AI eye scanning technology could detect Parkinson's disease early
Liu Huadong

British scientists recently revealed that using AI technology in retinal imaging can detect Parkinson's disease markers in advance through eye scanning.
Researchers say eye scanning is an emerging field of research, and its scan data can reveal signs of some neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia. Previously, clinicians often used the eyes as a "window" to identify and diagnose health conditions in other parts of the body. A 3D scanning technology called "optical coherence tomography (OCT)" is widely used in ophthalmology. In less than 1 minute, OCT scanning can obtain detailed images of retinal cross-sections and is accurate to one thousandth of a millimeter.
Retinal scanning is the only non-invasive way to see the layers of cells beneath the skin. In recent years, researchers have begun using powerful computer systems to accurately analyze large amounts of OCT and other eye images. A study of postmortem scans of people with Parkinson's disease revealed differences in their retinal inner nuclear layer (INL) and a thinner ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) compared with healthy people. Based on a "machine learning" artificial intelligence technology, the researchers obtained the hidden information of the human body through computer image analysis. For the first time, INL has been identified as a risk biomarker for Parkinson's disease, and it is also the first time that visual deterioration in Parkinson's disease patients has been detected approximately seven years before formal diagnosis.
It is important to detect signs of disease before symptoms appear, meaning people can make timely lifestyle changes and clinicians can help patients delay the onset and impact of neurodegenerative diseases. Alastair Denniston, Professor of Ophthalmology at the University of Birmingham, UK, said: "This study demonstrates the potential of ophthalmological data to detect subtle changes that humans cannot detect, helping to detect Parkinson's disease earlier. signs, bringing new possibilities for treatment.”
The above is the detailed content of AI eye scanning technology could detect Parkinson's disease early. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
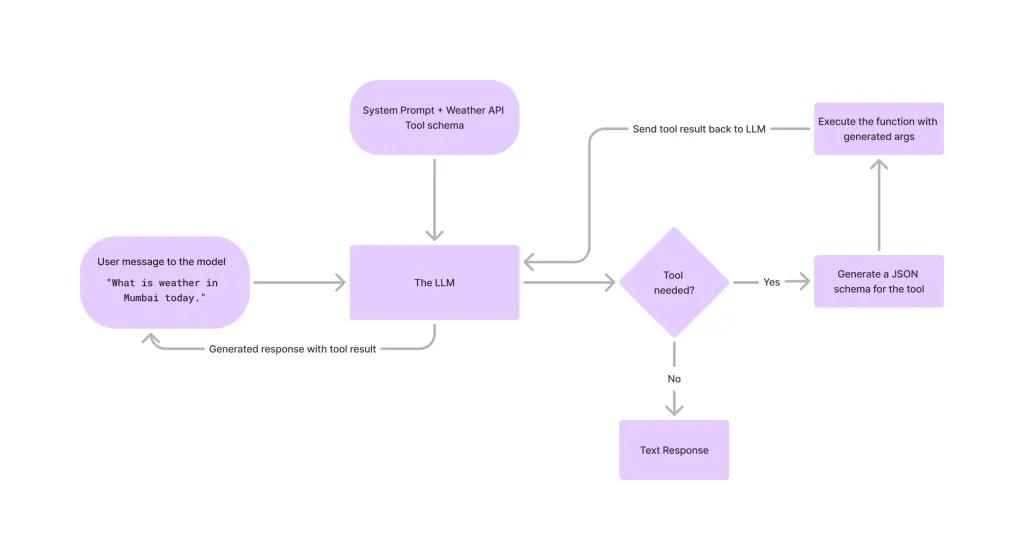 Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AMLarge language models (LLMs) have surged in popularity, with the tool-calling feature dramatically expanding their capabilities beyond simple text generation. Now, LLMs can handle complex automation tasks such as dynamic UI creation and autonomous a
 How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AMCan a video game ease anxiety, build focus, or support a child with ADHD? As healthcare challenges surge globally — especially among youth — innovators are turning to an unlikely tool: video games. Now one of the world’s largest entertainment indus
 UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM
UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM“History has shown that while technological progress drives economic growth, it does not on its own ensure equitable income distribution or promote inclusive human development,” writes Rebeca Grynspan, Secretary-General of UNCTAD, in the preamble.
 Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AMEasy-peasy, use generative AI as your negotiation tutor and sparring partner. Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining
 TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AM
TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AMThe TED2025 Conference, held in Vancouver, wrapped its 36th edition yesterday, April 11. It featured 80 speakers from more than 60 countries, including Sam Altman, Eric Schmidt, and Palmer Luckey. TED’s theme, “humanity reimagined,” was tailor made
 Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AMJoseph Stiglitz is renowned economist and recipient of the Nobel Prize in Economics in 2001. Stiglitz posits that AI can worsen existing inequalities and consolidated power in the hands of a few dominant corporations, ultimately undermining economic
 What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AM
What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AMGraph Databases: Revolutionizing Data Management Through Relationships As data expands and its characteristics evolve across various fields, graph databases are emerging as transformative solutions for managing interconnected data. Unlike traditional
 LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AM
LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AMLarge Language Model (LLM) Routing: Optimizing Performance Through Intelligent Task Distribution The rapidly evolving landscape of LLMs presents a diverse range of models, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Some excel at creative content gen


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





