 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Understanding the 5 audio interfaces on the back of the motherboard
Understanding the 5 audio interfaces on the back of the motherboardThe 5 audio interfaces on the back of the motherboard refer to the audio output and input interfaces on the back of the motherboard. These interfaces typically include microphone input, line input, line output, speaker output, and headphone output. Microphone input is used to connect an external microphone, and line input is used to connect other audio devices such as audio players or musical keyboards. The line output interface can be used to connect to an external sound system or speakers, and the headphone output interface is used to connect headphones. These audio interfaces provide users with convenient audio input and output options to meet different audio needs.

What do the 5 audio interfaces on the back of the motherboard mean?
The 5 audio interfaces are usually defined by colors:
1. Grass green: audio output port. Can be connected to the input of headphones or speakers.
2. Pink: Microphone port.
3. Blue: Audio input port.
4. Gray: Side surround speaker connector. (In eight-channel setting)
5. Black: Rear surround speaker connector. (In four-, six- and eight-channel settings)
Is there any noise in the motherboard audio interface?
Excluding the possibility of the sound itself, then the host is nothing more than the sound card. However, there are two aspects. On the one hand, it may be that your driver does not match, and of course, there is indeed a problem with the sound card hardware. . .
I wonder if you asked a friend whether the sound card driver comes with the original CD when installing the system. If it is an integrated sound card such as a clone version of Xp, this kind of situation may occur. Please replace the original After cleanly uninstalling the driver, install the original CD or download the corresponding model from the official website and install it again. . . .
If it still doesn’t work after updating the driver, then there may be a hardware failure in your sound card. You can take the motherboard you just bought to after-sales service, but the possibility of hardware failure in this type of new motherboard is very small. . . . .
Ask friends to focus on the software aspect. If necessary, make the system again (pure version), reinstall the driver and test again. If all the scripts have been passed, consider the hardware aspect last and take it directly. Just look for after-sales service. . . .
If you have any questions, please ask. .
I really hope I can help you!
What is the use of the audio input port on the motherboard?
The 6 audio interfaces at the bottom of the back of the motherboard, from top to bottom, from right to left, are represented by letters: J hole (cyan) I hole (black) H hole (light red) M hole (pink ) L (green) K (purple) I read the motherboard introduction and said: J: Side speaker output provides center surround channel output I: Rear speaker output provides rear surround channel output H: Center/subwoofer output provides center/subwoofer output Bass output M: Microphone plug in L: Audio source output (front speaker output) Stereo speaker or headphone audio source plug plug in K: Audio source input CD player, Walkman and other audio source input devices plug in
Which audio interface on the motherboard has good sound quality ?
Currently, the common audio interfaces on motherboards include 3.5mm audio interface and RCA audio interface. Generally speaking, the sound quality of the RCA audio interface is better because it can transmit higher-quality audio signals and is less likely to be subject to external interference.
In contrast, the 3.5mm audio interface may suffer a certain loss of sound quality during the transmission process, especially when transmitting over long distances.
Therefore, if you need higher quality audio output, it is recommended to choose a motherboard with an RCA audio interface, so that you can get a clearer and more realistic audio experience.
No sound from the motherboard audio port?
1. If the rear audio interface can output sound correctly, but the front audio interface has no sound output, there are two reasons. The first reason is that the audio cable of the front audio interface is not correctly connected. Connected to the motherboard. The second reason is that the audio driver control panel settings are incorrect.
Second, right-click the computer. Find Management and then Sound Video Game Controllers inside Device Manager. Then find High Definition Audio Manager. Click on the folder icon in the upper right corner. Then disable front panel jack detection in the pop-up window. Tick and OK. Then the green round hole icon in the front panel will light up and you can use it normally.
No sound from the rear audio jack on the computer motherboard?
The reason is poor contact and the aging of the internal circuit caused by using the speaker for a long time. When the speaker is connected to the computer, there may be no sound due to poor contact.
Solution: First check whether the audio connection is normal. If there is still no sound after making sure it is intact, you can install the driver and see. If it is still not good after installing the driver, it means the audio is broken.
Does the motherboard have 6 sound sockets?
The 6 audio interfaces at the bottom of the back of the motherboard are represented by letters from top to bottom and from right to left: J hole (cyan) I hole (black) H hole (light red) M hole (pink ) L (green) K (purple) I read the motherboard introduction and said: J: Side speaker output provides center surround channel output I: Rear speaker output provides rear surround channel output H: Center/subwoofer output provides center/heavy Bass output M: Microphone microphone plug-in L: Audio source output (front speaker output) Stereo speaker or headphone audio source plug plug in K: Audio source input CD player, Walkman and other audio source input devices plug in
Why isn’t there just one audio interface on the back of the motherboard?
1. The audio interface on the back of the motherboard is not made into one. 2. This is because different audio interfaces have different functions and characteristics. In order to meet the diverse needs of users, motherboard designers usually provide multiple different types of audio interfaces, such as headphone interfaces, microphone interfaces, optical fiber interfaces, etc. This allows users to choose the appropriate interface according to their own needs and improve audio transmission quality and compatibility. 3. In addition, designing the audio interface separately can also help reduce electromagnetic interference and signal interference, and improve audio stability and clarity. In addition, different audio interfaces can also support the connection of multiple devices at the same time, providing more scalability and flexibility. Therefore, although the audio interface on the back of the motherboard is not a whole, this design can better meet the needs of users and provide a better audio experience.
The above is the detailed content of Understanding the 5 audio interfaces on the back of the motherboard. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
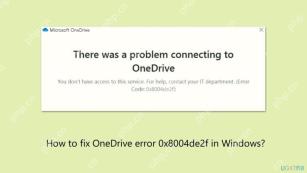 How to fix OneDrive error 0x8004de2f in Windows?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:00 AM
How to fix OneDrive error 0x8004de2f in Windows?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:00 AMOneDrive is Microsofts cloud storage which allows users to have their files backed up, synchronized, and accessible across devices. It is integrated into Window
 Windows 11 KB5055528: What's New & What if It Fails to InstallApr 16, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Windows 11 KB5055528: What's New & What if It Fails to InstallApr 16, 2025 pm 08:09 PMWindows 11 KB5055528 (released on April 8, 2025) Update detailed explanation and troubleshooting For Windows 11 23H2 users, Microsoft released the KB5055528 update on April 8, 2025. This article describes the improvements to this update and provides a solution to the installation failure. KB5055528 update content: This update brings many improvements and new features to Windows 11 23H2 users: File Explorer: Improved text scaling and improved accessibility to the file opening/save dialog and copy dialog. Settings page: Added "Top Card" function to quickly view processor, memory, storage and G
 Informative Guide: Computer Hardware VS Software ProblemsApr 16, 2025 pm 08:07 PM
Informative Guide: Computer Hardware VS Software ProblemsApr 16, 2025 pm 08:07 PMThis guide clarifies the key differences between computer hardware and software problems. Learn to identify and troubleshoot these issues effectively to keep your computer running smoothly. Quick Navigation: What are Computer Hardware Problems? Wha
 Error 0x80070643 After Windows 10 KB5057589, Learn EssentialsApr 16, 2025 pm 08:05 PM
Error 0x80070643 After Windows 10 KB5057589, Learn EssentialsApr 16, 2025 pm 08:05 PMMicrosoft's Windows 10 WinRE Update Glitch: Error 0x80070643 Explained Over a year later, Microsoft is still grappling with WinRE update issues. The recent Windows 10 KB5057589 update has brought the error 0x80070643 to light. This article explores
 Disk Encryption vs File Encryption: Which One Should You ChooseApr 16, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
Disk Encryption vs File Encryption: Which One Should You ChooseApr 16, 2025 pm 08:03 PMData security is paramount in today's digital landscape. Encryption offers robust protection, but choosing between disk encryption and file encryption can be confusing. This MiniTool guide clarifies the differences and helps you select the best appr
 Explained! Windows Server 2025 DCs Inaccessible After a RestartApr 16, 2025 pm 08:02 PM
Explained! Windows Server 2025 DCs Inaccessible After a RestartApr 16, 2025 pm 08:02 PMIs the Windows Server 2025 domain controller unreachable after restarting? This article provides a solution. Problem Description: Microsoft has confirmed that Windows Server 2025 domain controllers (such as Active Directory) may not handle network traffic properly after restarting. This can cause the domain controller to be inaccessible in the domain network or to be accessed incorrectly through ports and protocols that should be blocked by the domain firewall. Root Cause: The domain firewall configuration file is not applied when the domain controller restarts, but the standard firewall configuration file is used. Potential consequences: The domain controller may not be accessible within the domain network. Applications or services running on domain controllers or remote devices may occur
 Downgrade Windows Server 2022/2019 Datacenter to StandardApr 16, 2025 pm 08:01 PM
Downgrade Windows Server 2022/2019 Datacenter to StandardApr 16, 2025 pm 08:01 PMThis guide explains how to downgrade Windows Server Datacenter to Standard edition (Windows Server 2019 and 2022) without reformatting. While Microsoft doesn't officially support this, these methods work in practice. Always back up your system befo
 How to fix black screen on game launch on Windows?Apr 16, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
How to fix black screen on game launch on Windows?Apr 16, 2025 pm 08:00 PMA black screen on game launch on Windows is a serious hindrance for gamers. The issue is shared by a variety of games on numerous different launchers, and the m


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function





