Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >Use 'little artifacts' on Linux to extend disk life
Use 'little artifacts' on Linux to extend disk life
- 王林forward
- 2024-02-11 14:30:041348browse
Continuous logging and read/write operations can damage your storage disk. Install Log2Ram on your Linux desktop to extend disk life.
Almost everything a Linux machine does is written to disk as part of a log file. Even if you step away from your keyboard or sleep, dozens of logs are constantly updated, ready for you to search and diagnose problems or optimize processes.
This continued writing may have an impact on the lifespan of the storage media and cause it to wear out faster than it would otherwise. Minimize disk writes by saving your disk and wallet with the Log2Ram app!
How do Linux logs wear out disks?
Logs are a valuable troubleshooting resource on Linux and are used by the system, kernel, boot process, package managers, individual applications, and Xorg. If it's on your system, it may generate log files.
If there is a problem with your Linux computer, or any application behaves abnormally, your first action is to check the relevant log files and see what happened at that time.
You can find most logs in /var/log. This directory usually has dozens of files and subdirectories, and the disk space used can reach tens of GB. Mine also has 4 GB, as shown below
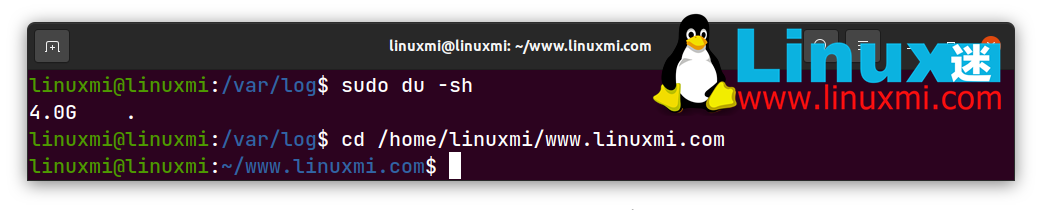
Modern solid-state drives (SSDs) have a limited number of read/write cycles, and the more data written to the disk, the shorter its lifespan becomes. Because Linux is constantly logging everything that happens on the system, these read/write cycles add up faster than they need to be. Buying new hardware for your computer is fun, but not if you're doing it because of a catastrophic drive failure.
Log2Ram How to save your disk
After installing Log2Ram on a Linux computer, the logs are not written directly to disk, but as the name suggests, they are written to RAM.
You can choose to delete the log permanently, write to disk at a set time every day, or write the final version to disk at shutdown.
Especially susceptible to damage due to excessive use.
Install and use Log2Ram on your Linux PC
Before you begin, you should update and upgrade all packages on your system. Open a terminal and enter:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Download the Log2Ram archive and unzip it:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ curl -L https://github.com/azlux/log2ram/archive/master.tar.gz | tar zxf -
Change to the new log2ram directory and make the installation script executable:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ cd log2ram-master linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com/log2ram-master$ chmod +x install.sh
Run the installation script:
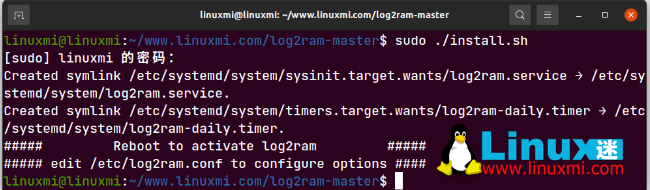
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com/log2ram-master$ sudo ./install.sh [sudo] linuxmi 的密码:
Output example:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/sysinit.target.wants/log2ram.service → /etc/systemd/system/log2ram.service. Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/timers.target.wants/log2ram-daily.timer → /etc/systemd/system/log2ram-daily.timer. ##### Reboot to activate log2ram ##### ##### edit /etc/log2ram.conf to configure options ####
Restart now:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ reboot
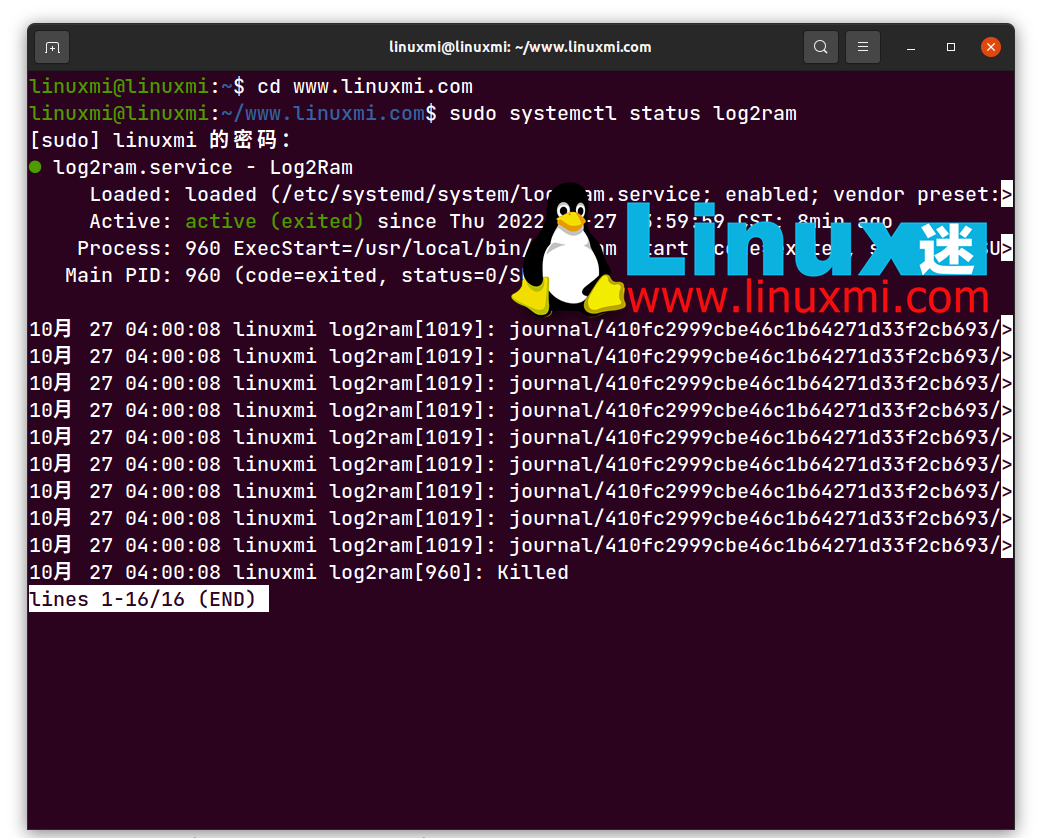
After logging back into the computer, check if log2ram is running:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo systemctl status log2ram
The output is as shown below:
Log 2ram is written to disk every day. If you want to change the frequency, enter:
sudo systemctl edit log2ram-daily.timer
…and edit the timer entry.
If you wish to only write to the log when the system is shut down or rebooted, you can disable the timer completely using the following command:
sudo systemctl disable log2ram-daily.timer
You can configure additional options by editing the log2ram configuration file using nano:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo vim /etc/log2ram.conf
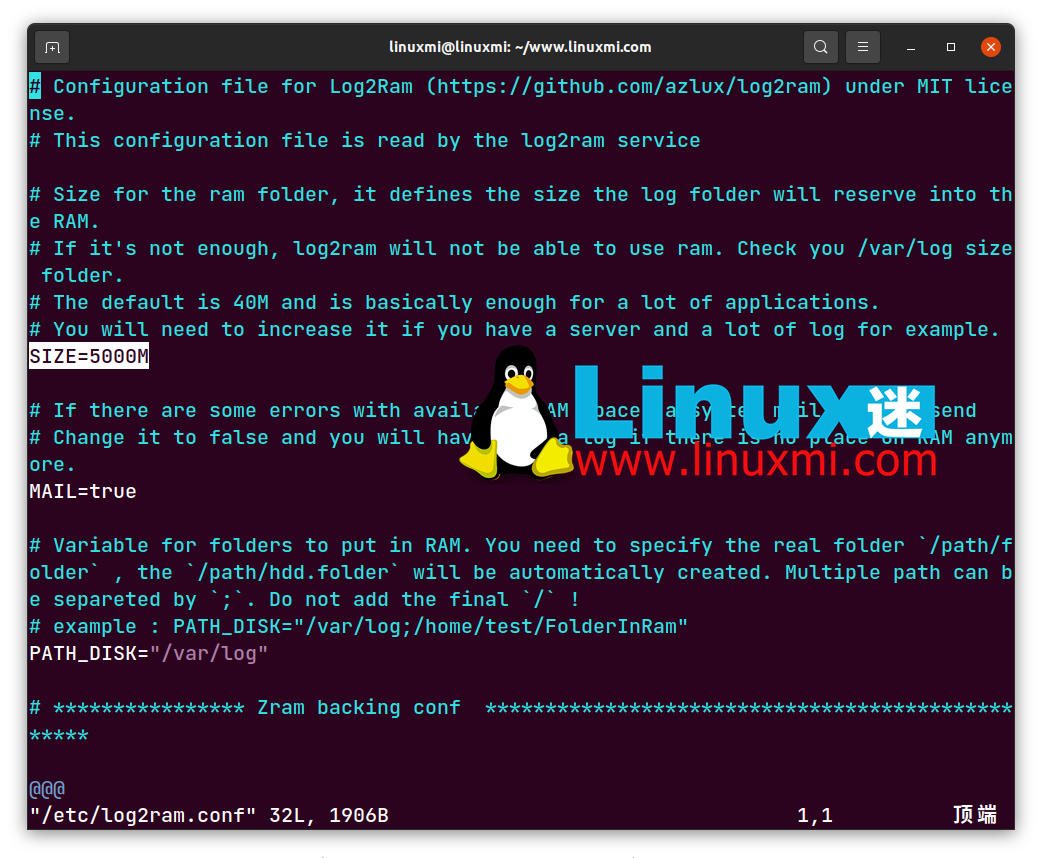
在这里,您将找到五个变量,您可以调整以使 Log2Ram 更适合您的系统。RAM 中日志文件夹的默认大小设置为 40MB,但如果您只在关机时提交写入,并且倾向于一次打开计算机数天,则需要将其增加到更现实的值。更改 PATH_DISK 变量将允许您将日志保存到非默认位置。
你应该在 Linux 上使用 Log2Ram 吗?
虽然 Log2Ram 可以减少磁盘磨损,但如果 Linux PC 意外崩溃,它会阻断您诊断问题。由于日志只是偶尔写入磁盘,因此您无法获得有关崩溃前所发生情况的最新微秒信息。
不过,通过在 Linux 中启用 Log2ram 服务,你的物理内存将开始更有效地工作,并且您将看到性能显著提高。
The above is the detailed content of Use 'little artifacts' on Linux to extend disk life. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

