 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI What are the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the Internet of Things?
What are the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the Internet of Things?What are the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the Internet of Things?

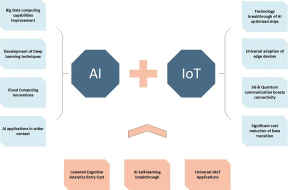
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into the Internet of Things (IoT) system marks an important progress in the development of intelligent technology. This convergence is called AIoT (artificial intelligence for the Internet of Things), and it not only enhances the capabilities of the system, but also changes the way IoT systems operate, learn and adapt in the environment. Let’s explore this integration and what it means.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Internet of Things
Enhanced Data Processing and Analysis
Advanced Data Interpretation: IoT devices generate massive amounts of data. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can cleverly cull this data, extract valuable insights, and identify patterns that are invisible to a human perspective or traditional data processing methods.
Predictive analytics uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict future trends based on historical data, which is especially useful in predictive maintenance of industrial equipment. The system can accurately predict the time before a failure occurs and take appropriate maintenance measures, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Autonomous decision-making and adaptive learning
Autonomous decision-making: Artificial intelligence enables IoT devices to make decisions based on the data they collect Make independent decisions. This autonomy is critical for applications such as self-driving cars or automated industrial processes, where real-time decision-making is critical.
Adaptive Learning: Machine learning algorithms learn and adapt over time, improving their decision-making capabilities. This means that IoT systems can become more efficient and effective through use because they can learn from past experiences and adjust their operations accordingly.

Personalization and User Experience
In consumer IoT areas such as smart homes, artificial intelligence and machine learning can customize the user experience based on the user’s preferences and Habits, automatically optimizing your device's settings for increased comfort and efficiency.
Through AI-driven voice assistants and chatbots, interactions between users and IoT devices become more natural, thereby improving user experience and accessibility.
Operational Efficiency and Automation
Process Optimization: In areas such as manufacturing, AIoT can streamline operations, optimize supply chains, and enhance quality control, thereby increasing productivity and reducing costs.
Energy Management: AIoT helps smart grid management, optimizes energy distribution and consumption, and contributes to sustainable development.
Predictive Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
Predictive maintenance enhanced by IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) and operational efficiency are crucial in modern industry.
Predictive maintenance involves using IoT sensors to collect equipment data, which is analyzed by artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Operational efficiency refers to using AIoT to optimize processes. This includes process optimization, resource management, quality control, supply chain optimization and improving employee productivity. IoT sensors provide real-time data that AI analyzes to enhance decision-making, streamline operations, and improve resource utilization.
Safety and Security
Improved security protocols: Artificial intelligence can enhance IoT security by detecting and responding to cyber threats in real-time, considering the proliferation of IoT devices and their access to sensitive data Access, this is a crucial aspect.
Safety Monitoring: In industrial environments, AIoT can improve worker safety by monitoring safety conditions, detecting dangerous situations and initiating emergency protocols.
Practical Applications and Case Studies of AIOT
Smart Cities
Traffic Management: AIoT Systems for Optimization Traffic flow in urban areas. Sensors collect vehicle movement data, which AI algorithms analyze to manage traffic lights and reduce congestion.
Case Study: Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative leverages AIoT for real-time traffic monitoring and dynamic public transport routes to improve urban mobility.
Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring: Wearable IoT devices collect health data (heart rate, blood pressure, etc.) and artificial intelligence analyzes this data to detect health problems in their early stages sign.
Case Study: Medtronic’s artificial intelligence blood glucose monitoring and insulin pump system continuously adjusts insulin levels for diabetic patients based on real-time data.
Manufacturing
Predictive Maintenance: AIoT sensors on machinery detect anomalies that indicate potential failures. This data helps schedule maintenance before failure occurs.
Case Study: Siemens uses AIoT in its gas turbines to predict maintenance needs, significantly reducing unplanned downtime.
Agriculture
PrecisionQuasi-agriculture: AIoT devices monitor soil conditions, weather and crop health, informing farmers of the best planting time, watering and fertilizing.
Case Study: John Deere’s AIoT tractors and equipment enable precision planting and fertilization, increasing crop yields and resource efficiency.
Retail
Enhanced Customer Experience: AIoT helps personalize the shopping experience. Sensors track customers’ movements, and artificial intelligence provides tailored recommendations.
Case Study: AmazonGo store uses AIoT to provide a checkout-free shopping experience, and the system will automatically charge customers for the goods they purchase.
Energy
Smart Grid: AIoT optimizes energy distribution and consumption, predicts demand peaks and adjusts supply accordingly.
Case Study: Italian energy company Enel uses AIoT for real-time grid management and efficient energy distribution.
Home Automation
Smart Home: AIoT devices such as thermostats, lights, and security systems can learn user preferences and automate the home environment for comfort and energy conservation.
Case Study: Nest’s smart thermostat uses AIoT to learn homeowners’ preferences and automatically adjust home temperatures for optimal comfort and efficiency.
Transportation Logistics
Fleet Management: AIoT devices track vehicle location, fuel usage and maintenance needs to optimize routes and schedules.
Case Study: UPS uses AIoT for route optimization, reducing fuel consumption and shortening delivery times.
Environmental Monitoring
Pollution Tracking: Sensors collect environmental data and artificial intelligence models predict pollution levels to inform public health responses.
Case Study: IBM’s “Green Horizon” program uses AIoT to monitor air quality and make recommendations for pollution control in cities such as Beijing.
Public Safety
Emergency Response: AIoT systems can detect emergencies (such as fires) and alert relevant authorities, thereby shortening response times.
Case Study: In California, AIoT sensors are used for early wildfire detection, allowing for faster emergency response and preventing widespread damage.
The above is the detailed content of What are the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the Internet of Things?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe legal tech revolution is gaining momentum, pushing legal professionals to actively embrace AI solutions. Passive resistance is no longer a viable option for those aiming to stay competitive. Why is Technology Adoption Crucial? Legal professional
 This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AM
This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AMMany assume interactions with AI are anonymous, a stark contrast to human communication. However, AI actively profiles users during every chat. Every prompt, every word, is analyzed and categorized. Let's explore this critical aspect of the AI revo
 7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AM
7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AMA successful artificial intelligence strategy cannot be separated from strong corporate culture support. As Peter Drucker said, business operations depend on people, and so does the success of artificial intelligence. For organizations that actively embrace artificial intelligence, building a corporate culture that adapts to AI is crucial, and it even determines the success or failure of AI strategies. West Monroe recently released a practical guide to building a thriving AI-friendly corporate culture, and here are some key points: 1. Clarify the success model of AI: First of all, we must have a clear vision of how AI can empower business. An ideal AI operation culture can achieve a natural integration of work processes between humans and AI systems. AI is good at certain tasks, while humans are good at creativity and judgment
 Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AMMeta upgrades AI assistant application, and the era of wearable AI is coming! The app, designed to compete with ChatGPT, offers standard AI features such as text, voice interaction, image generation and web search, but has now added geolocation capabilities for the first time. This means that Meta AI knows where you are and what you are viewing when answering your question. It uses your interests, location, profile and activity information to provide the latest situational information that was not possible before. The app also supports real-time translation, which completely changed the AI experience on Ray-Ban glasses and greatly improved its usefulness. The imposition of tariffs on foreign films is a naked exercise of power over the media and culture. If implemented, this will accelerate toward AI and virtual production
 Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AMArtificial intelligence is revolutionizing the field of cybercrime, which forces us to learn new defensive skills. Cyber criminals are increasingly using powerful artificial intelligence technologies such as deep forgery and intelligent cyberattacks to fraud and destruction at an unprecedented scale. It is reported that 87% of global businesses have been targeted for AI cybercrime over the past year. So, how can we avoid becoming victims of this wave of smart crimes? Let’s explore how to identify risks and take protective measures at the individual and organizational level. How cybercriminals use artificial intelligence As technology advances, criminals are constantly looking for new ways to attack individuals, businesses and governments. The widespread use of artificial intelligence may be the latest aspect, but its potential harm is unprecedented. In particular, artificial intelligence
 A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AM
A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe intricate relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (NI) is best understood as a feedback loop. Humans create AI, training it on data generated by human activity to enhance or replicate human capabilities. This AI
 AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AM
AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AMAnthropic's recent statement, highlighting the lack of understanding surrounding cutting-edge AI models, has sparked a heated debate among experts. Is this opacity a genuine technological crisis, or simply a temporary hurdle on the path to more soph
 Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AM
Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AMIndia is a diverse country with a rich tapestry of languages, making seamless communication across regions a persistent challenge. However, Sarvam’s Bulbul-V2 is helping to bridge this gap with its advanced text-to-speech (TTS) t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






