Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Code logic for implementing mini-batch gradient descent algorithm using Python
Code logic for implementing mini-batch gradient descent algorithm using Python
- PHPzforward
- 2024-01-22 12:33:191622browse
Let theta = model parameters and max_iters = number of epochs. For itr=1,2,3,...,max_iters: For mini_batch(X_mini,y_mini):
Forward pass of batch X_mini:
1. Predict small batches
2. Use the current value of the parameter to calculate the prediction error (J(theta))
Post-transmission: Calculate the gradient (theta)=J(theta)wrt the partial derivative of theta
Update parameters: theta=theta–learning_rate*gradient(theta)
Code process for implementing gradient descent algorithm in Python
Step 1: Import dependencies, generate data for linear regression, and visualize it generated data. Take 8000 data examples, each example has 2 attribute features. These data samples are further divided into training set (X_train, y_train) and test set (X_test, y_test), with 7200 and 800 samples respectively.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mean=np.array([5.0,6.0]) cov=np.array([[1.0,0.95],[0.95,1.2]]) data=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean,cov,8000) plt.scatter(data[:500,0],data[:500,1],marker='.') plt.show() data=np.hstack((np.ones((data.shape[0],1)),data)) split_factor=0.90 split=int(split_factor*data.shape[0]) X_train=data[:split,:-1] y_train=data[:split,-1].reshape((-1,1)) X_test=data[split:,:-1] y_test=data[split:,-1].reshape((-1,1)) print(& quot Number of examples in training set= % d & quot % (X_train.shape[0])) print(& quot Number of examples in testing set= % d & quot % (X_test.shape[0]))
Number of examples in the training set = 7200 Number of examples in the test set = 800
Step 2:
Code to implement linear regression using mini-batch gradient descent . gradientDescent() is the main driving function, and other functions are auxiliary functions:
Prediction-hypothesis()
Calculate gradient-gradient()
Calculate error- —cost()
Create mini-batches —create_mini_batches()
Driver function initializes parameters, calculates the optimal parameter set for the model, and returns these parameters along with a list containing parameter updates error history.
def hypothesis(X,theta):
return np.dot(X,theta)
def gradient(X,y,theta):
h=hypothesis(X,theta)
grad=np.dot(X.transpose(),(h-y))
return grad
def cost(X,y,theta):
h=hypothesis(X,theta)
J=np.dot((h-y).transpose(),(h-y))
J/=2
return J[0]
def create_mini_batches(X,y,batch_size):
mini_batches=[]
data=np.hstack((X,y))
np.random.shuffle(data)
n_minibatches=data.shape[0]//batch_size
i=0
for i in range(n_minibatches+1):
mini_batch=data[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size,:]
X_mini=mini_batch[:,:-1]
Y_mini=mini_batch[:,-1].reshape((-1,1))
mini_batches.append((X_mini,Y_mini))
if data.shape[0]%batch_size!=0:
mini_batch=data[i*batch_size:data.shape[0]]
X_mini=mini_batch[:,:-1]
Y_mini=mini_batch[:,-1].reshape((-1,1))
mini_batches.append((X_mini,Y_mini))
return mini_batches
def gradientDescent(X,y,learning_rate=0.001,batch_size=32):
theta=np.zeros((X.shape[1],1))
error_list=[]
max_iters=3
for itr in range(max_iters):
mini_batches=create_mini_batches(X,y,batch_size)
for mini_batch in mini_batches:
X_mini,y_mini=mini_batch
theta=theta-learning_rate*gradient(X_mini,y_mini,theta)
error_list.append(cost(X_mini,y_mini,theta))
return theta,error_listCall the gradientDescent() function to calculate the model parameters (theta) and visualize the changes in the error function.
theta,error_list=gradientDescent(X_train,y_train)
print("Bias=",theta[0])
print("Coefficients=",theta[1:])
plt.plot(error_list)
plt.xlabel("Number of iterations")
plt.ylabel("Cost")
plt.show()Deviation=[0.81830471]Coefficient=[[1.04586595]]
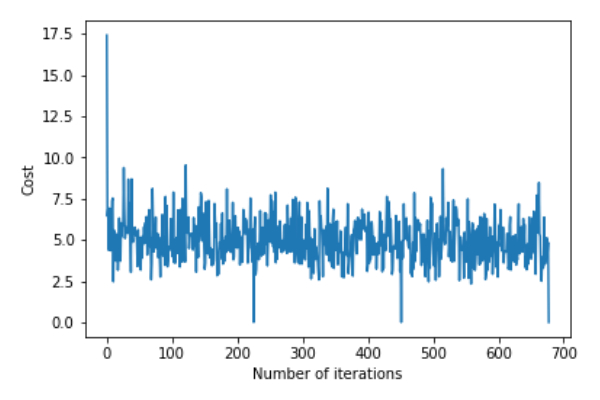
Step 3: Predict the test set and calculate the average absolute error in the prediction.
y_pred=hypothesis(X_test,theta) plt.scatter(X_test[:,1],y_test[:,],marker='.') plt.plot(X_test[:,1],y_pred,color='orange') plt.show() error=np.sum(np.abs(y_test-y_pred)/y_test.shape[0]) print(& quot Mean absolute error=",error)
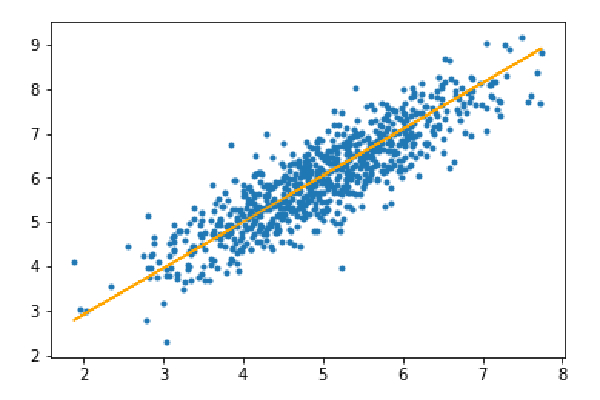
Mean absolute error=0.4366644295854125
The orange line represents the final hypothesis function: theta[0] theta[1]*X_test[:,1] theta[2]*X_test[ :,2]=0
The above is the detailed content of Code logic for implementing mini-batch gradient descent algorithm using Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

