 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Demystifying front-end closures: What common application scenarios do you know?
Demystifying front-end closures: What common application scenarios do you know?
Revealing the common application scenarios of front-end closures: Do you know where it is widely used?
Closure is a very important concept in JavaScript and one of the features often used in front-end development. It can handle variable scope and protect data efficiently, while also providing a powerful mechanism to handle asynchronous operations and function encapsulation.
So, do you know what common application scenarios of closures in front-end development? Next, we will reveal some common application scenarios of closures and give specific code examples.
1. Modular development
In front-end development, we often use modular development to organize code structure and encapsulate functions. Closures can help us achieve modular development. By using closures, we can hide some private variables and methods and only expose some public interfaces for external use.
The following is a simple example showing how to use closures to implement a counter module:
var Counter = (function() {
var count = 0;
function increment() {
count++;
console.log(count);
}
function decrement() {
count--;
console.log(count);
}
return {
increment: increment,
decrement: decrement
};
})();
Counter.increment(); // 输出 1
Counter.increment(); // 输出 2
Counter.decrement(); // 输出 1In the above code, we create a closure using an immediate execution function. The package contains a private variable count and two private methods increment and decrement. In this way, the outside world cannot directly access and modify count, and can only operate through the exposed public interface increment and decrement methods.
2. Event processing
Closure can also help us save some status or data during event processing. Usually, when binding an event handling function, we cannot directly pass some additional parameters to the function. However, by using closures, we can save these parameters in the closure and retrieve and use them when the event fires.
Here is a simple example showing how to use closures to save and use additional parameters:
function createButton(text) {
var button = document.createElement('button');
button.innerHTML = text;
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert(text);
});
return button;
}
var button1 = createButton('Button 1');
var button2 = createButton('Button 2');
document.body.appendChild(button1);
document.body.appendChild(button2);In the above code, we define a createButton Function, this function accepts a text parameter text and returns a created button element. While creating the button, we use a closure to save the text corresponding to the button. When the button is clicked, the text saved in the closure will pop up.
3. Asynchronous operations
Closures are also very useful when dealing with asynchronous operations. By using closures, we can access and process some variables or data after the asynchronous operation is completed. This method is often used in Ajax requests, timers, event binding and other scenarios.
The following is a simple example showing how to use closures to handle an asynchronous operation:
function fetchData(url, callback) {
setTimeout(function() {
var data = 'Some data';
callback(data);
}, 1000);
}
var result;
fetchData('https://example.com/api', function(data) {
result = data;
});
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(result); // 输出 'Some data'
}, 2000);In the above code, we define a fetchData function, This function returns some data by simulating an asynchronous operation. After the asynchronous operation is completed, we use a closure to save the returned data and then access and use it again at a later time.
Closure is a very powerful and important concept in JavaScript. It has a wide range of application scenarios in front-end development. Not only can it help us achieve modular development, but it can also handle events and asynchronous operations. By using closures flexibly, we can better write maintainable and performant front-end code.
I hope the application scenarios of closures introduced in this article can be helpful to you and can be used flexibly in actual development.
The above is the detailed content of Demystifying front-end closures: What common application scenarios do you know?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 5个常见的JavaScript内存错误Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AM
5个常见的JavaScript内存错误Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AMJavaScript 不提供任何内存管理操作。相反,内存由 JavaScript VM 通过内存回收过程管理,该过程称为垃圾收集。
 实战:vscode中开发一个支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:43 PM
实战:vscode中开发一个支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:43 PMvscode自身是支持vue文件组件跳转到定义的,但是支持的力度是非常弱的。我们在vue-cli的配置的下,可以写很多灵活的用法,这样可以提升我们的生产效率。但是正是这些灵活的写法,导致了vscode自身提供的功能无法支持跳转到文件定义。为了兼容这些灵活的写法,提高工作效率,所以写了一个vscode支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件。
 Node.js 19正式发布,聊聊它的 6 大特性!Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node.js 19正式发布,聊聊它的 6 大特性!Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PMNode 19已正式发布,下面本篇文章就来带大家详解了解一下Node.js 19的 6 大特性,希望对大家有所帮助!
 聊聊如何选择一个最好的Node.js Docker镜像?Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
聊聊如何选择一个最好的Node.js Docker镜像?Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM选择一个Node的Docker镜像看起来像是一件小事,但是镜像的大小和潜在漏洞可能会对你的CI/CD流程和安全造成重大的影响。那我们如何选择一个最好Node.js Docker镜像呢?
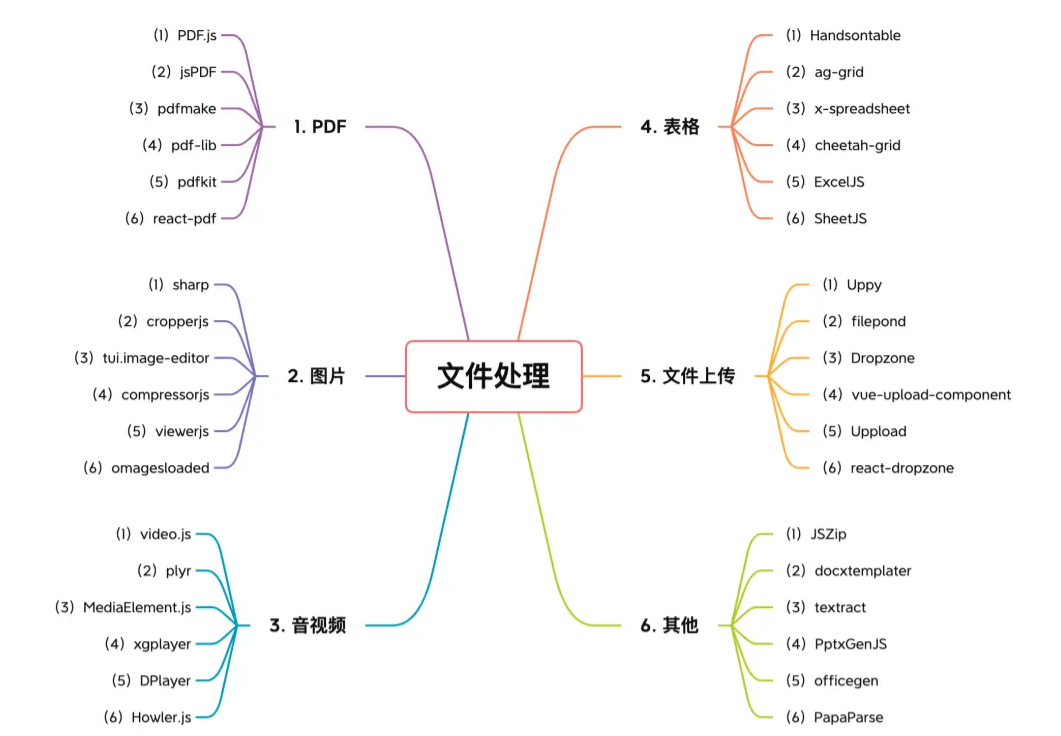 【6大类】实用的前端处理文件的工具库,快来收藏吧!Jul 15, 2022 pm 02:58 PM
【6大类】实用的前端处理文件的工具库,快来收藏吧!Jul 15, 2022 pm 02:58 PM本篇文章给大家整理和分享几个前端文件处理相关的实用工具库,共分成6大类一一介绍给大家,希望对大家有所帮助。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.








