 System Tutorial
System Tutorial LINUX
LINUX Detailed explanation of Ubuntu server SSH security hardening strategy development process and reminders
Detailed explanation of Ubuntu server SSH security hardening strategy development process and remindersphp editor Banana specially introduced the process of formulating the Ubuntu server SSH security hardening strategy in detail, and provided some reminders. In an era where network security is becoming increasingly important, protecting the security of your servers is crucial. SSH is a commonly used remote login protocol, but it also faces some security risks. By understanding the process of formulating security hardening strategies and following precautions, we can help us improve the security of our servers and avoid being attacked by hackers. In this article, we will start with the preparation work, introduce the process of formulating the SSH security hardening strategy step by step, and remind everyone of the things you need to pay attention to.

Before formulating an SSH security hardening strategy, you first need to understand the working principle of SSH. SSH uses encryption and authentication technology to achieve secure remote access. Understand the working principle of SSH. , helpful for subsequent strategy formulation and configuration.
Different servers have different security requirements. Therefore, before formulating an SSH security hardening strategy, it is necessary to analyze the security requirements of the server, whether it is necessary to restrict remote access IPs, whether it is necessary to use key authentication, etc.
According to the security requirements of the server, formulate specific SSH security policies, restrict remote access IP range, disable root user login, enable two-step verification, etc.
Configure the SSH server accordingly according to the established security policy, which can be achieved by editing the SSH configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config) and modifying parameters such as PermitRootLogin, PasswordAuthentication, etc.
After completing the configuration of the SSH server, testing and verification are required. You can log in to the server remotely to check whether it takes effect according to the policy and whether there are security vulnerabilities.
Regularly update the system and SSH software to repair known security vulnerabilities in a timely manner and improve the security of the server.
When logging in through SSH, using a complex password can effectively prevent brute force cracking. The password should contain uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and be no less than 8 characters in length.
Disabling unnecessary SSH services can reduce the risk of the server being exposed to the external network. Only opening necessary ports and services can effectively reduce the attack surface.
Enabling login auditing can record information related to each SSH login, including login time, logged in user, etc. When a security event occurs, it can be traced and analyzed through the audit log.
Regularly back up important data to quickly restore data in the event of a security incident. Backup data should be stored in a safe and reliable place to avoid data leakage.
In SSH security hardening, disabling root user login is a very important strategy. By disabling root user login, you can prevent attackers from directly using root privileges to perform malicious operations. In order to facilitate management, you can create an ordinary The user is given sudo permissions to manage the server, which not only improves the security of the server but also facilitates management. Security is an ongoing task that requires constant monitoring and updates.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Ubuntu server SSH security hardening strategy development process and reminders. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
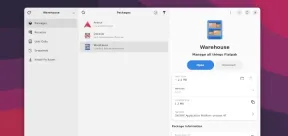 Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AM
Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AMA GUI for Effortless Flatpak Management: Introducing Warehouse Managing a growing collection of Flatpak applications can be cumbersome using only the command line. Enter Warehouse, a user-friendly graphical interface designed to streamline Flatpak a
 8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AM
8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AMThis article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying and resolving hard drive bottlenecks in Linux systems. Experienced server administrators will find this particularly useful. Slow disk operations can severely impact application performance,
 4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AM
4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AMEfficient QR code generation tool under Linux system In today's digital world, QR codes have become a way to quickly and conveniently share information, simplifying data access from URLs, texts, contacts, Wi-Fi credentials, and even payment information. Linux users can use a variety of tools to create QR codes efficiently. Let's take a look at some popular QR code generators that can be used directly on Linux systems. QRencode QRencode is a lightweight command line tool for generating QR codes on Linux. It is well-received for its simplicity and efficiency and is popular with Linux users who prefer direct methods. Using QRencode, you can use the URL,
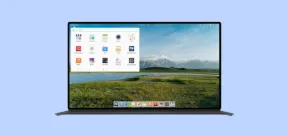 elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AM
elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AMElementary OS 8 Circe: A Smooth and Stylish Linux Experience Elementary OS, a Ubuntu-based Linux distribution, has evolved from a simple theme pack into a fully-fledged, independent operating system. Known for its user-friendly interface, elegant de
 40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AM
40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AMMastering Linux is crucial for any machine learning (ML) engineer. Its command-line interface offers unparalleled flexibility and control, streamlining workflows and boosting productivity. This article outlines essential Linux commands, explained fo
 Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AMArch Linux: A Beginner's Command-Line Cheat Sheet Arch Linux offers unparalleled control but can feel daunting for newcomers. This cheat sheet provides essential commands to confidently manage your system. System Information & Updates These com
 How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AM
How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AMThis guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of installing and using the Scikit-learn machine learning library on Linux systems. Scikit-learn (sklearn) is a powerful, open-source Python library offering a wide array of tools for various machine l
 How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AM
How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AMThis guide explains how to leverage Docker for accessing Kali Linux tools, a safer and more efficient alternative to outdated methods like Katoolin. Katoolin is no longer actively maintained and may cause compatibility problems on modern systems. Do


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools





