 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Meituan, Zhejiang University and others cooperate to create a full-process mobile multi-modal large model MobileVLM, which can run in real time and uses the Snapdragon 888 processor
Meituan, Zhejiang University and others cooperate to create a full-process mobile multi-modal large model MobileVLM, which can run in real time and uses the Snapdragon 888 processorThe wave of large models coming to the mobile terminal is getting stronger and stronger, and finally someone has moved multi-modal large models to the mobile terminal. Recently, Meituan, Zhejiang University, etc. have launched multi-modal large models that can be deployed on the mobile terminal, including the entire process of LLM base training, SFT, and VLM. Perhaps in the near future, everyone will be able to own their own large model conveniently, quickly and at low cost.

Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.16886.pdf - ##Code address: https://github.com/Meituan- AutoML/MobileVLM
- This article proposes MobileVLM, which is a full-stack transformation of a multi-modal visual language model customized for mobile scenarios. . According to the authors, this is the first visual language model to deliver detailed, reproducible, and powerful performance from scratch. Through controlled and open source data sets, researchers have established a set of high-performance basic language models and multi-modal models.
- This paper conducts extensive ablation experiments on the design of visual encoders and systematically evaluates the performance sensitivity of VLMs to various training paradigms, input resolutions, and model sizes.
- This paper designs an efficient mapping network between visual features and text features, which can better align multi-modal features while reducing reasoning consumption.
- The model designed in this article can run efficiently on low-power mobile devices, with a measured speed of 21.5 tokens/s on Qualcomm’s mobile CPU and 65.5-inch processor.
- MobileVLM performs equally well on benchmarks as a large number of multi-modal large models, proving its application potential in many practical tasks. While this article focuses on edge scenarios, MobileVLM outperforms many state-of-the-art VLMs that can only be supported by powerful GPUs in the cloud.
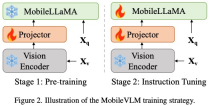
Considering the main goal of achieving efficient visual perception and reasoning for resource-limited edge devices, the researchers designed the overall architecture of MobileVLM, as shown in Figure 1 , the model consists of three components: 1) a visual encoder, 2) a customized LLM edge device (MobileLLaMA), and 3) an efficient mapping network (referred to in the paper as "Lightweight Downsampling Mapping", LDP) for alignment Visual and textual space.
 as input, the visual encoder F_enc extracts the visual embedding
as input, the visual encoder F_enc extracts the visual embedding  for image perception, where N_v = HW/P^2 represents the number of image blocks and D_v represents the hidden layer size of the visual embedding. In order to alleviate the efficiency problem of processing image tokens, the researchers designed a lightweight mapping network P for visual feature compression and visual-text modal alignment. It transforms f into the word embedding space and provides appropriate input dimensions for the subsequent language model, as follows:
for image perception, where N_v = HW/P^2 represents the number of image blocks and D_v represents the hidden layer size of the visual embedding. In order to alleviate the efficiency problem of processing image tokens, the researchers designed a lightweight mapping network P for visual feature compression and visual-text modal alignment. It transforms f into the word embedding space and provides appropriate input dimensions for the subsequent language model, as follows:
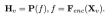
 , where N_t represents the number of text tokens, and D_t represents the size of the word embedding space. In the current MLLM design paradigm, LLM has the largest amount of calculation and memory consumption. In view of this, this article tailors a series of inference-friendly LLM for mobile applications, which has considerable advantages in speed and can perform autoregressive methods. Predict multi-modal input
, where N_t represents the number of text tokens, and D_t represents the size of the word embedding space. In the current MLLM design paradigm, LLM has the largest amount of calculation and memory consumption. In view of this, this article tailors a series of inference-friendly LLM for mobile applications, which has considerable advantages in speed and can perform autoregressive methods. Predict multi-modal input , where L represents the length of the output tokens. This process can be expressed as
, where L represents the length of the output tokens. This process can be expressed as  .
. 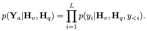
- Apply RoPE to inject location information.
- Apply pre-normalization to stabilize training. Specifically, this paper uses RMSNorm instead of layer normalization, and the MLP expansion ratio uses 8/3 instead of 4.
- Use SwiGLU activation function instead of GELU.

 and outputs an efficiently extracted and aligned visual token
and outputs an efficiently extracted and aligned visual token  .
. 



In Table 7, the researchers compared the multi-modal performance at different scales and different numbers of visual tokens. All experiments used CLIP ViT as the visual encoder.

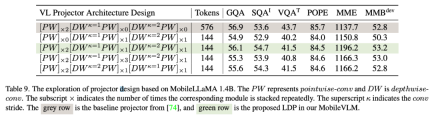
Due to feature interaction and token Both interactions are beneficial. The researchers used depth convolution for the former and point convolution for the latter. Table 9 shows the performance of various VL mapped networks. Row 1 in Table 9 is the module used in LLaVA, which only transforms the feature space through two linear layers. Line 2 adds a DW (depthwise) convolution before each PW (pointwise) for token interaction, which uses 2x downsampling with a stride of 2. Adding two front-end PW layers will bring more feature-level interactions, thus making up for the performance loss caused by the reduction of tokens. Lines 4 and 5 show that adding more parameters does not achieve the desired effect. Lines 4 and 6 show that downsampling tokens at the end of the mapping network has a positive effect.
Since the number of visual tokens directly affects the entire For modal model inference speed, this paper compares two design options: reducing the input resolution (RIR) and using a lightweight downsampling projector (LDP).
at Vicuna fine-tuned on LLaMA is widely used for large multimodal models. Table 10 compares two common SFT paradigms, Alpaca and Vicuna. The researchers found that the scores of SQA, VQA, MME, and MMBench all improved significantly. This shows that fine-tuning large language models using data from ShareGPT in Vicuna conversational mode ultimately yields the best performance. In order to better integrate SFT's prompt format with the training of downstream tasks, this paper removes the conversation mode on MobileVLM and finds that vicunav1 performs best.

In short, MobileVLM is a suite of tools designed for mobile and An efficient and powerful mobile visual language model customized for IoT devices. This paper resets the language model and visual mapping network. The researchers conducted extensive experiments to select an appropriate visual backbone network, design an efficient mapping network, and enhance model capabilities through training solutions such as language model SFT (a two-stage training strategy including pre-training and instruction adjustment) and LoRA fine-tuning. . Researchers rigorously evaluated the performance of MobileVLM on mainstream VLM benchmarks. MobileVLM also shows unprecedented speeds on typical mobile and IoT devices. The researchers believe that MobileVLM will open up new possibilities for a wide range of applications such as multi-modal assistants deployed on mobile devices or autonomous vehicles, as well as broader artificial intelligence robots.
The above is the detailed content of Meituan, Zhejiang University and others cooperate to create a full-process mobile multi-modal large model MobileVLM, which can run in real time and uses the Snapdragon 888 processor. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 As AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO To GEOMay 05, 2025 am 11:09 AM
As AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO To GEOMay 05, 2025 am 11:09 AMWith the explosion of AI applications, enterprises are shifting from traditional search engine optimization (SEO) to generative engine optimization (GEO). Google is leading the shift. Its "AI Overview" feature has served over a billion users, providing full answers before users click on the link. [^2] Other participants are also rapidly rising. ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot and Perplexity are creating a new “answer engine” category that completely bypasses traditional search results. If your business doesn't show up in these AI-generated answers, potential customers may never find you—even if you rank high in traditional search results. From SEO to GEO – What exactly does this mean? For decades
 Big Bets On Which Of These Pathways Will Push Today's AI To Become Prized AGIMay 05, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Big Bets On Which Of These Pathways Will Push Today's AI To Become Prized AGIMay 05, 2025 am 11:08 AMLet's explore the potential paths to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). This analysis is part of my ongoing Forbes column on AI advancements, delving into the complexities of achieving AGI and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). (See related art
 Do You Train Your Chatbot, Or Vice Versa?May 05, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Do You Train Your Chatbot, Or Vice Versa?May 05, 2025 am 11:07 AMHuman-computer interaction: a delicate dance of adaptation Interacting with an AI chatbot is like participating in a delicate dance of mutual influence. Your questions, responses, and preferences gradually shape the system to better meet your needs. Modern language models adapt to user preferences through explicit feedback mechanisms and implicit pattern recognition. They learn your communication style, remember your preferences, and gradually adjust their responses to fit your expectations. Yet, while we train our digital partners, something equally important is happening in the reverse direction. Our interactions with these systems are subtly reshaping our own communication patterns, thinking processes, and even expectations of interpersonal conversations. Our interactions with AI systems have begun to reshape our expectations of interpersonal interactions. We adapted to instant response,
 California Taps AI To Fast-Track Wildfire Recovery PermitsMay 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
California Taps AI To Fast-Track Wildfire Recovery PermitsMay 04, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI Streamlines Wildfire Recovery Permitting Australian tech firm Archistar's AI software, utilizing machine learning and computer vision, automates the assessment of building plans for compliance with local regulations. This pre-validation significan
 What The US Can Learn From Estonia's AI-Powered Digital GovernmentMay 04, 2025 am 11:09 AM
What The US Can Learn From Estonia's AI-Powered Digital GovernmentMay 04, 2025 am 11:09 AMEstonia's Digital Government: A Model for the US? The US struggles with bureaucratic inefficiencies, but Estonia offers a compelling alternative. This small nation boasts a nearly 100% digitized, citizen-centric government powered by AI. This isn't
 Wedding Planning Via Generative AIMay 04, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Wedding Planning Via Generative AIMay 04, 2025 am 11:08 AMPlanning a wedding is a monumental task, often overwhelming even the most organized couples. This article, part of an ongoing Forbes series on AI's impact (see link here), explores how generative AI can revolutionize wedding planning. The Wedding Pl
 What Are Digital Defense AI Agents?May 04, 2025 am 11:07 AM
What Are Digital Defense AI Agents?May 04, 2025 am 11:07 AMBusinesses increasingly leverage AI agents for sales, while governments utilize them for various established tasks. However, consumer advocates highlight the need for individuals to possess their own AI agents as a defense against the often-targeted
 A Business Leader's Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)May 03, 2025 am 11:14 AM
A Business Leader's Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)May 03, 2025 am 11:14 AMGoogle is leading this shift. Its "AI Overviews" feature already serves more than one billion users, providing complete answers before anyone clicks a link.[^2] Other players are also gaining ground fast. ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, and Pe


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool





