
Text data clustering is an unsupervised learning method used to group similar texts into one category. It can discover hidden patterns and structures and is suitable for applications such as information retrieval, text classification and text summarization.
The basic idea of text data clustering is to divide text data sets into multiple categories or clusters based on similarities. Each cluster contains a group of texts with similar words, topics, or semantics. The goal of the clustering algorithm is to maximize the similarity of texts within the same cluster and to maximize the difference of texts between different clusters. Through clustering, we can effectively classify and organize text data to better understand and analyze text content.
The following are the general steps for text data clustering:
1. Collect and prepare data sets
First, collect the text data set that needs to be clustered. Next, the text data is preprocessed and cleaned, including removing unnecessary punctuation, stop words, numbers, and special characters, and converting all words to lowercase.
2. Feature extraction
Next, the text data needs to be converted into a vector representation that can be processed by the clustering algorithm. Commonly used techniques include Bag-of-Words and Word Embedding. The bag-of-words model represents each text as a word frequency vector, where each element of the vector represents the number of times a word appears in the text. Word vectors are a technique for mapping words into a low-dimensional vector space, often trained using deep learning methods.
3. Select a clustering algorithm
Choosing an appropriate clustering algorithm is one of the key steps in the clustering task. The choice of clustering algorithm is usually based on the size, nature and objectives of the data set. Commonly used clustering algorithms include K-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, density clustering, spectral clustering, etc.
4. Determine the number of clusters
Before starting clustering, you need to determine how many clusters the text data set should be divided into. This is often a challenging task since the number of categories may be unknown. Commonly used methods include the elbow method and the silhouette coefficient method.
5. Apply the clustering algorithm
#Once the appropriate clustering algorithm and number of clusters have been selected, the algorithm can be applied to the text data Set and generate clusters. The clustering algorithm iteratively assigns texts into different clusters until a stopping criterion or a maximum number of iterations is reached.
6. Evaluate the clustering effect
Finally, the clustering effect needs to be evaluated to determine the quality of the clustering algorithm. Commonly used evaluation indicators include clustering purity, clustering accuracy, F-measure, etc. These metrics can help determine whether the clustering is correct and whether improvements are necessary.
It should be noted that text data clustering is an important data mining and information retrieval technology, involving a variety of clustering algorithms. Different clustering algorithms have different advantages, disadvantages and scope of application. It is necessary to select the appropriate algorithm based on specific application scenarios.
In text data clustering, commonly used clustering algorithms include K-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, density clustering, spectral clustering, etc.
1. K-means clustering
K-means clustering is a distance-based clustering algorithm that divides text data sets is K clusters, minimizing the distance between texts within the same cluster. The main idea of this algorithm is to first select K random center points, then iteratively assign each text to the nearest center point, and update the center points to minimize the average intra-cluster distance. The algorithm usually requires a specified number of clusters, so an evaluation metric is needed to determine the optimal number of clusters.
2. Hierarchical clustering
Hierarchical clustering is a similarity-based clustering algorithm that divides text data sets into A series of nested clusters. The main idea of the algorithm is to first treat each text as a cluster, and then iteratively merge these clusters into larger clusters until a predetermined stopping condition is reached. There are two types of hierarchical clustering algorithms: agglomerative hierarchical clustering and divisive hierarchical clustering. In agglomerative hierarchical clustering, each text starts as a separate cluster, and then the most similar clusters are merged into a new cluster until all texts belong to the same cluster. In divisive hierarchical clustering, each text initially belongs to a large cluster, and then this large cluster is divided into smaller clusters until a predetermined stopping condition is reached.
3. Density clustering
Density clustering is a density-based clustering algorithm that can discover clusters with arbitrary shapes. . The main idea of this algorithm is to divide the text data set into different density areas, and the text within each density area is regarded as a cluster. Density clustering algorithms use density reachability and density connectivity to define clusters. Density reachability means that the distance between texts is less than a certain density threshold, while density connectivity means that texts can reach each other through a series of density-reachable texts.
4. Spectral clustering
Спектральная кластеризация — это алгоритм кластеризации, основанный на теории графов, который использует метод спектральной декомпозиции для преобразования набора текстовых данных в маломерное пространство признаков, а затем выполняет кластеризацию в этом пространстве. Основная идея этого алгоритма — рассматривать набор текстовых данных в виде графа, где каждый текст является узлом, а ребра между узлами представляют сходство между текстами. Затем граф преобразуется в низкоразмерное пространство признаков с использованием метода спектральной декомпозиции, и в этом пространстве выполняется кластеризация с использованием кластеризации K-средних или других алгоритмов кластеризации. По сравнению с другими алгоритмами кластеризации, спектральная кластеризация может обнаруживать кластеры произвольной формы и имеет более высокую устойчивость к шуму и выбросам.
Вкратце, кластеризация текстовых данных — это метод, который группирует похожие тексты в наборе текстовых данных в одну категорию. Это важный метод интеллектуального анализа данных и поиска информации, который можно использовать во многих приложениях. Этапы кластеризации текстовых данных включают сбор и подготовку наборов данных, извлечение признаков, выбор алгоритма кластеризации, определение количества кластеров, применение алгоритма кластеризации и оценку эффекта кластеризации.
The above is the detailed content of Understand and implement text data clustering. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
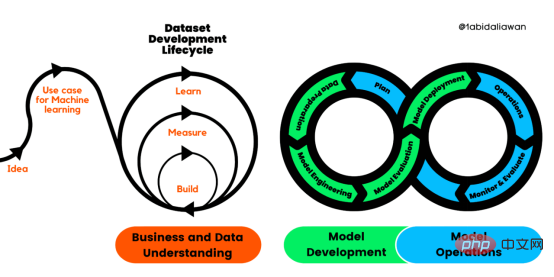 解读CRISP-ML(Q):机器学习生命周期流程Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:21 PM
解读CRISP-ML(Q):机器学习生命周期流程Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:21 PM译者 | 布加迪审校 | 孙淑娟目前,没有用于构建和管理机器学习(ML)应用程序的标准实践。机器学习项目组织得不好,缺乏可重复性,而且从长远来看容易彻底失败。因此,我们需要一套流程来帮助自己在整个机器学习生命周期中保持质量、可持续性、稳健性和成本管理。图1. 机器学习开发生命周期流程使用质量保证方法开发机器学习应用程序的跨行业标准流程(CRISP-ML(Q))是CRISP-DM的升级版,以确保机器学习产品的质量。CRISP-ML(Q)有六个单独的阶段:1. 业务和数据理解2. 数据准备3. 模型
 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
 2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。 本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术是一个教计算机从数据中学习的过程,无需明确的编程。机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。为了保持领先,数据科学家应该关注其中一些网站,以跟上最新的发展。这将有助于了解机器学习中的技术如何在实践中使用,并为自己的业务或工作领域中的可能应用提供想法。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术:1. 深度神经网
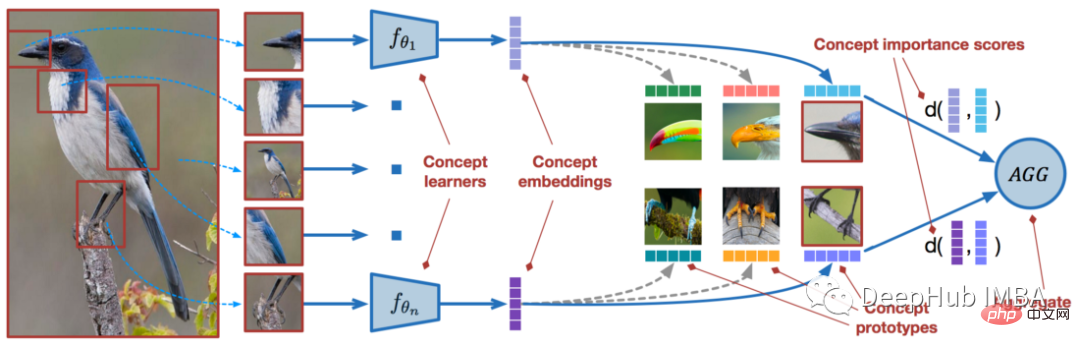 使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM
使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM近年来,基于深度学习的模型在目标检测和图像识别等任务中表现出色。像ImageNet这样具有挑战性的图像分类数据集,包含1000种不同的对象分类,现在一些模型已经超过了人类水平上。但是这些模型依赖于监督训练流程,标记训练数据的可用性对它们有重大影响,并且模型能够检测到的类别也仅限于它们接受训练的类。由于在训练过程中没有足够的标记图像用于所有类,这些模型在现实环境中可能不太有用。并且我们希望的模型能够识别它在训练期间没有见到过的类,因为几乎不可能在所有潜在对象的图像上进行训练。我们将从几个样本中学习
 LazyPredict:为你选择最佳ML模型!Apr 06, 2023 pm 08:45 PM
LazyPredict:为你选择最佳ML模型!Apr 06, 2023 pm 08:45 PM本文讨论使用LazyPredict来创建简单的ML模型。LazyPredict创建机器学习模型的特点是不需要大量的代码,同时在不修改参数的情况下进行多模型拟合,从而在众多模型中选出性能最佳的一个。 摘要本文讨论使用LazyPredict来创建简单的ML模型。LazyPredict创建机器学习模型的特点是不需要大量的代码,同时在不修改参数的情况下进行多模型拟合,从而在众多模型中选出性能最佳的一个。本文包括的内容如下:简介LazyPredict模块的安装在分类模型中实施LazyPredict
 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
 人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM
人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM实现自我完善的过程是“机器学习”。机器学习是人工智能核心,是使计算机具有智能的根本途径;它使计算机能模拟人的学习行为,自动地通过学习来获取知识和技能,不断改善性能,实现自我完善。机器学习主要研究三方面问题:1、学习机理,人类获取知识、技能和抽象概念的天赋能力;2、学习方法,对生物学习机理进行简化的基础上,用计算的方法进行再现;3、学习系统,能够在一定程度上实现机器学习的系统。
 超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM本文将详细介绍用来提高机器学习效果的最常见的超参数优化方法。 译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟简介通常,在尝试改进机器学习模型时,人们首先想到的解决方案是添加更多的训练数据。额外的数据通常是有帮助(在某些情况下除外)的,但生成高质量的数据可能非常昂贵。通过使用现有数据获得最佳模型性能,超参数优化可以节省我们的时间和资源。顾名思义,超参数优化是为机器学习模型确定最佳超参数组合以满足优化函数(即,给定研究中的数据集,最大化模型的性能)的过程。换句话说,每个模型都会提供多个有关选项的调整“按钮


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






