 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Chinese Academy of Sciences team creates a unified framework for improving prediction accuracy of enzyme kinetic parameters
Chinese Academy of Sciences team creates a unified framework for improving prediction accuracy of enzyme kinetic parameters
Editor | Radish Skin
Prediction of enzyme kinetic parameters is crucial for the design and optimization of enzymes in biotechnology and industrial applications. However, current prediction tools are Limited performance on various tasks limits their practical applications.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently proposed UniKP, a unified framework based on pre-trained language models that can be used to predict enzyme kinetic parameters, including enzyme turnover number (kcat), Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) and catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km), these parameters were obtained from the protein sequence and substrate structure.
A two-layer framework based on UniKP (EF-UniKP) is also proposed, which is capable of stably predicting kcat values taking into account environmental factors such as pH and temperature. At the same time, the research team also systematically explored four representative reweighting methods, successfully reducing prediction errors in high-value prediction tasks.
The study is titled "UniKP: a unified framework for the prediction of enzyme kinetic parameters" and was published in the journal "Nature Communications" on December 11, 2023.

Studying the catalytic efficiency of enzymes towards specific substrates is an important issue in biology and has a profound impact on enzyme evolution, metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. In vitro experimental data measuring kcat and Km, as well as the maximum turnover rate and Michaelis-Menten constant, can be used as indicators to measure the efficiency of enzymes in catalyzing specific reactions and to compare the relative catalytic activities of different enzymes.
At present, the measurement of enzyme kinetic parameters mainly relies on experimental measurement, which is time-consuming, costly and labor-intensive, resulting in a small database of experimentally measured kinetic parameter values. For example, the sequence database UniProt contains over 230 million enzyme sequences, while the enzyme databases BRENDA and SABIO-RK contain tens of thousands of experimentally measured kcat values. The integration of Uniprot identifiers in these enzyme databases facilitates the connection between measured parameters and protein sequences. However, the scale of these connections is still much smaller compared to the number of enzyme sequences, limiting progress in downstream applications such as directed evolution and metabolic engineering.
Enzyme kinetic parameter prediction framework
In this study, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a new framework called UniKP, which is based on pre-training Language model designed to improve the accuracy of predicting enzyme kinetic parameters. These parameters include kcat, Km and kcat/Km, which can be predicted given the enzyme sequence and substrate structure. The researchers conducted a comprehensive comparison of 16 different machine learning models and 2 deep learning models and found that UniKP performed well in terms of prediction accuracy. This research is expected to provide new tools and methods for research and applications in the field of enzyme kinetics.
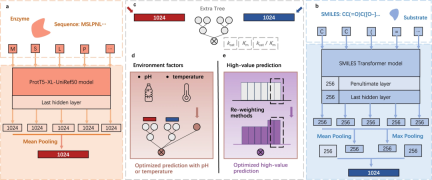
Illustration: UniKP overview. (Source: paper)
Compared with the previous state-of-the-art model DLKcat, UniKP shows superior performance in the kcat prediction task, with an average coefficient of determination of 0.68, an improvement of 20%. The researchers speculate that the pretrained models contributed significantly to UniKP's performance by using unsupervised information from the entire database to create easy-to-learn representations of enzyme sequences and substrate structures.
Analysis of model learning showed that protein information has a dominant role, possibly due to the complexity of the enzyme structure compared to the substrate structure. Furthermore, UniKP can effectively capture small differences in kcat values between enzymes and their mutants, including experimentally measured cases, which is crucial for enzyme design and modification. The difference between the R^2 of UniKP predictions and the R^2 of the gmean method for high- and low-identity regions demonstrates UniKP's ability to extract deeper interconnected information and thus perform well in these tasks. Higher forecast accuracy.
Two-layer framework EF-UniKP
Most current models do not consider environmental factors, which is a key limitation in simulating real experimental conditions. To solve this problem, the researchers proposed a two-layer framework EF-UniKP, which takes environmental factors into account. Based on two newly constructed datasets with pH and temperature information respectively, EF-UniKP shows improved performance compared to the initial UniKP. This is an accurate, high-throughput, organism-independent and context-dependent kcat prediction. Additionally, this approach has the potential to be expanded to include other factors such as co-substrate and NaCl concentration.
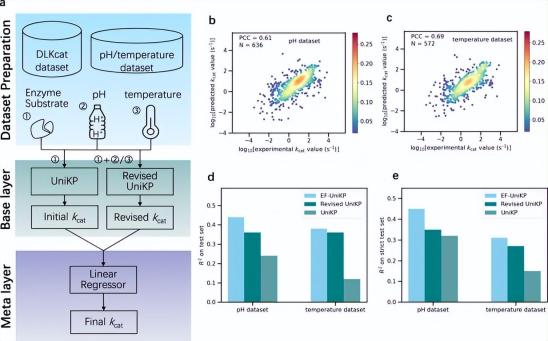
Illustration: Two-layer framework considering environmental factors. (Source: paper)
However, existing models do not consider the interaction between these factors due to a lack of comprehensive data. As experimental techniques advance, including biocast laboratory automation and continuous evolution methods, researchers anticipate a proliferation of enzyme kinetic data. This influx has not only enriched the field but also improved the accuracy of predictive models.
Due to the high imbalance of the kcat dataset, resulting in higher errors in high kcat value predictions, the team systematically explored four representative reweighting methods to alleviate this problem. The results show that the hyperparameter settings of each method are critical to improving high kcat value predictions.
The team confirmed the strong generality of the current framework in terms of Michaelis constant (Km) prediction and kcat/Km prediction. UniKP achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting Km values and, more impressively, outperforms the combined results of current state-of-the-art models in predicting kcat/Km values. Furthermore, the researchers validated the UniKP framework based on experimentally measured kcat/Km values and kcat/Km values calculated using kcat and Km prediction models on the kcat/Km dataset.
It is worth noting that the correlation observed between the values derived from UniKP kcat / UniKP Km and the experimental kcat / Km is relatively low (PCC = −0.01). This difference may be due to the different data sets used in building the respective models, thus requiring the development of a different model to predict kcat/Km values. In the future, with the emergence of unified data sets containing kcat and Km values, it is expected that the computational output of the kcat and Km models will be closely consistent with the output generated by the kcat/Km dedicated model.
Specific application in enzyme mining and evolution
The application of UniKP in the mining and directed evolution of tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) enzyme has demonstrated its ability to revolutionize synthetic biology and potential for biochemical research. This study shows that UniKP effectively recognizes highly active TALs and rapidly improves the catalytic efficiency of existing TALs, with RgTAL-489T having a kcat/Km value 3.5 times higher than that of the wild-type enzyme.
Furthermore, the derived framework EF-UniKP was always able to identify highly active TAL enzymes with extremely high accuracy, with kcat/Km values 2.6-fold higher for TrTAL from Tephrocybe rancida than the wild-type enzyme. The results showed that the kcat and kcat/Km values of the five sequences exceeded those of the wild-type enzyme.
By accelerating the enzyme discovery and optimization process, UniKP is expected to become a powerful tool for advancing biocatalysis, drug discovery, metabolic engineering and other fields that rely on enzyme-catalyzed processes.
Limitations and Outlook
However, the current version of UniKP still has some limitations. For example, while UniKP is able to differentiate between experimentally measured kcat values of an enzyme and its variants, the predicted kcat values are not accurate enough. This may be due to insufficient data sets compared to the number of known protein sequences and substrate structures.
While the reweighting method can alleviate the prediction bias caused by the unbalanced kcat dataset to a certain extent (about 6.5% improvement), more can be achieved through synthetic minority oversampling techniques and other sample synthesis methods. Significant improvement.
A central goal of synthetic biology is the development of digital cells that will revolutionize the way scientists study biology. A key prerequisite for this study is the careful determination of enzymatic parameters for all enzymes within the pathway. Artificial intelligence-assisted tools shed light on this challenge, providing a high-throughput method for predicting enzyme kinetics.
Although the UniKP predictor error is reduced compared to earlier models, inaccuracy remains a significant obstacle to building accurate metabolic models. Incorporating an increasing number of experimentally determined kcat and Km values can improve model accuracy.
Next, the researchers plan to combine state-of-the-art algorithms such as transfer learning, reinforcement learning, and other small-shot learning algorithms to effectively handle imbalanced data sets. And, the team aims to explore additional applications, including enzyme evolution and global analysis of organisms.
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-44113-1
The above is the detailed content of Chinese Academy of Sciences team creates a unified framework for improving prediction accuracy of enzyme kinetic parameters. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 五个时间序列预测的深度学习模型对比总结May 05, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
五个时间序列预测的深度学习模型对比总结May 05, 2023 pm 05:16 PMMakridakisM-Competitions系列(分别称为M4和M5)分别在2018年和2020年举办(M6也在今年举办了)。对于那些不了解的人来说,m系列得比赛可以被认为是时间序列生态系统的一种现有状态的总结,为当前得预测的理论和实践提供了经验和客观的证据。2018年M4的结果表明,纯粹的“ML”方法在很大程度上胜过传统的统计方法,这在当时是出乎意料的。在两年后的M5[1]中,最的高分是仅具有“ML”方法。并且所有前50名基本上都是基于ML的(大部分是树型模型)。这场比赛看到了LightG
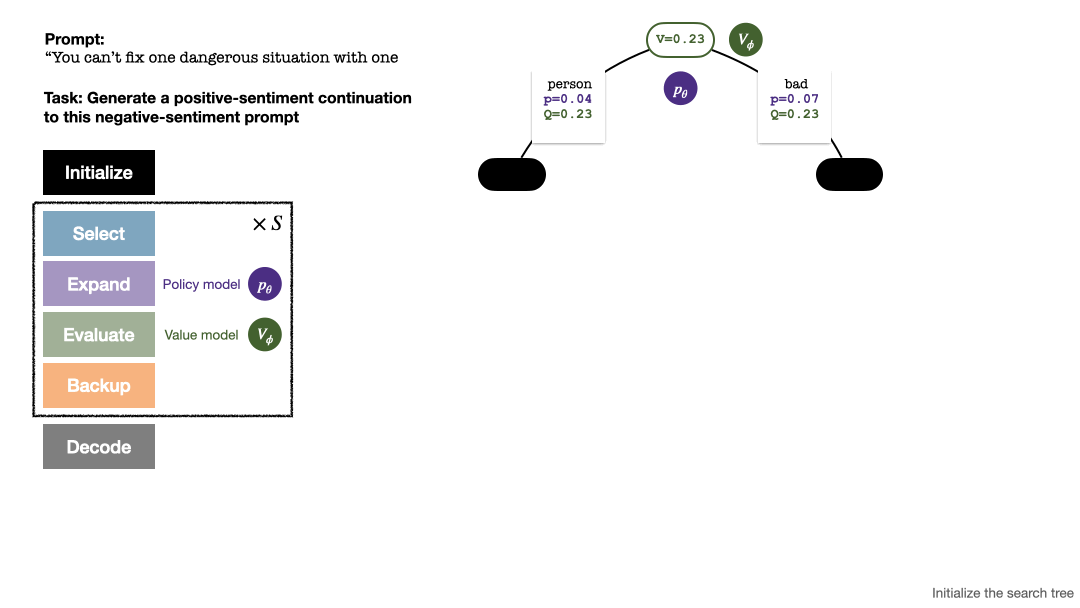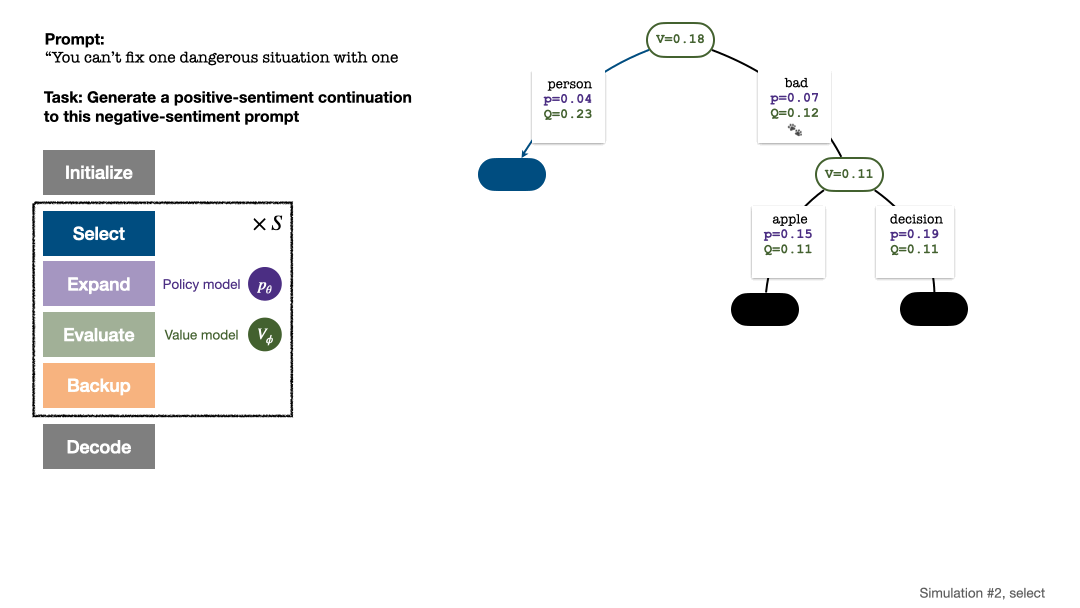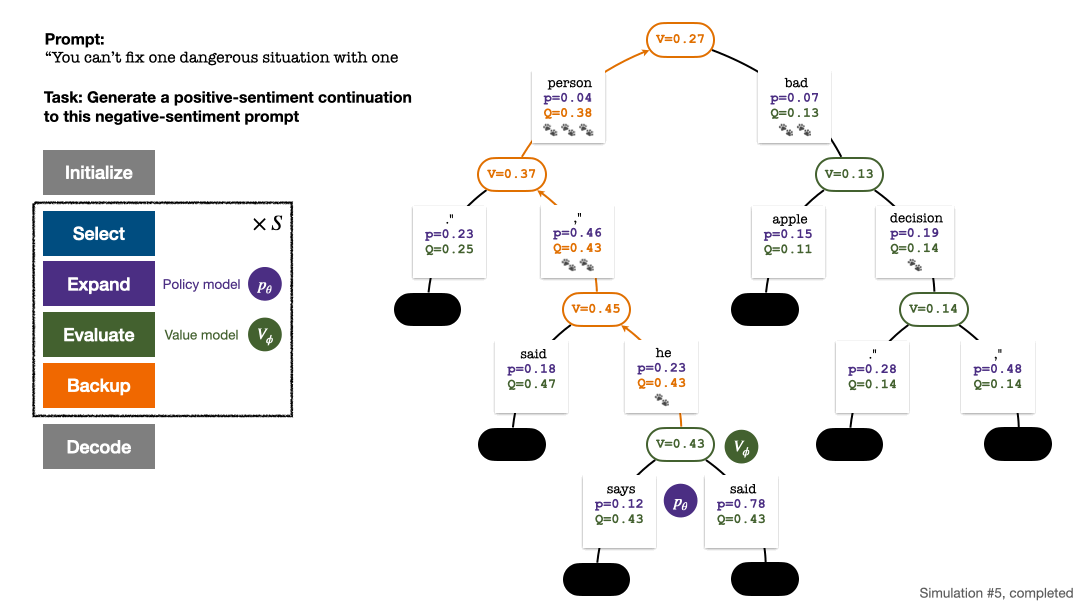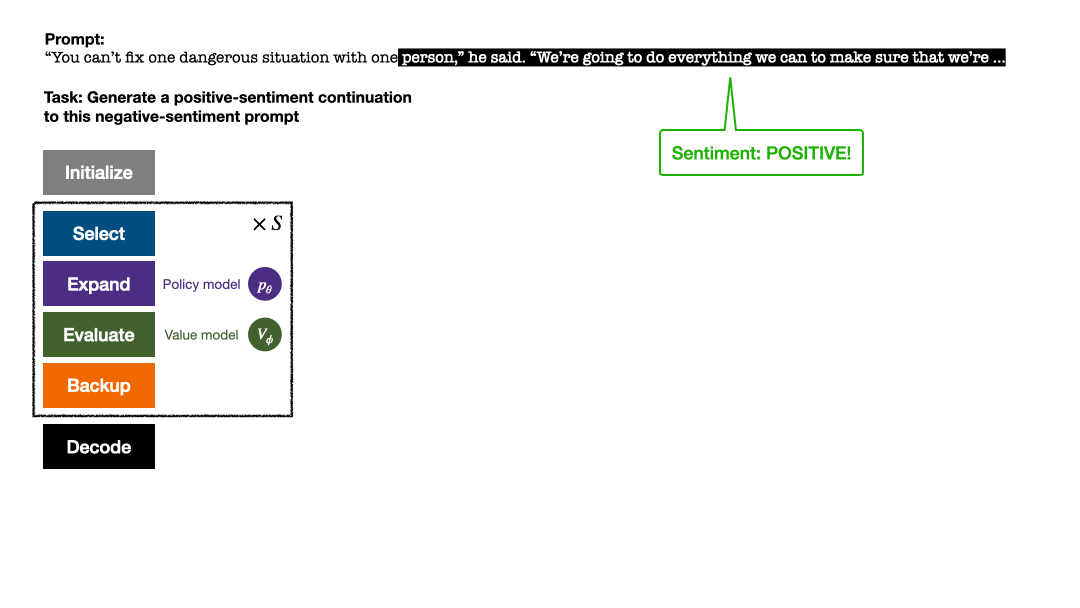 RLHF与AlphaGo核心技术强强联合,UW/Meta让文本生成能力再上新台阶Oct 27, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
RLHF与AlphaGo核心技术强强联合,UW/Meta让文本生成能力再上新台阶Oct 27, 2023 pm 03:13 PM在一项最新的研究中,来自UW和Meta的研究者提出了一种新的解码算法,将AlphaGo采用的蒙特卡洛树搜索算法(Monte-CarloTreeSearch,MCTS)应用到经过近端策略优化(ProximalPolicyOptimization,PPO)训练的RLHF语言模型上,大幅提高了模型生成文本的质量。PPO-MCTS算法通过探索与评估若干条候选序列,搜索到更优的解码策略。通过PPO-MCTS生成的文本能更好满足任务要求。论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.150
 MIT团队运用机器学习闭环自主分子发现平台,成功发现、合成和描述了303种新分子Jan 04, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
MIT团队运用机器学习闭环自主分子发现平台,成功发现、合成和描述了303种新分子Jan 04, 2024 pm 05:38 PM编辑|X传统意义上,发现所需特性的分子过程一直是由手动实验、化学家的直觉以及对机制和第一原理的理解推动的。随着化学家越来越多地使用自动化设备和预测合成算法,自主研究设备越来越接近实现。近日,来自MIT的研究人员开发了由集成机器学习工具驱动的闭环自主分子发现平台,以加速具有所需特性的分子的设计。无需手动实验即可探索化学空间并利用已知的化学结构。在两个案例研究中,该平台尝试了3000多个反应,其中1000多个产生了预测的反应产物,提出、合成并表征了303种未报道的染料样分子。该研究以《Autonom
 AI助力脑机接口研究,纽约大学突破性神经语音解码技术,登Nature子刊Apr 17, 2024 am 08:40 AM
AI助力脑机接口研究,纽约大学突破性神经语音解码技术,登Nature子刊Apr 17, 2024 am 08:40 AM作者|陈旭鹏编辑|ScienceAI由于神经系统的缺陷导致的失语会导致严重的生活障碍,它可能会限制人们的职业和社交生活。近年来,深度学习和脑机接口(BCI)技术的飞速发展为开发能够帮助失语者沟通的神经语音假肢提供了可行性。然而,神经信号的语音解码面临挑战。近日,约旦大学VideoLab和FlinkerLab的研究者开发了一个新型的可微分语音合成器,可以利用一个轻型的卷积神经网络将语音编码为一系列可解释的语音参数(例如音高、响度、共振峰频率等),并通过可微分神经网络将这些参数合成为语音。这个合成器
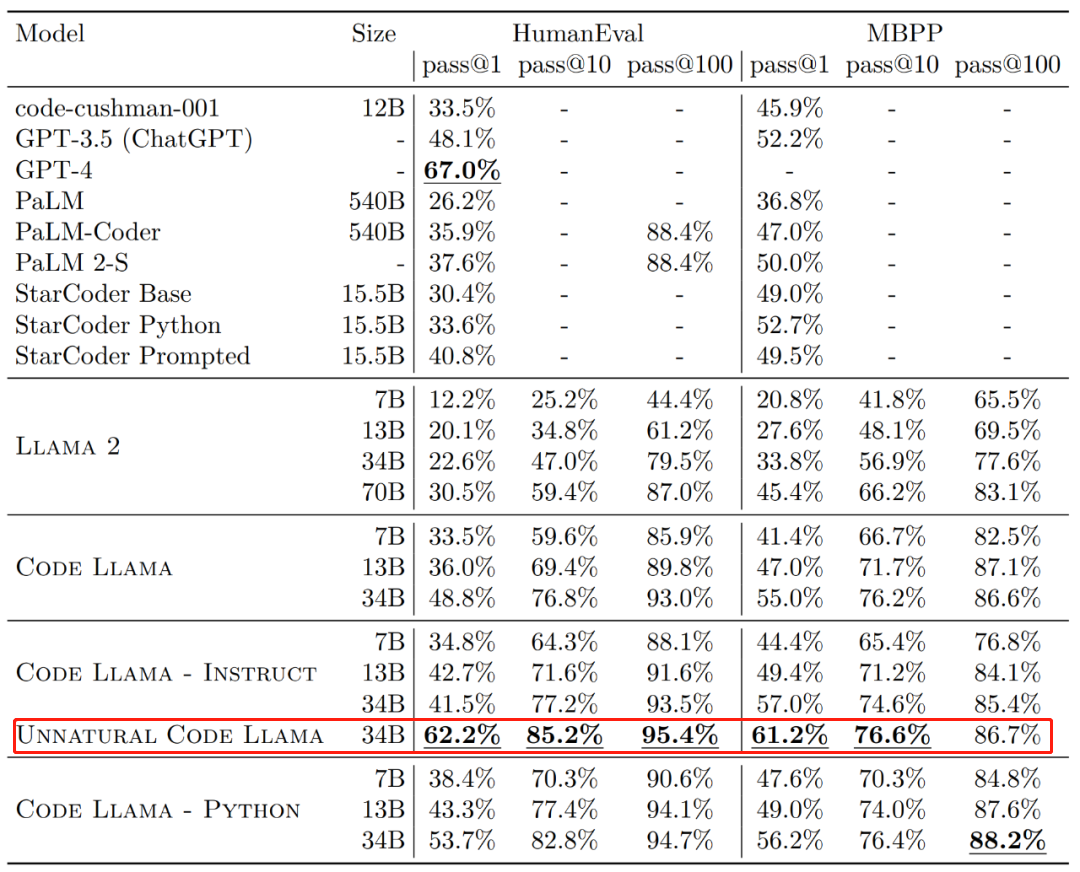 Code Llama代码能力飙升,微调版HumanEval得分超越GPT-4,一天发布Aug 26, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
Code Llama代码能力飙升,微调版HumanEval得分超越GPT-4,一天发布Aug 26, 2023 pm 09:01 PM昨天,Meta开源专攻代码生成的基础模型CodeLlama,可免费用于研究以及商用目的。CodeLlama系列模型有三个参数版本,参数量分别为7B、13B和34B。并且支持多种编程语言,包括Python、C++、Java、PHP、Typescript(Javascript)、C#和Bash。Meta提供的CodeLlama版本包括:代码Llama,基础代码模型;代码羊-Python,Python微调版本;代码Llama-Instruct,自然语言指令微调版就其效果来说,CodeLlama的不同版
 手机摄影技术让以假乱真的好莱坞级电影特效视频走红Sep 07, 2023 am 09:41 AM
手机摄影技术让以假乱真的好莱坞级电影特效视频走红Sep 07, 2023 am 09:41 AM一个普通人用一台手机就能制作电影特效的时代已经来了。最近,一个名叫Simulon的3D技术公司发布了一系列特效视频,视频中的3D机器人与环境无缝融合,而且光影效果非常自然。呈现这些效果的APP也叫Simulon,它能让使用者通过手机摄像头的实时拍摄,直接渲染出CGI(计算机生成图像)特效,就跟打开美颜相机拍摄一样。在具体操作中,你要先上传一个3D模型(比如图中的机器人)。Simulon会将这个模型放置到你拍摄的现实世界中,并使用准确的照明、阴影和反射效果来渲染它们。整个过程不需要相机解算、HDR
 准确率 >98%,基于电子密度的 GPT 用于化学研究,登 Nature 子刊Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:16 PM
准确率 >98%,基于电子密度的 GPT 用于化学研究,登 Nature 子刊Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:16 PM编辑|紫罗可合成分子的化学空间是非常广阔的。有效地探索这个领域需要依赖计算筛选技术,比如深度学习,以便快速地发现各种有趣的化合物。将分子结构转换为数字表示形式,并开发相应算法生成新的分子结构是进行化学发现的关键。最近,英国格拉斯哥大学的研究团队提出了一种基于电子密度训练的机器学习模型,用于生成主客体binders。这种模型能够以简化分子线性输入规范(SMILES)格式读取数据,准确率高达98%,从而实现对分子在二维空间的全面描述。通过变分自编码器生成主客体系统的电子密度和静电势的三维表示,然后通
 谷歌用大型模型训练机器狗理解模糊指令,激动不已准备去野餐Jan 16, 2024 am 11:24 AM
谷歌用大型模型训练机器狗理解模糊指令,激动不已准备去野餐Jan 16, 2024 am 11:24 AM人类和四足机器人之间简单有效的交互是创造能干的智能助理机器人的途径,其昭示着这样一个未来:技术以超乎我们想象的方式改善我们的生活。对于这样的人类-机器人交互系统,关键是让四足机器人有能力响应自然语言指令。近来大型语言模型(LLM)发展迅速,已经展现出了执行高层规划的潜力。然而,对LLM来说,理解低层指令依然很难,比如关节角度目标或电机扭矩,尤其是对于本身就不稳定、必需高频控制信号的足式机器人。因此,大多数现有工作都会假设已为LLM提供了决定机器人行为的高层API,而这就从根本上限制了系统的表现能


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





