Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >Solve Linux disk partition problems easily! Seven methods to help you completely uninstall the partition
Solve Linux disk partition problems easily! Seven methods to help you completely uninstall the partition
- 王林forward
- 2024-02-10 08:36:161189browse
As a Linux user, we often need to partition the disk to ensure the management and use of the file system. However, sometimes we need to remove certain partitions, which requires some special skills and tools. This article will introduce seven methods to help you completely uninstall partitions in Linux and make your system more efficient and stable.
warn!
If you delete a partition, you will lose your data. Whenever you are working on a partition, be sure to back up your data. A slight typo or slippage can be costly. Don't say we didn't warn you!
Use GParted to delete disk partitions (GUI method)
As a desktop Linux user, you may feel more comfortable, and perhaps more secure, with GUI-based tools. There are several tools that let you manage partitions on Linux. Depending on your distribution, you may have one or more of these tools installed on your system. In this tutorial, I will use GParted. It is a popular open source tool that is very simple and intuitive to use.
The first step is to install GParted if it is not already on your system. You should be able to find it in your distribution's Software Center.
Alternatively, you can install it using your distribution’s package manager. In Linux distributions based on Debian and Ubuntu, you can use the apt install command:
sudo apt install gparted
After the installation is complete, let’s open GParted. Since you are dealing with disk partitions, you need root access. It will ask for authentication, and once it opens, you should see a window similar to this:
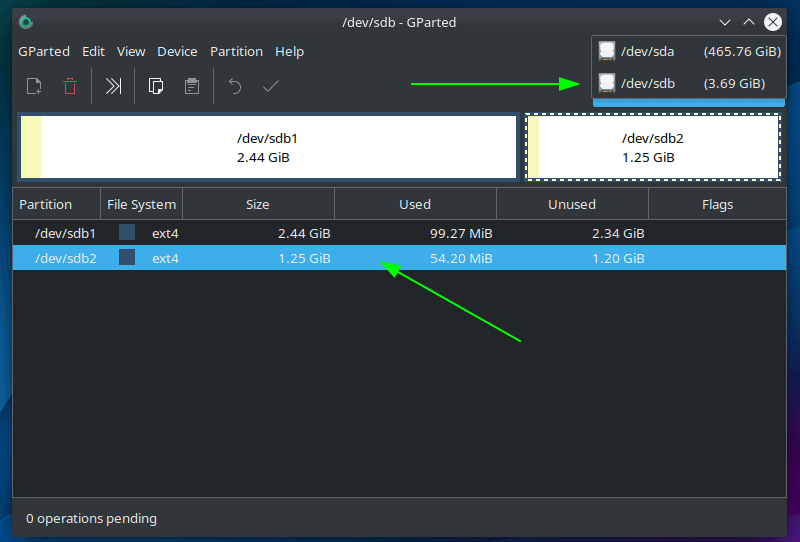
In the upper right corner, you can select the disk and select the partition you want to delete below.
Next, select the “Delete” option from the partition menu:
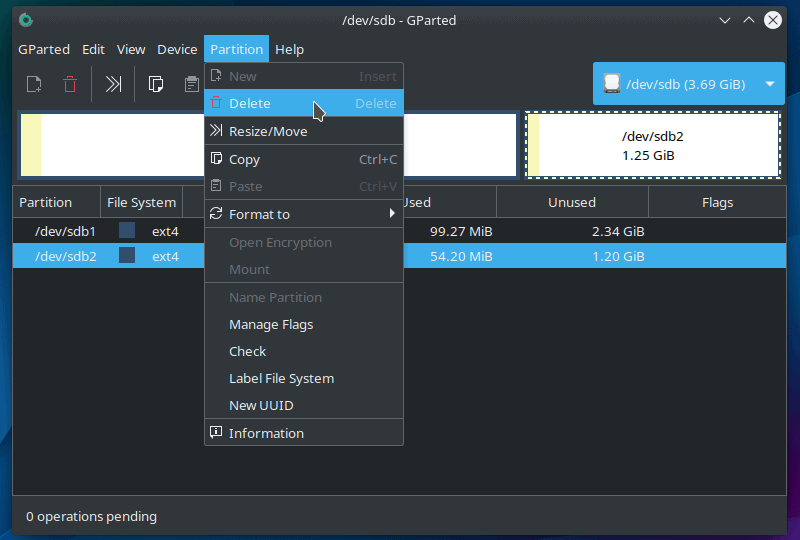
This process is not complete until you rewrite the partition table. This is a security measure that gives you the option to review changes before confirming.
To complete it, just click on the “Apply All Actions” button located in the toolbar and then click on “Apply” when asked for confirmation. 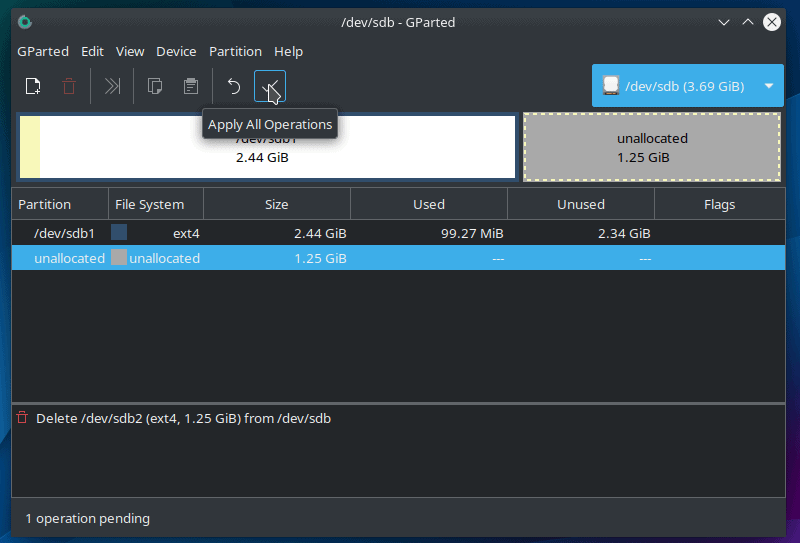
After clicking "Apply", you will see a progress bar and a result message saying that all operations were successful. You can close this message and the main window and consider your partition completely deleted from the disk.
Now that you know the GUI approach, let's move on to the command line.
Use the fdisk command to delete a partition (CLI method)
Almost every Linux distribution comes with fdisk by default, we will use this tool today. The first thing you need to know is which device the partition you want to delete is assigned to. To do this, enter the following in the terminal:
sudo fdisk --list
This will print out all the drives and partitions on our system, as well as assigned devices. You need root access for this to work.
In this example, I will use a USB drive with two partitions as shown below:
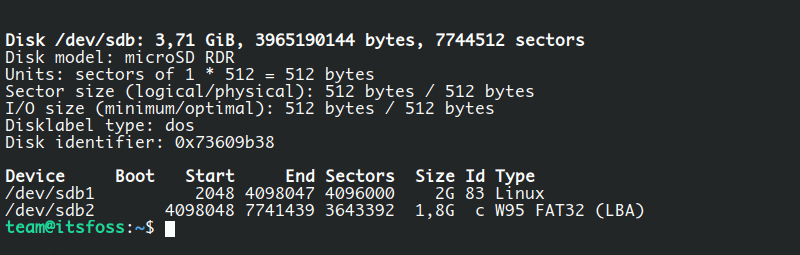
The device allocated in the system is /sdb, which has two partitions: sdb1 and sdb2. Now that you have determined which device contains these partitions, you can get started by using fdisk and the path to the device:
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
This will start fdisk in command mode. You can press m at any time to see a list of options.
Next, type p and press Enter to view the partition information and confirm that you are using the correct device. If the wrong device is used, you can use the q command to exit fdisk and start over.
Now enter d to delete a partition and it will immediately ask for the partition number, which corresponds to the number listed in the "Device" column, in this case 1 and 2 (as can be seen in the screenshot below), but it can Also varies depending on the current partition table.
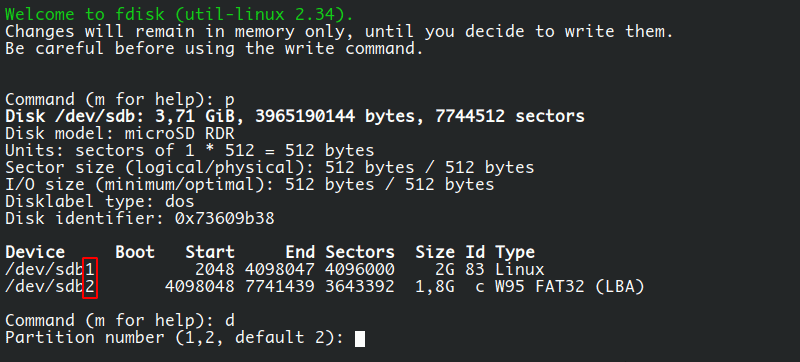
Let’s delete the second partition by entering 2 and pressing enter. You should see a message: "Partition 2 has been deleted", but in fact, it has not been deleted. fdisk also requires a step to rewrite the partition table and apply the changes. You see, this is the complete network.
You need to type w and press enter to make these changes permanent. No further confirmation was asked.
After this, you should see feedback like this:
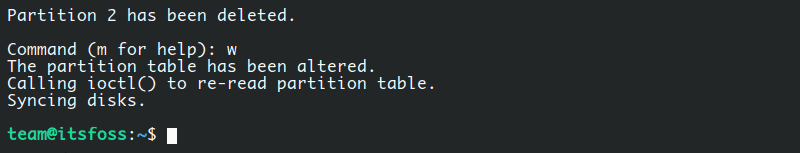
现在,使用
sudo fdisk --list /dev/sdb
查看该设备的当前分区表,你可以看到第二个分区已经完全消失。你已经完成了使用终端和 fdisk 命令来删除你的分区。成功了!
通过本文,我们学习了七种不同的方法来卸载Linux分区,包括使用fdisk、parted、mkfs等命令,以及使用GParted、KDE Partition Manage等图形工具来快速、轻松地完成磁盘分区操作。无论你是新手还是老手,都可以通过这些方法很容易地卸载Linux分区,更好地管理你的磁盘空间。让我们动手实践吧,享受Linux给我们带来的便利和高效!
The above is the detailed content of Solve Linux disk partition problems easily! Seven methods to help you completely uninstall the partition. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

