 Backend Development
Backend Development Golang
Golang hmac.New(h func() hash.Hash, key byte) hash.Hash equivalent in JavaScript
hmac.New(h func() hash.Hash, key byte) hash.Hash equivalent in JavaScript
In PHP, we often need to use encryption algorithms to protect data security. HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) is a commonly used encryption algorithm used to verify data integrity and identity authentication. In PHP, we can create an HMAC instance using the hmac.New() function, which requires specifying a hash function and a key. Similarly, in JavaScript, we can use equivalent methods to achieve the same functionality. In this article, I'll show you how to create an HMAC instance using equivalent methods in JavaScript, as well as how to encrypt and decrypt data between PHP and JavaScript.
Question content
I almost got stuck in the js implementation of go lang hmac.new for several days. However, there was no success. I use the crypto, crypto-js and stablelib modules for implementation. The problem is that in go lang version, hmac instances can be created from hmac instances. For example (code block is correct and tested):
hmacf := hmac.New(func() hash.Hash {
return hmac.New(func() hash.Hash {
return hmac.New(func() hash.Hash {
return hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(SALT))
}, []byte(path[0]))
}, []byte(path[1]))
}, []byte(path[2]))
Actually, I don’t know how it works either! Because in all javascript related modules you cannot create hmac from hmac and they accept string values that determine the hashing algorithm.
Maybe it's better to ask how to create hmac from hmac in javascript.
What is the solution?
When the output of the go version is the same as the output of your implementation; your solution is correct.
Workaround
According to the specification (rfc 2104), hmac uses digest functions internally, such as sha256.
However, your implementation applies (and is actually incompatible with) the hmac that uses another hmac internally instead of digest, where only the lowest level hmac uses regular digest internally. This creates a nested structure.
Based on the specification of regular hmac (with digest), this can be extended to hmac with hmac (instead of digest) used in go code:
hmac(k xor opad, hmac(k xor ipad, text)) s. rfc2104, Section 2. Definition of hmac
Due to differences from the specification, it may not be that easy to find a javascript library that supports such functionality out of the box.
While most libraries certainly support hmac, only allow specifying the digest (not hmac), e.g. nodejs's crypto module's crypto.createhmac(), see also Others Answer. I don't think this approach can be used to implement logic in go code.
If the other answers' approaches don't work, and you can't find another javascript library with the functionality you want, you can implement the logic in javascript yourself, since hmac's specification is relatively simple (see above).
The following code is an example implementation of the crypto module of nodejs:
var crypto = require('crypto')
const digest = 'sha256'
const blocksize = 64 // block size of the digest
// define input parameter
var salt = buffer.from('salt')
var path = [ buffer.from('alfa'), buffer.from('beta'), buffer.from('gamma') ]
var data = buffer.from('data')
// calculate hmac
var hmac = hmac(data, salt, path)
console.log(hmac.tostring('hex'))
function hmac(data, salt, path) {
// create keylist
var keylist = []
keylist.push(salt)
keylist = keylist.concat(path)
// determine hmac recursively
var result = hmac_rec(data, keylist)
return result
}
function hmac_rec(data, keylist) {
// adjust key (according to hmac specification)
var key = keylist.pop()
if (key.length > blocksize) {
k = buffer.allocunsafe(blocksize).fill('\x00');
if (keylist.length > 0) {
hmac_rec(key, [...keylist]).copy(k)
} else {
gethash(key).copy(k)
}
} else if (key.length < blocksize) {
k = buffer.allocunsafe(blocksize).fill('\x00');
key.copy(k)
} else {
k = key
}
// create 'key xor ipad' and 'key xor opad' (according to hmac specification)
var ik = buffer.allocunsafe(blocksize)
var ok = buffer.allocunsafe(blocksize)
k.copy(ik)
k.copy(ok)
for (var i = 0; i < ik.length; i++) {
ik[i] = 0x36 ^ ik[i]
ok[i] = 0x5c ^ ok[i]
}
// calculate hmac
if (keylist.length > 0) {
var innerhmac = hmac_rec(buffer.concat([ ik, data ]), [...keylist])
var outerhmac = hmac_rec(buffer.concat([ ok, innerhmac ]), [...keylist])
} else {
var innerhmac = gethash(buffer.concat([ik, data]))
var outerhmac = gethash(buffer.concat([ok, innerhmac]))
}
return outerhmac
}
// calculate sha256 hash
function gethash(data){
var hash = crypto.createhash(digest);
hash.update(data)
return hash.digest()
}
result:
2e631dcb4289f8256861a833ed985fa945cd714ebe7c3bd4ed4b4072b107b073
test:
The following go code produces the same result:
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"hash"
)
func main() {
salt := "salt"
path := []string{"alfa", "beta", "gamma"}
hmacf := hmac.new(func() hash.hash {
return hmac.new(func() hash.hash {
return hmac.new(func() hash.hash {
return hmac.new(sha256.new, []byte(salt))
}, []byte(path[0]))
}, []byte(path[1]))
}, []byte(path[2]))
hmacf.write([]byte("data"))
result := hmacf.sum(nil)
fmt.println(hex.encodetostring(result)) // 2e631dcb4289f8256861a833ed985fa945cd714ebe7c3bd4ed4b4072b107b073
}
edit:
Inspired by this article, here is a more compact/efficient implementation of hmac_rec() that uses hmac for the regular last iteration step (which also makes gethash() Obsolete):
function hmac_rec(data, keyList) {
var key = keyList.pop()
if (keyList.length > 0) {
// adjust key (according to HMAC specification)
if (key.length > blockSize) {
k = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize).fill('\x00');
hmac_rec(key, [...keyList]).copy(k)
} else if (key.length < blockSize) {
k = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize).fill('\x00');
key.copy(k)
} else {
k = key
}
// create 'key xor ipad' and 'key xor opad' (according to HMAC specification)
var ik = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize)
var ok = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize)
k.copy(ik)
k.copy(ok)
for (var i = 0; i < ik.length; i++) {
ik[i] = 0x36 ^ ik[i]
ok[i] = 0x5c ^ ok[i]
}
// calculate HMAC
var innerHMac = hmac_rec(Buffer.concat([ ik, data ]), [...keyList])
var outerHMac = hmac_rec(Buffer.concat([ ok, innerHMac ]), [...keyList])
} else {
var outerHMac = crypto.createHmac(digest, key).update(data).digest();
}
return outerHMac
}
The above is the detailed content of hmac.New(h func() hash.Hash, key byte) hash.Hash equivalent in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
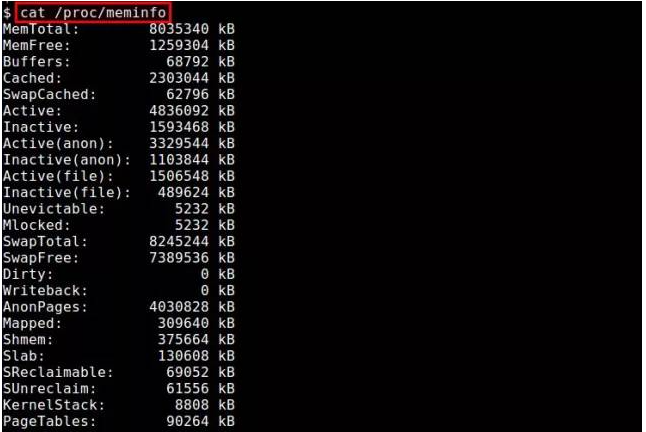 Linux下查看内存使用情况方法总结Feb 05, 2024 am 11:45 AM
Linux下查看内存使用情况方法总结Feb 05, 2024 am 11:45 AMQ:我有一个问题,我想要监视Linux系统的内存使用情况。在Linux下有哪些可用的视图或命令行工具可以使用呢?A:在Linux系统中,有多种方法可以监视内存使用情况。下面是一些通过视图工具或命令行来查看内存使用情况的方法。/proc/meminfo:最简单的方法是查看/proc/meminfo文件。这个虚拟文件会动态更新,并提供了关于内存使用情况的详细信息。它列出了各种内存指标,可以满足你对内存使用情况的大部分需求。另外,你还可以通过/proc//statm和/proc//status来查看进
 揭秘NVIDIA大模型推理框架:TensorRT-LLMFeb 01, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
揭秘NVIDIA大模型推理框架:TensorRT-LLMFeb 01, 2024 pm 05:24 PM一、TensorRT-LLM的产品定位TensorRT-LLM是NVIDIA为大型语言模型(LLM)开发的可扩展推理方案。它基于TensorRT深度学习编译框架构建、编译和执行计算图,并借鉴了FastTransformer中高效的Kernels实现。此外,它还利用NCCL实现设备间的通信。开发者可以根据技术发展和需求差异,定制算子以满足特定需求,例如基于cutlass开发定制的GEMM。TensorRT-LLM是NVIDIA官方推理方案,致力于提供高性能并不断完善其实用性。TensorRT-LL
 Linux 上的最佳白板应用程序Feb 05, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
Linux 上的最佳白板应用程序Feb 05, 2024 pm 12:48 PM“我们将介绍几款适用于Linux系统的白板应用程序,相信这些信息对您会非常有帮助。请继续阅读!”一般来说,数字白板是一种用于大型互动显示面板的工具,常见的设备类型包括平板电脑、大屏手机、触控笔记本和表面显示设备等。当教师使用白板时,您可以使用触控笔、手写笔、手指甚至鼠标在设备屏幕上进行绘画、书写或操作元素。这意味着您可以在白板上拖动、点击、删除和绘画,就像在纸上使用笔一样。然而,要实现这一切,需要有一款软件来支持这些功能,并实现触控和显示之间的精细协调。目前市面上有许多商业应用可以完成这项工作。
 ZR币升值空间大吗? ZR币在哪里购买交易?Feb 01, 2024 pm 08:09 PM
ZR币升值空间大吗? ZR币在哪里购买交易?Feb 01, 2024 pm 08:09 PMZRX(0x)是一个基于以太坊区块链的开放协议,用于实现分布式交易和去中心化交易所(DEX)功能。作为0x协议的原生代币,ZRX可用于支付交易费用、治理协议变更和获取平台优惠。1.ZRX币升值空间展望:从技术角度来看,ZRX作为0x协议的核心代币,在去中心化交易所的应用逐渐增多,市场对其认可度也在增加。以下是几个关键因素,有助于提升ZRX币的价值空间:市场需求潜力大、社区活跃度高、开发者生态繁荣等。这些因素共同促进了ZRX的广泛应用和使用,进而推动了其市场价格的上升。市场需求的增长潜力,意味着更
 手把手教你构建linux rootfsFeb 05, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
手把手教你构建linux rootfsFeb 05, 2024 pm 03:51 PMbusybox概述众所周知,在Linux环境下,一切皆文件,文件可以表示一切。而文件系统则是这些普通组件的集合。在嵌入式领域中,常常使用基于busybox构建的rootfs来构建文件系统。busybox诞生至今已有近20年的历史,如今已成为嵌入式行业中主流的rootfs构建工具。busybox的代码是完全开源的。你可以进入官方网站,点击”GetBusyBox”下面的”DownloadSource”进入源码下载界面。“官方网站链接:https://busybox.net/”2.busybox的配置
 BOSS直聘怎么创建多个简历Feb 05, 2024 pm 02:18 PM
BOSS直聘怎么创建多个简历Feb 05, 2024 pm 02:18 PMBOSS直聘怎么创建多个简历?BOSS直聘是很多小伙伴找工作的一大招聘平台,为用户们提供了非常多便利的求职服务。各位在使用BOSS直聘的时候,可以创建多个不同的简历,以便投送到不同的工作岗位上,获取到更高成功率的求职操作,各位如果对此感兴趣的话,就随小编一起来看看BOSS直聘双简历创建教程吧。BOSS直聘怎么创建多个简历1.登录Boss直聘:在您的电脑或手机上,登录您的Boss直聘账户。2.进入简历管理:在Boss直聘首页,点击“简历管理”,进入简历管理页面。3.创建新简历:在简历管理页面,点击
 Linux字节对齐的那些事Feb 05, 2024 am 11:06 AM
Linux字节对齐的那些事Feb 05, 2024 am 11:06 AM最近,我正在进行一个项目,遇到了一个问题。在ARM上运行的ThreadX与DSP通信时采用了消息队列的方式传递消息(最终实现使用了中断和共享内存的方法)。然而,在实际的操作过程中,发现ThreadX经常崩溃。经过排查,发现问题出在传递消息的结构体没有考虑字节对齐的问题上。我想顺便整理一下关于C语言中字节对齐的问题,并与大家分享。一、概念字节对齐与数据在内存中的位置有关。如果一个变量的内存地址恰好是它长度的整数倍,那么它就被称为自然对齐。例如,在32位CPU下,假设一个整型变量的地址为0x0000
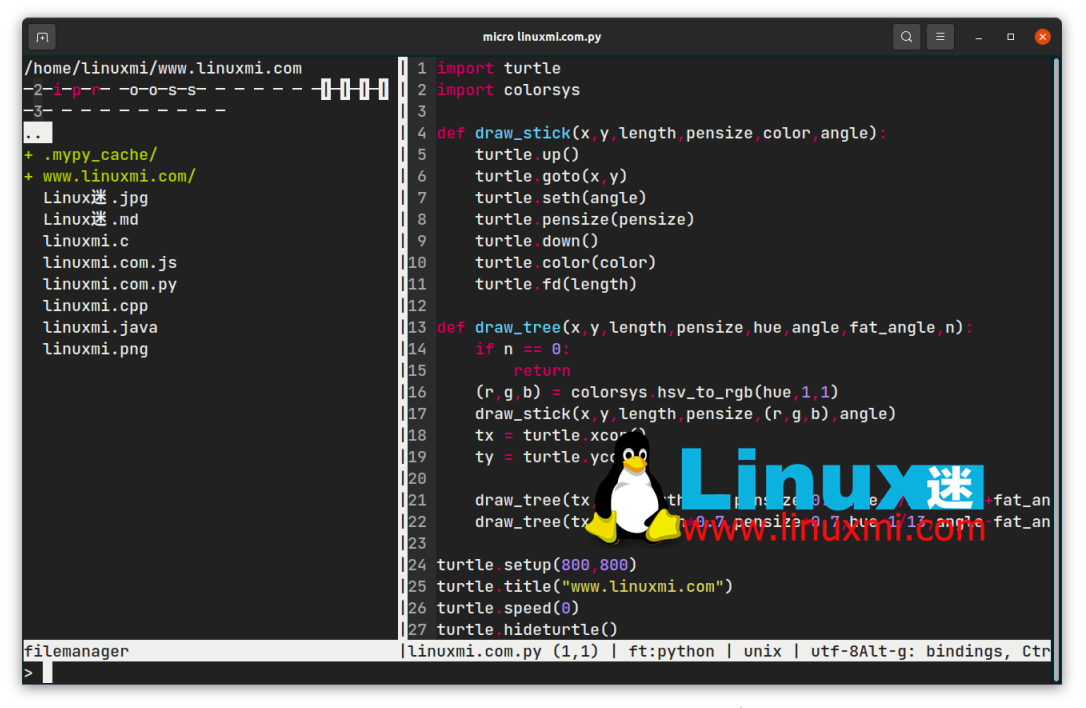 比 Vim 更现代直观的 Linux 文本编辑器Feb 05, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
比 Vim 更现代直观的 Linux 文本编辑器Feb 05, 2024 pm 02:00 PM如果你厌倦了Vi和Vim的奇怪界面和繁琐的键绑定,为什么不试试Micro编辑器呢?命令行文本编辑器证明了Linux终端的实用性,让您可以在不离开终端的情况下进行文件编辑。这些编辑器使用的资源更少,速度也非常快,非常适合进行一些快速编辑。一些流行的命令行文本编辑器包括Vi、Vim和Nano。它们在大多数Linux发行版中都预装了。然而,对于初学者来说,学习Vi或Vim的曲线和键绑定可能有些困难。这时,Micro文本编辑器就成为了一个更简单的选择。Micro与其他编辑相比的表现如何Micro宣称自己


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






