Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >No longer be afraid of the chmod command, let Linux permission management no longer become your nightmare!
No longer be afraid of the chmod command, let Linux permission management no longer become your nightmare!
- PHPzforward
- 2024-02-12 09:24:151138browse
If you are a Linux system administrator or developer, then you will definitely encounter file permission problems. In Linux, file permissions can be set and modified through the chmod command, but the use of this command is quite complicated, which brings a lot of trouble to many beginners. Today, we will take an in-depth look at the chmod command so that Linux permission management will no longer be your nightmare.
For directories, the function of the execution bit is to control whether to enter or pass the directory, not to control whether to list its contents. The combination of the read bit and the execute bit controls whether the contents of the directory are listed. The combination of the write bit and the execute bit allows the creation, deletion, and renaming of files in the directory.
The following uses examples to illustrate the problem: the main command is chmod
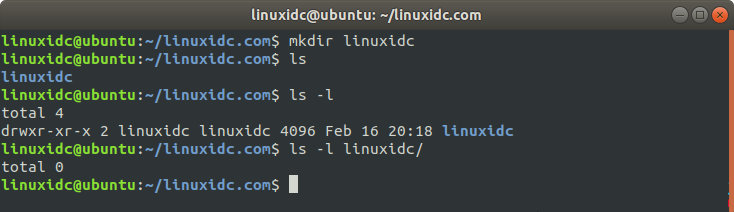
Ordinary users create the folder linuxidc, the default permission is 775
linuxidc@Ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ mkdir linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 drwxr-xr-x 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:18 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ total 0
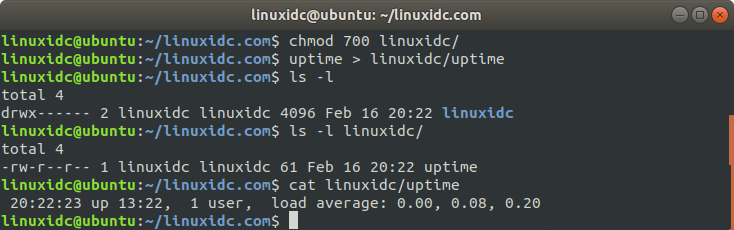
Change the directory permissions to 700, and files can be listed and created in the directory
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 700 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ uptime > linuxidc/uptime linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 drwx------ 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 linuxidc linuxidc 61 Feb 16 20:22 uptime linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cat linuxidc/uptime 20:22:23 up 13:22, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.08, 0.20
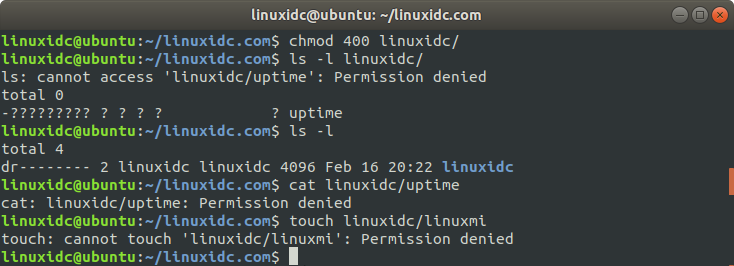
Change the directory permissions to 400. Details cannot be listed in the directory, CAT cannot be used, and files cannot be created
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 400 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ ls: cannot access 'linuxidc/uptime': Permission denied total 0 -????????? ? ? ? ? ? uptime linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 dr-------- 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cat linuxidc/uptime cat: linuxidc/uptime: Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ touch linuxidc/linuxmi touch: cannot touch 'linuxidc/linuxmi': Permission denied
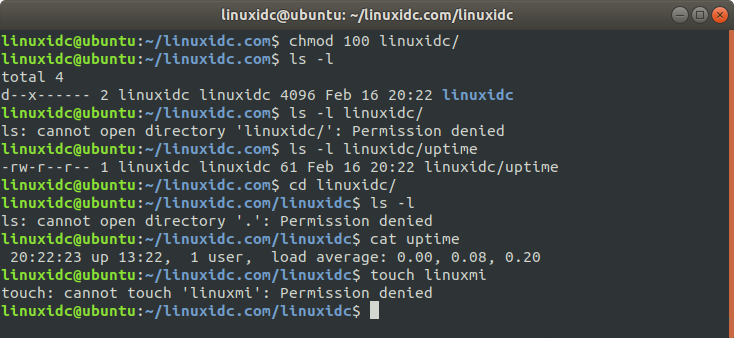
Change the directory permissions to 100, the directory cannot be listed, the directory can be entered, files cannot be created, and files in Cat (of course the permissions of the file must be there, and you know its name, you cannot associate it)
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 100 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 d--x------ 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ ls: cannot open directory 'linuxidc/': Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/uptime -rw-r--r-- 1 linuxidc linuxidc 61 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc/uptime linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cd linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com/linuxidc$ ls -l ls: cannot open directory '.': Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com/linuxidc$ cat uptime 20:22:23 up 13:22, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.08, 0.20 linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com/linuxidc$ touch linuxmi touch: cannot touch 'linuxmi': Permission denied
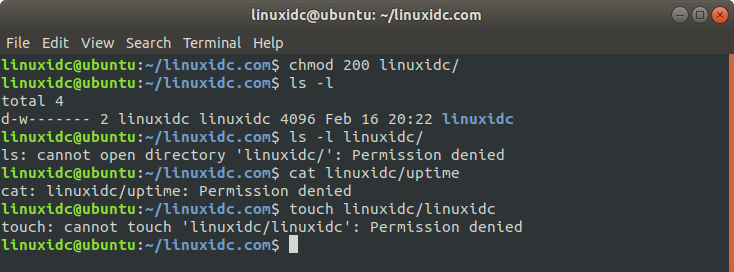
Change the directory permissions to 200. Listing, CAT, and file creation are not allowed in the directory.
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 200 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 d-w------- 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ ls: cannot open directory 'linuxidc/': Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cat linuxidc/uptime cat: linuxidc/uptime: Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ touch linuxidc/linuxidc touch: cannot touch 'linuxidc/linuxidc': Permission denied
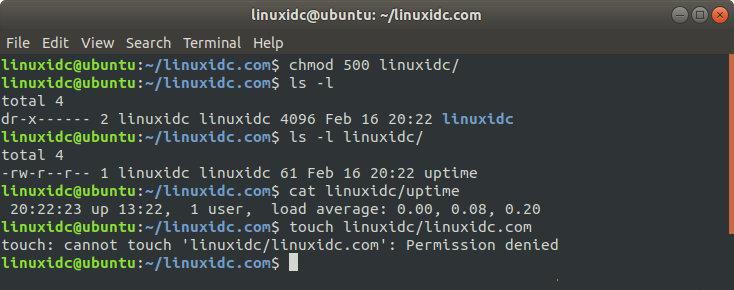
Change the directory permissions to 500, the directory can be listed, CAT can be used, but files cannot be created,
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 500 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 dr-x------ 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 linuxidc linuxidc 61 Feb 16 20:22 uptime linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cat linuxidc/uptime 20:22:23 up 13:22, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.08, 0.20 linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ touch linuxidc/linuxidc.com touch: cannot touch 'linuxidc/linuxidc.com': Permission denied
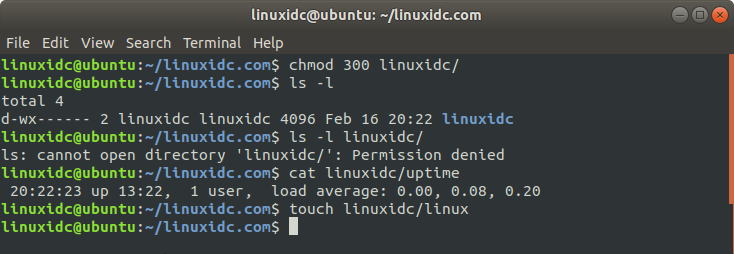
Change the directory permissions to 300, the directory cannot be listed, but CAT (of course the permissions of the file must be there, and you know its name, you cannot associate it), you can create files,
linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ chmod 300 linuxidc/ linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l total 4 d-wx------ 2 linuxidc linuxidc 4096 Feb 16 20:22 linuxidc linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ ls -l linuxidc/ ls: cannot open directory 'linuxidc/': Permission denied linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ cat linuxidc/uptime 20:22:23 up 13:22, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.08, 0.20 linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$ touch linuxidc/linux linuxidc@ubuntu:~/linuxidc.com$
Remarks: 700=rwx, 400=r, 100=x, 200=w, 500=rx, 300=wx
Through the introduction of this article, we have in-depth understanding and study of the commonly used file permission management command chmod in Linux. It provides detailed explanations on command syntax, permission types, digital representation and actual usage scenarios, which I believe will be very helpful for beginners. At the same time, it is recommended that you practice more and combine it with actual operations to deepen your understanding and mastery of file permissions. Correct permission management can ensure the security and stability of the system, and is also an indispensable part of operation and maintenance work!
The above is the detailed content of No longer be afraid of the chmod command, let Linux permission management no longer become your nightmare!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

