 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Exploring Computer Vision (CV): Meaning, Principles, Applications, and Research
Exploring Computer Vision (CV): Meaning, Principles, Applications, and ResearchExploring Computer Vision (CV): Meaning, Principles, Applications, and Research

Computer vision (CV) is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that aims to enable computers to imitate the human visual system to better understand and interpret digital images and videos. content. This process mainly involves image acquisition, screening, analysis, recognition and information extraction. It can be said that AI gives computers the ability to think, while CV gives them the ability to observe and understand.
The value of computer vision
Computer vision systems are trained and optimized to analyze a large number of products or processes in real time to help identify problems. Its speed, objectivity, continuity, accuracy and scalability exceed human capabilities. It is able to inspect products, observe infrastructure or production processes, and perform real-time analysis. The application of this technology makes problem discovery more efficient and accurate.
The latest computer vision deep learning models have demonstrated superhuman accuracy and performance in real-world image recognition tasks. These models have achieved significant breakthroughs in facial recognition, object detection, and image classification. With the advancement of technology, computer vision has been widely used in various industries. It plays an important role in security and medical imaging, manufacturing, automotive, agriculture, construction, smart cities, transportation, and more. Moreover, with the continuous development of technology, computer vision has become more flexible and scalable, which also brings the possibility of more practical application cases.
According to relevant media estimates, the computer vision market will reach US$144 billion by 2028.
Computer vision working steps and principles
Let us first understand the basic working steps of computer vision:
Step 1, image acquisition, the camera or image sensor inputs digital images.
Step 2, preprocessing, the original image input needs to be preprocessed to optimize the performance of subsequent computer vision tasks. Preprocessing includes noise reduction, contrast enhancement, rescaling or image cropping.
Step 3, algorithm processing, computer vision algorithms perform object detection, image segmentation and classification on each image or video frame.
Step 4, rule processing, the output information needs to be processed according to the use case condition rules. This part performs automation based on information obtained from computer vision tasks.
Let’s take a look at the working principle of computer vision:
Modern computer vision systems combine image processing, machine learning and deep learning technology, relying on Pattern recognition and deep learning to self-train and understand visual data. Traditional computer vision uses machine learning, but now deep learning methods have evolved into better solutions in this field.
Many high-performance methods in modern computer vision applications are based on convolutional neural networks (CNN). This layered neural network allows computers to understand image data contextually. Given enough data, the computer learns how to differentiate between images. As the image data passes through the model, the computer applies a CNN to view the data. CNNs help deep learning models understand images by breaking them down into pixels, which are given labels to train specific features, so-called image annotations. The model performs convolutions using the labels and makes predictions about what it sees, and iteratively checks the accuracy of the predictions until the predictions are as expected. Deep learning relies on neural networks and uses examples to solve problems. It learns on its own by using labeled data to identify common use cases in examples.
Application fields of computer vision
Manufacturing industry: Industrial computer vision is used in the manufacturing industry for automated product inspection, object counting, and process automation. , and improve employee safety through PPE testing and mask testing.
Healthcare: Among the applications of computer vision in healthcare, a prominent example is automatic human fall detection to create fall risk scores and trigger alerts.
Security: In video surveillance and security, personnel detection is performed to achieve intelligent perimeter monitoring.
Agriculture: A use case for computational vision in agriculture is to automatically monitor animals and detect animal diseases and abnormalities early.
Smart Cities: Computer vision is used in smart cities for crowd analysis, traffic analysis, vehicle counting and infrastructure inspection.
Retail: Video from retail store surveillance cameras can be used to track customer movement patterns for people counting or traffic analysis.
Insurance: Computer Vision in Insurance leverages AI vision for automated risk management and assessment, claims management, and forward-looking analysis.
Logistics: Automation to save costs through reduced human error, predictive maintenance and accelerated operations across the supply chain.
Pharmaceutical: Computer vision in the pharmaceutical industry is used for packaging inspection, capsule identification, and visual inspection of equipment cleaning.
Computer Vision Research Direction
Object recognition: Determine whether image data contains one or more specified or learned objects or object classes.
Facial recognition: Recognize faces by matching them to a database.
Object detection: Analyze image data for specific conditions and locate semantic objects of a given class.
Pose estimation: Estimating the relative direction and position of a specific object.
Optical character recognition: Recognizes characters in images, often combined with text encoding.
Scene understanding: Parse images into meaningful segments for analysis.
Motion Analysis: Track the movement of points of interest or objects in an image sequence or video.
The above is the detailed content of Exploring Computer Vision (CV): Meaning, Principles, Applications, and Research. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s
 New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AMGoogle's Gemini Advanced: New Subscription Tiers on the Horizon Currently, accessing Gemini Advanced requires a $19.99/month Google One AI Premium plan. However, an Android Authority report hints at upcoming changes. Code within the latest Google P
 How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AMDespite the hype surrounding advanced AI capabilities, a significant challenge lurks within enterprise AI deployments: data processing bottlenecks. While CEOs celebrate AI advancements, engineers grapple with slow query times, overloaded pipelines, a
 MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AM
MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AMHandling documents is no longer just about opening files in your AI projects, it’s about transforming chaos into clarity. Docs such as PDFs, PowerPoints, and Word flood our workflows in every shape and size. Retrieving structured
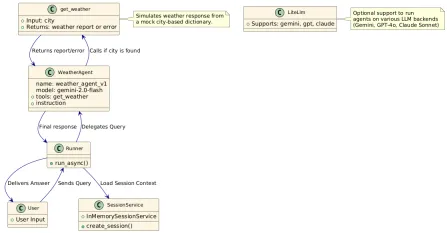 How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AMHarness the power of Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) to create intelligent agents with real-world capabilities! This tutorial guides you through building conversational agents using ADK, supporting various language models like Gemini and GPT. W
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
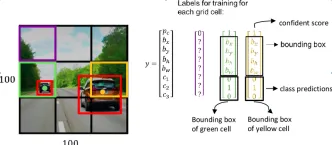 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize
 Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AM
Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AMThe AI landscape of 2025 is electrifying with the arrival of Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash and OpenAI's o4-mini. These cutting-edge models, launched weeks apart, boast comparable advanced features and impressive benchmark scores. This in-depth compariso


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function






