Home >Technology peripherals >AI >Computer science giant Niklaus Wirth passed away, and a generation of godfathers in the programming world fell from Euler to Pascal.
Computer science giant Niklaus Wirth passed away, and a generation of godfathers in the programming world fell from Euler to Pascal.
- 王林forward
- 2024-01-06 09:08:56754browse
The founder of programmingNiklaus Wirth passed away on January 1 at the age of 89.
He is a Turing Award winner and is known as one of the greatest programmers of all time. Programming languages Pascal, Euler, Algol W, Modula, Modula-2, Oberon, Oberon-2, Oberon-07 Everything comes from his hand.

He also led the design and development of the Lilith and Oberon operating systems, and wrote more than a dozen books in the field of computer science, including "Algorithmic Data Structure = Program 》(1975)、《Compiler Construction》(1996).
Different from the stereotype of computer scientists, Niklaus Wirth shows a great sense of humor and personality in life.
He often makes a joke:
In Europe people usually call him with the correct pronunciation "Nick-louse Veert", but in the United States, people always confuse him with "Nickel's" Worth”. (that is, Europeans call him by his first name, while Americans call him by value)
For people who know programming, they all know that "call by name" and "Call by value" are two different ways of passing parameters. This pun is considered the best CS pun ever.
Bertrand Meyer, the creator of the Eiffel language, issued a message to pay tribute to his contribution. We should remember his outstanding achievements in computer science and lament the loss his death has had on the entire industry. His creations will continue to influence and promote the development of software engineering, providing us with better programming tools and methods. Let us miss him and pay tribute to Niklaus Wirth, a leading figure in the fields of programming languages, programming methodologies, software engineering and hardware design, who passed away on January 1. We are deeply saddened by the passing of this pioneer in his field, close colleague, inspiring mentor and best friend.
 A legend in the programming world
A legend in the programming world
In 1934, Niklaus Wirth was born in a small town in northern Switzerland.
When he was a teenager, he was as keen on hands-on practice and thinking as the mathematician Pascal, especially assembling airplane models.
After that, he received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, a master of science from Laval University in Canada, and a doctorate in computer science from the University of California, Berkeley. The doctoral supervisor is computer design pioneer Harry Huskey.
 In the early days, Wirth became famous in the field of computer science for creating two languages:
In the early days, Wirth became famous in the field of computer science for creating two languages:
. Euler is a general programming language developed based on his doctoral thesis work. It introduces new concepts such as non-numeric data types and operator precedence. It is considered an important step in formal programming language design. try.
The PL360 system programming language is specially designed for IBM System/360 series computers. It uses a specific parsing method to provide direct control of the hardware, making programming more efficient and easier to write and maintain. .
Both languages are deeply influenced by the early programming language
Algol. Niklaus Wirth was an elite member of the ALGOL project team that defined and created a series of language standards, such as FORTRAN, the first high-level languages.
In the late 1950s, when computer scientists did not have dedicated academic departments and regular conferences, the
ALGOLproject laid an important foundation for this emerging discipline. Through ALGOL, Wirth has launched in-depth cooperation with other future Turing Award winners C.A.R. (Tony) Hoare, Edsger Dijkstra and Peter Naur. Algol 60 is one of the most important results of the
ALGOLproject, which introduced concepts such as recursive functions, structured code blocks, and local variables. In 1966, Wirth proposed that the next language of ALGOL should be designed as an extended and improved version of Algol 60 influenced by the Euler language. However, the team voted against it, and the team finally chose the highly complex Algol 68. proposal.
In 1968, Niklaus Wirth resigned from the team and worked with Tony Hoare to transform the rejected proposal into an unofficial version of Algol, known as Algol-W.
In the same year, Niklaus Wirth returned to teach at ETH Zurich, where he worked until his retirement in 1999.
 Among them, Niklaus Wirth created his most influential work, the Pascal language, based on Algol-W.
Among them, Niklaus Wirth created his most influential work, the Pascal language, based on Algol-W.
Following his personal aesthetic, Pascal retains Algol's code structure, logical integrity, and support for recursion, but removes the complexity, making it simple, flexible, and capable of quickly compiling efficient code.
Wirth later wrote:
The most critical principle is to include features that are well understood while excluding features that have not been tried or implemented, especially for developers.
In 1971, Pascal was adopted in teaching at ETH Zurich and was quickly promoted to other universities around the world.
In order to be suitable for different computers, Wirth also designed a new compiler that can not only write code for the virtual machine, but also generate code that can be run on the virtual machine.
Using this method to simulate a virtual machine on a new computer greatly simplifies the compiler porting process. With the widespread popularity of personal computers, Pascal is very adaptable to the limited memory and storage space of personal computers and has become a mainstream programming language.
At that time, Borland launched the affordable and fast Turbo Pascal compiler, which further consolidated Pascal's status as an important high-level programming language for personal computers in the 1980s.
also created the Borland legend that year.
Until now, Pascal is considered one of the best programming languages before the advent of C language. The International Olympiad in Informatics (IOI) also Pascal language is one of the three programming languages.
From Euler to Pascal, you can get a glimpse of Wirth's habit. His academic achievements or programming languages are often named after famous scientists. Euler was named in memory of the famous Swiss mathematician Euler, and Pascal was named in memory of the French mathematician Euler. Named after mathematician Blaise Pascal.
Later, Wirth, together with other veterans of the Algol project such as Edsger Dijksta, became interested in programming methods and formal methods. He participated in the IFIP Programming Methods Working Group and came up with the idea of gradually improving the code as a complement to the various "structured programming" visions they proposed.
After that, he expanded Pascal, proposed Modula, Modula-2, Oberon, etc., and also led the design and development of Lilith and Oberon operating systems.
In addition, Wirth also made many contributions in other aspects, such as expanding the famous Backus paradigm, inventing syntax diagrams, and writing "Introduction to System Programming", "Algorithmic Data Structure = Program", etc. Many classic works in the field of computer science.
In 1984, Niklaus Wirth won the Turing Award, the highest honor in computer science, for "developing a series of innovative computer languages".
In his award speech, Niklaus Wirth preached that people must "distinguish early on what is essential and what is ephemeral" and ensure that "ephemeral things never infringe on the systematic and structured nature of core facilities." design".
Every project is first and foremost a learning experiment. You learn best through invention. Only by working on development projects myself could I gain enough understanding of the inherent difficulties and be confident enough in the underlying details to be able to master them.
In addition to the Turing Award, Wilt also won the IEEE Computer Pioneer Award (1988), and the IBM European Science and Technology Award (1988). He was also elected as an academician of the Swiss Academy of Engineering (1992) and a foreign academician of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering (1994) .
Great sense of humor and personality
Genius computer scientists or software engineers are often regarded as isolated "outsiders", but Niklaus Wirth does not fit this stereotype. , he has his own personality and sense of humor.
According to netizens, in 1968, Niklaus Wirth's friend and computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra submitted a paper to "Communications of the ACM" . The original title was " A case against the goto statement"(A case against the goto statement).
In order to speed up publication, the publishing editor changed it to the form of "Letter to the Editor", and then Niklaus Wirth also changed the title to "The goto statement considered harmful"(Thinking that the goto statement is harmful) harmful).
The title subsequently became widely cited and inspired many similar article titles such as "X considered harmful" and even an article titled "Dijkstra considered harmful".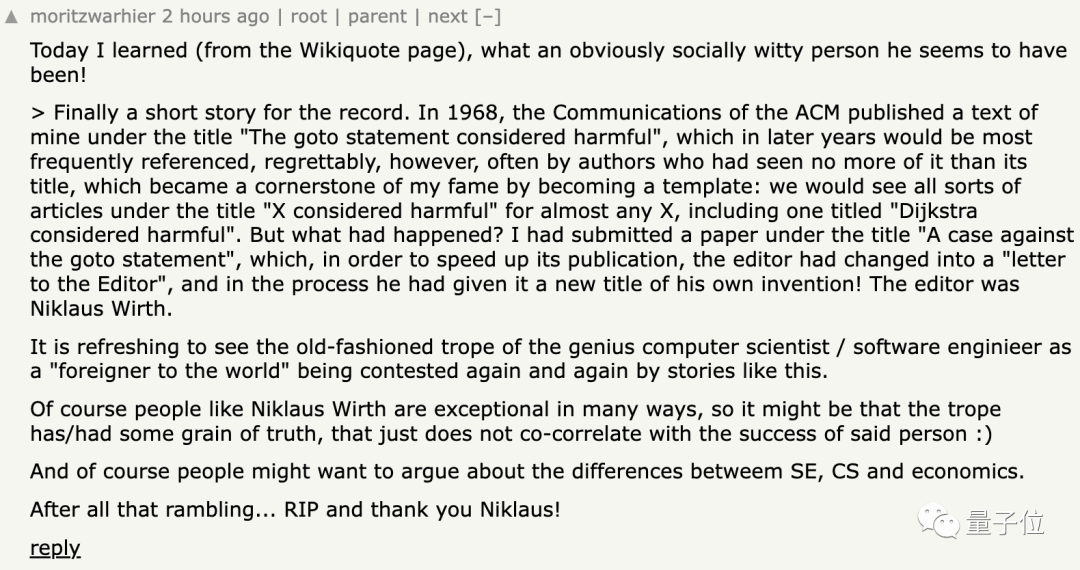
My first paid programming job was in Pascal, and then Modula, which had a profound impact on many of my subsequent jobs.
I never had the opportunity to meet him, but he had a major impact on my career and on many others.
The above is the detailed content of Computer science giant Niklaus Wirth passed away, and a generation of godfathers in the programming world fell from Euler to Pascal.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

