modern systems. Do


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)







