Aave Governance V3 is officially launched, pushing on-chain governance to a new level!
- 王林forward
- 2024-01-23 22:57:121117browse
Blue chip lending protocol AAVE today launched its latest governance module - Aave Governance V3, which brings a series of advantages, including reducing voting costs, adding automated robots, and Complete cross-chain infrastructure. This will set a new paradigm for on-chain governance.
Aave Governance Module Reference Value
The Aave lending protocol has attracted approximately US$6.5 billion in funding so far, making it the top three on-chain products (after Lido and Maker ). Given this, any updates to the protocol require extreme caution. Therefore, Aave has adopted a very complete set of specifications and contract execution mechanisms in terms of governance to reduce the impact of human errors or centralization risks as much as possible.
Different from other projects, the Aave protocol adopts a relatively safe mechanism and does not rely on multi-signature control protocol backdoor functions or even multi-signature functions. This governance model has a high reference value and provides a useful reference for imagining ideal governance mechanisms in the future.
AAVE Governance V2 has been fully verified since it began operation in 2020, proving its feasibility. What is amazing is that through the operation of this governance module, the issuance and protocol integration of GHO stablecoins have even been successfully achieved. This complex project demonstrates the power of the governance module and is really interesting.
Aave Governance Module V2 Introduction
The original AAVE Governance V2 module will be discontinued, but V3 will inherit its general structure and be optimized, so a basic understanding is required.
Basic Architecture
AAVE Governance V2 aims to achieve the goal of complete decentralization, automatically carrying out protocol updates through on-chain governance results, without relying on the founding team to approve on-chain proposals.
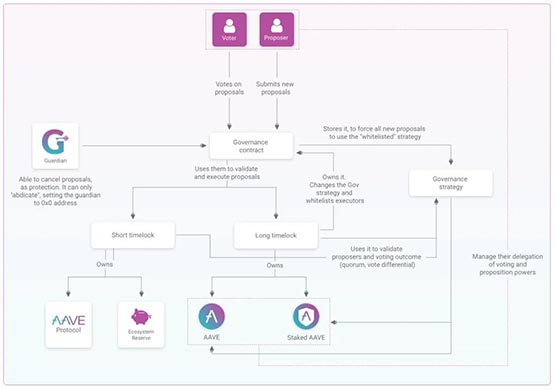
Aave Governance V2 architecture
In practice, Aave Governance V2 can be broken down into the following components:
Aave Governance v2 : Responsible for handling the creation, information submission, parameter setting, etc. of AIP.
Short Executor: Used to make minor changes to the protocol, responsible for executing the content of proposals passed with a lower threshold to complete rapid iterations, such as proposals to increase or decrease the list of acceptable assets in the protocol.
Long Executor: Used to make major changes to the core code of the protocol, responsible for executing proposals that pass with a higher threshold, such as proposals to modify the logic rules of the protocol itself.
Governance Strategy: handles the operational logic of user proposals and voting, and defines which tokens can be used for voting. The tokens that can be used for voting in V2 include AAVE and stkAAVE (Stake AAVE).
There is also a set of contracts called Aave Guardian, which is controlled by multi-signatures of ten addresses. Its main responsibility is to be responsible for the contract modification of the agreement in emergency situations to protect the security of the agreement. Depending on the situation, malicious proposals can be canceled or even the protocol operations can be shut down.
Operation process
In the past, the basic structure of the governance process of the AAVE Governance V2 module was as follows:
Proposal submission: The proposal was discussed in the community forum, and Temperaturecheck was performed, followed by follow-up Enter the off-chain Snapshot vote.
ARFC: Compile the proposals that pass off-chain voting into a complete proposal (AIP), submit the complete code at the same time, and conduct off-chain Snapshot voting again.
Submit AIP: Usually the team will submit the AIP to the governance contract for proposals that pass the second off-chain vote, but in fact anyone can submit AIP.
Delay period: After a delay period of about one day, the governance contract completes the token status snapshot and confirms voting rights.
On-chain voting: There are different passing thresholds for proposals with different levels of impact.
Proposal execution: After the proposal is passed, there will be a lock-in period. After the end, Short Executor or Long Executor will be used to execute the update code according to the proposals with different levels of impact. This part needs to be triggered by an external address.
Cross-chain execution: If the proposal is on a network other than Ethereum, you need to execute cross-chain transactions and execute the execution contract of the corresponding network, which also needs to be triggered by an external address.
Existing Problems
Problems discovered by AAVE Governance V2 after three years of operation:
The voting cost is too high: the existing design consumes a lot of fuel, which is not suitable for small businesses This is especially true for users. The voting rights of Aave and stkAAVE tokens are decentralized. There are more than 150,000 Aave holders and 20,000 stkAAVE holders respectively. Many of these users only hold a small number of tokens and voting rights. Even at the relatively low Ethereum gas price level (20gwei), it still costs about $5 to complete a vote, not to mention that the voting cost may be five to ten times higher when the network is congested.
Conflict of interest between governance and tokens: In order to cooperate with the existing governance module, the tokens need to be queried by the contract to confirm the voting rights of AAVE and stkAAVE token holders. The token itself needs to record additional The balance history records, which increases the transfer fuel fee of AAVE and stkAAVE tokens, which in disguise increases the operating costs of token holders.
Aave Governance Module V3 Introduction
A quick look at the similarities and differences between Aave Governance V3 and V2
Proposal creation: The governance rules of V3 require the proposer to deploy it in the Aave contract before creating a proposal Executable and valid contract code, and complete registration to obtain proposal recognition.
Voting Delay: Almost the same as V2, there will be a 1-day delay between proposal creation and the start of voting, with a snapshot of voting rights taken after the end. However, due to some technical reasons, the delay time on v3 will vary by hours.
Proposal Voting: Voters will in most cases not vote on Ethereum, but on other networks such as Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum or Optimism, with more networks to be opened in the future. Supplement: Voting for a proposal will only be conducted in one network, rather than in multiple networks simultaneously. The proposer can choose which network to vote on based on preferences or other factors.
Proposal Execution: The time lock and execution phase of the proposal will be exactly the same as V2, and execution will be extended to other networks.
Accept more voting rights for asset recognition: AAVE, aAAVE, stkAAVE, and stkABPT will all receive voting rights.
Implementation Structure: Governance Operation Process
All future proposals in the AAVE governance module will go through the following process:
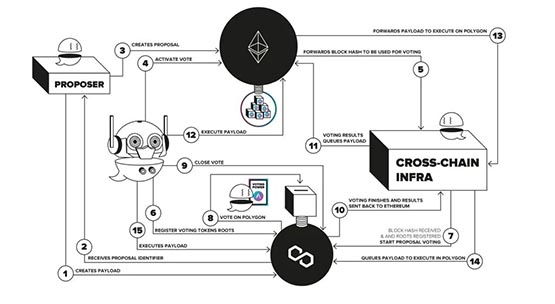
Aave Governance V3 operation process
Submit code: The proposer creates a proposal and submit code, and registers it in the controller contract of the target network. For example, if a proposal is expected to add a new asset class on Aave v3 Avalanche, you need to submit the proposal and deploy the code on Avalanche, and the entire process does not require permission.
Return the proposal identification certificate: When the proposer completes the proposal creation process, he will receive the identification certificate transmitted by the target network.
Create a proposal: Qualified proposers (with identification certificates and sufficient proposal rights) create proposals through the core governance contract on Ethereum and select the network to which the code is submitted.
Launch Proposal: After the delay period is over, the Aave bot, or any other Ethereum address, will be able to launch the proposal and complete a snapshot of the blockchain state.
Submit block hash value: The governance core contract submits the proposal information (Ethereum block hash) to the Aave cross-chain infrastructure.
Target network state settlement: On the target voting network, the Aave robot or other address completes the settlement of the global state for voting verification, including the Ethereum block hash value, its state tree, and the voting assets status tree.
Start voting: Start voting on the target network.
Proposal voting: Every user with voting rights on Ethereum can vote on the target network through the voting machine contract.
Close voting: Aave robot or other address calls the voting machine to close voting.
Result settlement: The voting results are sent to the Ethereum main network through the Aave cross-chain infrastructure in the form of "yes" and "no" counts.
Waiting for execution: The voting results arrive at the core governance contract on Ethereum, and after verifying the confirmation information, wait for execution.
Proposal execution: Aave robot or other address will execute the update code.
Cross-chain execution: Transfer the code to the corresponding execution contract on Ethereum or other networks, and start the time lock period.
Waiting for execution: Updates outside Ethereum will be queued on the corresponding controller.
Proposal Execution: Once the locking period ends, the updated code of the target network is executed by the Aave robot or other address.
Implementation Architecture
With the above operational architecture, we can better understand what components are included in the core module of Aave Governance V3:
Ethereum Core Governance Contract: Responsible Settlement decisions for all governance modules. Responsible for verifying user voting rights, status snapshots, determining voting tokens, determining voting rule logic, canceling malicious proposals through Guardian, forwarding proposals to the target network, and retaining most of the operating principles of Aave Governance V2.
Target network governance contract (Aave voting machine): Responsible for the governance operations of the target network. Contains the code and interaction of the proposer, execution of voting logic, return of voting results, etc.
Cross-chain communication facilities: Brand-new cross-chain communication facilities to meet the bridging needs of various networks in the future. The main functions include two-way communication, customized functions, and emergency backdoor mechanism.
Aave Robot: To realize the automation of most governance functions, the cost of interacting with the network is directly borne by Aave DAO, and Chainlink Automation is selected as the core of the operation. The main functions include triggering proposals after the delay period, providing status proof to the target network, executing update codes of Ethereum and the target network, etc.
In addition, due to the significant changes in the overall governance structure rules, users need to access the voting machines of each network, so the core team BGDLabs re-created the open source front-end interface and provided users with the code to create their own copies.

Currently there are no proposals for this front-end interface
Aave Governance V3 Advantages
The cost of voting is greatly reduced: by voting on the external network, taking the current gas fee level on Polygon as an example, voting The cost will be between $0.05 and $0.1. About 100 times cheaper than the current cost of voting in Aave Governance v2. It is even possible to allow participants to vote completely free. In the future, it will be recommended that the DAO bear the voting costs of all participants. If there are 10,000 participants, the total cost will only be $750, which is affordable.
Native token operation costs are reduced: There are no longer balance history snapshots on AAVE and stkAAVE. These token smart contracts will be upgraded in Aave Governance V3. It is expected that transfers of AAVE and stkAAVE will be about 75% cheaper.
License-free automation: Although Aave Governance V3 has many links that require interaction with the blockchain to produce state transitions, these links can be automatically executed by Aave robots. Compared with V2, which requires manual execution by users, Much more convenient.
The above is the detailed content of Aave Governance V3 is officially launched, pushing on-chain governance to a new level!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Is the SEC suspected of market manipulation? Industry experts' views on fake news about Bitcoin ETF approval
- Sony, Fidelity, Ark and other companies submitted securities registration applications for Bitcoin spot ETFs to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
- Summary of fees for various Bitcoin spot ETFs: Grayscale fees are up to 1.5%, and Ark and Bitwise are free in the initial stage.
- Tim Draper calls again: Bitcoin will be worth $250,000 by 2024! He Praises Bitcoin's Second Layer Solution Stacks
- SEC is about to approve multiple companies' Bitcoin spot ETFs, and final opinions will be given soon

