Home >Technology peripherals >AI >Realistic, controllable, and scalable, the autonomous driving lighting simulation platform LightSim is newly launched
Realistic, controllable, and scalable, the autonomous driving lighting simulation platform LightSim is newly launched
- 王林forward
- 2023-12-15 15:09:482526browse
Recently, researchers from Waabi AI, University of Toronto, University of Waterloo and MIT proposed a new autonomous driving lighting simulation platform LightSim at NeurIPS 2023. The researchers proposed a method to generate paired illumination training data from real data, solving the problems of missing data and model migration loss. LightSim uses neural radiation fields (NeRF) and physics-based deep networks to render vehicle driving videos, achieving lighting simulation of dynamic scenes on large-scale real data for the first time

- Project website: https://waabi.ai/lightsim
- Paper link: https://openreview.net /pdf?id=mcx8IGneYw
Why is automatic driving lighting simulation needed?
In robotics, camera simulation is very important, especially for autonomous vehicles to perceive outdoor scenes. However, existing camera perception systems perform poorly when encountering untrained outdoor lighting conditions. By using camera simulation to generate diverse outdoor lighting change data sets, the stability of the autonomous driving system can be improved.
Common camera simulation methods are generally based on physics engines. This method renders the scene by setting the 3D model and lighting conditions. However, simulation effects often lack diversity and are not realistic enough. Furthermore, due to the limited number of high-quality 3D models, the physical rendering results do not exactly match the real-world scenes. This leads to poor generalization ability of the trained model on real data.
Another approach is based on data-driven simulation. This approach uses neural rendering technology to reconstruct a digital twin of the real world to replicate the data observed by the sensors. This way we can create scenes with more flexibility and increase realism. However, the current technology embeds the lighting information of the scene into the 3D model, which limits the editing of the digital twin, such as changing lighting conditions or adding or deleting objects.
In a work from NeurIPS 2023, researchers from Waabi AI demonstrated a lighting simulation system LightSim based on a physics engine and neural network: Neural Lighting Simulation for Urban Scenes.

Different from previous work, LightSim can achieve the following points at the same time:
1. Realistic: For the first time, it can be done correctly Perform lighting simulation on large-scale outdoor dynamic scenes, and can more accurately simulate shadows, lighting effects between objects, etc.
2. Controllable: Supports editing of dynamic driving scenes (adding, deleting objects, camera positions and parameters, changing lighting, and generating safety-critical scenes etc.), thereby generating more realistic and consistent videos to improve the system's robustness to lighting and edge conditions.
3. Scalable: It is easy to expand to more scenarios and different data sets. You only need to collect data once (single pass). Reconstruct and conduct realistic and controllable simulation tests.

Building a simulation system
Step one: Build a real-world reusable Lighting Digital Twin
To reconstruct autonomous driving scenes in the digital world, LightSim first divides dynamic objects and static scenes from the collected data. This step uses UniSim to reconstruct the scene and remove camera view dependence in the network. Then use the marching cube to get the geometry, and further convert it to a mesh with basic materials.

In addition to materials and geometry, LightSim can also estimate outdoor lighting based on the sun and sky, the main light sources of outdoor daytime scenes, and obtain a high dynamic range environment map (HDR Sky dome). Using sensor data and extracted geometry, LightSim can estimate an incomplete panoramic image and then complete it to obtain a full 360° view of the sky. This panoramic image and GPS information are then used to generate an HDR environment map that accurately estimates sun intensity, sun direction and sky appearance.

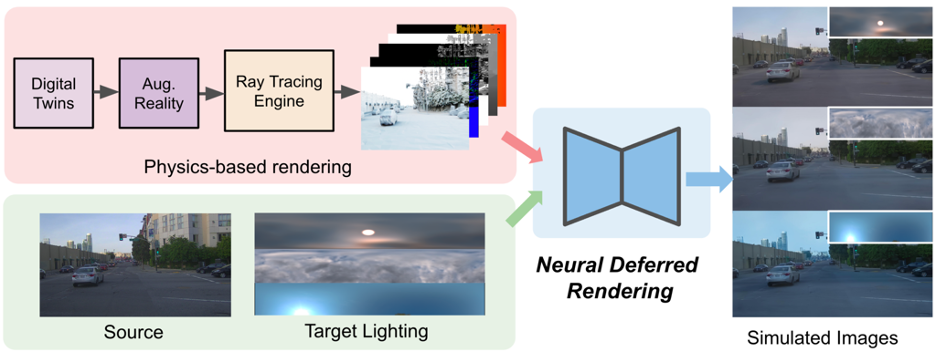
#After the digital twin is obtained, it can be further modified, such as adding or removing objects, changing vehicle trajectories or changing lighting, etc., to Generating representations for augmented reality. LightSim will perform physically based rendering, generating lighting-related data such as base color, depth, normal vectors, and shadows for modifying the scene. Using this lighting-related data and an estimate of the scene's source and target lighting conditions, the LightSim workflow is as follows.
Although physically based rendered images are good at reconstructing the lighting effects in a scene, they suffer from imperfections in geometry and material/lighting decomposition. Errors in rendering results often lack realism, such as blur, unrealistic surface reflections, and boundary artifacts. Therefore, researchers propose neural deferred rendering for enhanced realism. They introduced an image synthesis network that generates the final image using source images in a precomputed buffer and lighting-related data generated by the rendering engine. At the same time, the method in the paper also provides the network with an environment map to enhance the lighting context, and generates paired images through the digital twin, providing a novel pairwise simulation and real data training scheme
Simulation capability display
Change the lighting of the scene (Scene Relighting)
LightSim can render the same scene in a time-consistent manner under new lighting conditions. As shown in the video, the new sun position and sky appearance cause the scene's shadows and appearance to change.
LightSim can automatically batch re-light the scene. It can generate new, time-consistent, 3D-aware lighting changes from estimated and real HDR environment maps that are identical to the original scene
Image Correction (Image Correction)
LightSim's lighting representation is editable and can change the direction of the sun, thus updating lighting changes and shadows related to the direction of the sun's light. By rotating the HDR environment map and passing it to the Neural Deferred Rendering module, LightSim generates the following videoLightSim also supports batch editing of shadows
Lighting-Aware Character Insertion
In addition to modifying lighting, LightSim can also modify unusual objects ( such as architectural obstacles) to perform lighting-aware additions. These added objects can update the object's lighting shadows, accurately occlude objects, and spatially adapt to the entire camera configuration.
############Simulation migration (Generalization to nuScenes)#####################Due to LightSim’s neural deferred rendering network It is trained on multiple driving videos, so LightSim can be generalized to new scenarios. The following video demonstrates LightSim's generalization capabilities for driving scenes in nuScenes. LightSim can build a lighting-aware digital twin of each scene, which is then applied to a neural deferred rendering model pre-trained on PandaSet. LightSim has good migration performance and can provide a more robust solution for scene relighting############Real and controllable camera simulation############Comprehensive With all the features demonstrated above, LightSim enables controllable, diverse and realistic camera simulations. The following video demonstrates LightSim's scene simulation capabilities. In the video, a white car made an emergency lane change to the SDV lane, introducing a new roadblock, which caused the white car to enter a completely new scene. The effects generated by LightSim under various lighting conditions in the new scene are as follows: . ######In the video below, a new example is demonstrated. New obstacles have been inserted into existing road obstacles and a new set of vehicles have been added. By using LightSim for simulated lighting, newly added vehicles can be perfectly integrated into the scene
Summary and Outlook
LightSim is a tool that can A lighting-aware camera simulation platform that provides services for processing large-scale dynamic driving scenarios. It can build a lighting-aware digital twin based on real-world data and modify it to create new scenes with different object layouts and autonomous vehicle perspectives. LightSim is capable of simulating new lighting conditions, enabling diverse, realistic and controllable camera simulations to produce temporally/spatially consistent videos. It is worth noting that LightSim can also be combined with reverse rendering, weather simulation and other technologies to further improve simulation performance
The above is the detailed content of Realistic, controllable, and scalable, the autonomous driving lighting simulation platform LightSim is newly launched. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Detailed explanation of Three.js using orbit controls plug-in (orbit control) to control model interaction
- Understanding the css box model: Understand what the css box model is in 5 minutes?
- What are the layers of the tcp/ip reference model?
- NUS and Byte collaborated cross-industry to achieve 72 times faster training through model optimization, and won the AAAI2023 Outstanding Paper.
- Use vision to prompt! Shen Xiangyang showed off the new model of IDEA Research Institute, which requires no training or fine-tuning and can be used out of the box.

