 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Language, robot breaking, MIT and others use GPT-4 to generate simulation tasks and migrate them to the real world
Language, robot breaking, MIT and others use GPT-4 to generate simulation tasks and migrate them to the real worldRewritten content as: Machine Heart Report
Editors: Du Wei, Xiaozhou
GPT-4 and robots have created new sparks.

In the field of robotics, implementing universal robotic strategies requires a large amount of data, and collecting this data in the real world is time-consuming and laborious. Although simulation provides an economical solution for generating different volumes of data at the scene and instance levels, increasing task diversity in simulated environments still faces challenges due to the large amount of manpower required (especially for complex tasks). This results in typical artificial simulation benchmarks typically containing only tens to hundreds of tasks.
How to solve it? In recent years, large language models have continued to make significant progress in natural language processing and code generation for various tasks. Likewise, LLM has been applied to multiple aspects of robotics, including user interfaces, task and motion planning, robot log summary, cost and reward design, revealing strong capabilities in both physics-based and code generation tasks.
In a recent study, researchers from MIT CSAIL, Shanghai Jiao Tong University and other institutions further explored whether LLM can be used to create diverse simulation tasks and further explore their capabilities.
Specifically, the researchers proposed an LLM-based framework, GenSim, which provides an automated mechanism for designing and verifying task asset arrangements and task progress. More importantly, the generated tasks exhibit great diversity, promoting task-level generalization of robot strategies. Furthermore, conceptually, with GenSim, the reasoning and encoding capabilities of LLM are refined into language-visual-action strategies through intermediate synthesis of simulated data.

What needs to be rewritten is: Paper link:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.01361.pdf
The GenSim framework consists of the following three parts:
- The first is to propose new tasks through natural language instructions and the prompt mechanism implemented by the corresponding code;
- Second is a task library that caches previously generated high-quality instruction codes for verification and language model fine-tuning, and returns them as a comprehensive task data set;
- Finally, the language-adapted multi-task strategy training process uses the generated data to enhance task-level generalization capabilities.
At the same time, the framework operates through two different modes. Among them, in the goal-oriented setting, the user has a specific task or wishes to design a task course. At this time, GenSim adopts a top-down approach, taking the expected tasks as input and iteratively generating related tasks to achieve the expected goals. In an exploratory environment, if there is a lack of prior knowledge of the target task, GenSim gradually explores content beyond the existing tasks and establishes a basic strategy that is independent of the task.
In Figure 1 below, the researcher initialized a task library containing 10 manually planned tasks, used GenSim to extend it and generate more than 100 tasks.

The researchers also proposed several customized metrics to progressively measure the quality of generated simulation tasks, and evaluated several LLMs in goal-oriented and exploratory settings. For the task library generated by GPT-4, they performed supervised fine-tuning on LLMs such as GPT-3.5 and Code-Llama, further improving the task generation performance of LLM. At the same time, the achievability of tasks is quantitatively measured through strategy training, and task statistics of different attributes and code comparisons between different models are provided.
Not only that, the researchers also trained multi-task robot strategies. Compared with models trained only on human planning tasks, these strategies generalized well on all generation tasks and improved zero-shot generalization. chemical performance. Joint training with the GPT-4 generation task can improve generalization performance by 50% and transfer approximately 40% of zero-shot tasks to new tasks in simulations.
Finally, the researchers also considered simulation-to-real transfer, showing that pre-training on different simulation tasks can improve real-world generalization ability by 25%.
In summary, policies trained on different LLM-generated tasks achieve better task-level generalization to new tasks, highlighting the potential of extending simulated tasks through LLM to train base policies.
Tenstorrent AI Product Management Director Shubham Saboo gave this research high praise. He said that this is a breakthrough research on GPT-4 combined with robots, using LLM such as GPT-4 to generate a series of simulated robots on autopilot. tasks, making zero-shot learning and real-world adaptation of robots a reality.

Method introduction
As shown in Figure 2 below, the GenSim framework generates simulation environments, tasks and demonstrations through program synthesis. The GenSim pipeline starts from the task creator and the prompt chain runs in two modes, goal-directed mode and exploratory mode, depending on the target task. The task library in GenSim is an in-memory component used to store previously generated high-quality tasks. The tasks stored in the task library can be used for multi-task policy training or fine-tuning LLM.

Task Creator
As shown in Figure 3 below, the language chain will first generate the task description, and then generate the related implementation. The task description includes the task name, resources, and task summary. This study uses a few-sample prompt in the pipeline to generate code.

Task Library
The task library in the GenSim framework stores tasks generated by the task creator to generate better new tasks and train multi-task strategies. The task library is initialized based on tasks from manually created benchmarks.
The task library provides the task creator with the previous task description as a condition for the description generation phase, provides the previous code for the code generation phase, and prompts the task creator to select a reference task from the task library as the basis for writing a new task Sample. After task implementation is complete and all tests have passed, LLM is prompted to "reflect" on the new task and task library and form a comprehensive decision on whether the newly generated task should be added to the library.
As shown in Figure 4 below, the study also observed that GenSim exhibits interesting task-level combination and extrapolation behavior:

LLM Supervised Multi-Task Strategy
After generating the tasks, this study uses these task implementations to generate demonstration data and train operational policies, using a dual-stream transmission network architecture similar to Shridhar et al. (2022).
As shown in Figure 5 below, this study regards the program as an effective representation of the task and related demonstration data (Figure 5). It is possible to define the embedding space between tasks, and its distance index is sensitive to various factors from perception (such as Object pose and shape) are more robust.

In order to rewrite the content, the language of the original text needs to be rewritten into Chinese, and the original sentence does not need to appear
This study validates the GenSim framework through experiments and addresses the following specific questions: (1) How effective is LLM in designing and implementing simulation tasks? Can GenSim improve the performance of LLM in task generation? (2) Can training on tasks generated by LLM improve policy generalization ability? Would policy training benefit more if given more generation tasks? (3) Is pre-training on LLM-generated simulation tasks beneficial to real-world robot policy deployment?
Evaluate the generalization ability of LLM robot simulation tasks
As shown in Figure 6 below, for exploration mode and goal-oriented mode task generation, the two-stage prompt chain of few samples and task library can effectively improve the success rate of code generation.

Task level generalization
Few-sample strategy optimization for related tasks. As can be observed from the left side of Figure 7 below, jointly training the tasks generated by LLM can improve the policy performance on the original CLIPort task by more than 50%, especially in low data situations (such as 5 demos).
Zero-shot policy generalization to unseen tasks. As can be seen in Figure 7, by pre-training on more tasks generated by LLM, our model can better generalize to tasks in the original Ravens benchmark. In the middle right of Figure 7, the researchers also pre-trained on 5 tasks on different task sources, including manually written tasks, closed-source LLM, and open-source fine-tuned LLM, and observed similar zero-shot task-level generalization.

Adapting pre-trained models to the real world
Researchers transferred the strategies trained in the simulation environment to the real environment. The results are shown in Table 1 below. The model pre-trained on 70 GPT-4 generated tasks conducted 10 experiments on 9 tasks and achieved an average success rate of 68.8%, which is better than pre-training on the CLIPort task only. Compared with the baseline model, it has improved by more than 25%, and compared with the model pre-trained on only 50 tasks, it has improved by 15%.

The researchers also observed that pre-training on different simulation tasks improved the robustness of long-term complex tasks. For example, GPT-4 pre-trained models show more robust performance on real-world build-wheel tasks.

Ablation experiment
Simulation training success rate. In Table 2 below, the researchers demonstrate the success rates of single-task and multi-task policy training on a subset of generated tasks with 200 demos. For policy training on GPT-4 generation tasks, its average task success rate is 75.8% for single tasks and 74.1% for multi-tasks.

Generate task statistics. In Figure 9 (a) below, the researcher shows the task statistics of different features of the 120 tasks generated by LLM. There is an interesting balance between the colors, assets, actions, and number of instances generated by the LLM model. For example, the generated code contains a lot of scenes with more than 7 object instances, as well as a lot of pick-and-place primitive actions and assets like blocks.
In the comparison of code generation, the researcher qualitatively evaluated the failure cases in the top-down experiments of GPT-4 and Code Llama in Figure 9(b) below

For more technical details, please refer to the original paper.
The above is the detailed content of Language, robot breaking, MIT and others use GPT-4 to generate simulation tasks and migrate them to the real world. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 机器人学我表情的样子,让人感到一丝恐惧Apr 09, 2023 am 10:11 AM
机器人学我表情的样子,让人感到一丝恐惧Apr 09, 2023 am 10:11 AM通常,机器人的主要功能是完成一些简单的操作任务,我们希望机器人可以模仿人,让能力尽可能接近人类水平。不论是小米的 CyberOne 还是特斯拉的 Optimus,人们关心的主要是其机械关节数量,控制算法和行走速度。不过在这个领域,有些人探索的方向更加脑洞大开:现在,有一种机器人把模仿真人表情做到了极致:先尝试一下自拍。从「嫌弃」到「惊讶」,都可以做到完全同步:这个机器人名叫 Ameca,是个表情怪。除了模仿,它自己也能照镜子做很多小表情,看起来非常像真人。Ameca「假装」第一次见到镜子,首
 拿破仑、孔子在线陪聊!AI聊天机器人「复活」历史名人,网友:真上头!Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:11 PM
拿破仑、孔子在线陪聊!AI聊天机器人「复活」历史名人,网友:真上头!Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:11 PM和活生生的已故历史名人聊天是个什么感觉?近日,就有一群开发者利用语言模型,把千百年来各行各业的历史名人全部「复活」成了聊天机器人,做进了一款手机app里,起名叫「你好,历史」!开发者声称,这个与古代名人聊天的app涉及的内容几乎无所不包。比如可以:与玛丽莲·梦露聊好莱坞八卦与弗里达·卡洛讨论现代艺术问问圣诞老人他有多少只驯鹿问问科特·科本为什么自杀向穴居人学习如何生火与宇宙意识辩论生命的意义不过他们也没忘记提醒用户,这些对话是由人工智能生成的,所以不要太认真。而且每个对话都是独一无二的,你永远不
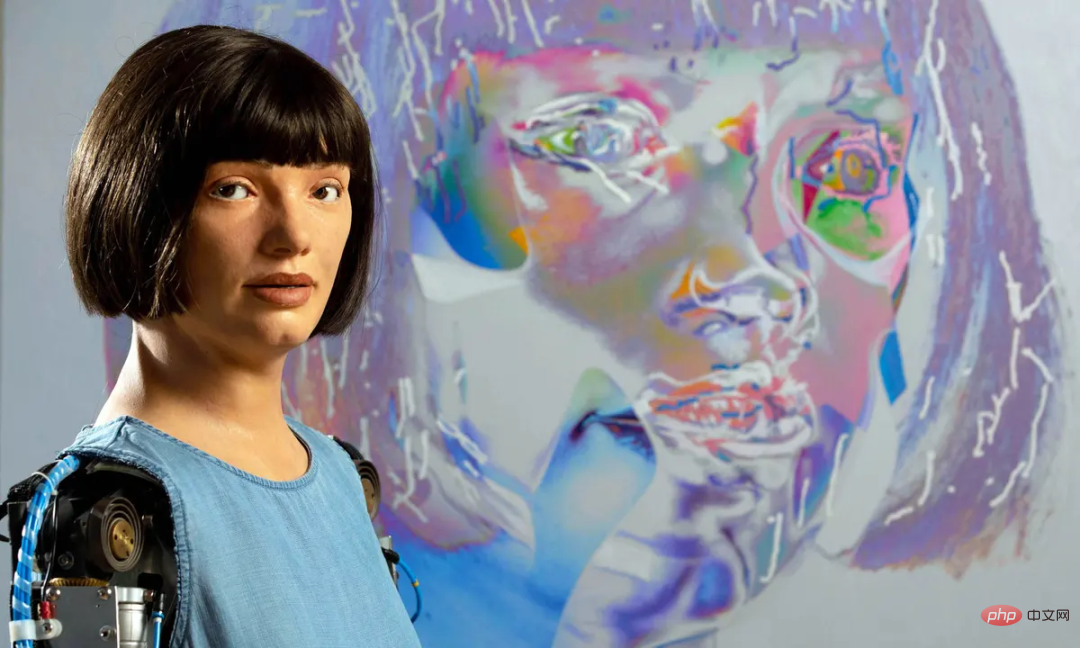 女王登基70周年,世上首个超逼真人形机器艺术家献上肖像画作,被锐评“缺少信念”Apr 08, 2023 pm 08:11 PM
女王登基70周年,世上首个超逼真人形机器艺术家献上肖像画作,被锐评“缺少信念”Apr 08, 2023 pm 08:11 PM大数据文摘出品作者:Caleb为庆祝英国女王伊丽莎白二世登基70周年,英国也是早早就洋溢出了庆典的味道。据了解,英国将于6月2日至5日连放4天公众假期,并在期间举行多项庆祝活动。英国皇家铸币厂也在精心打造有史以来最大的硬币,直径220毫米,重15公斤,面值15000英镑,耗时近400小时打造,是该厂1100年来生产的最大硬币。这枚金币一面雕刻着代表英国女王伊丽莎白二世的符号EⅡR,周围环绕着代表英国的玫瑰、水仙、蓟和三叶草。另一面有女王骑在马背上的图案。在这么热闹的日子里,AI当然也必须来凑一凑
 人类与人工智能如何建立关系Apr 09, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
人类与人工智能如何建立关系Apr 09, 2023 pm 07:41 PM人类与人工智能相比,哪个更擅长建立关系?事实上,这项革命性的技术已经存在了很长一段时间。然而,直到最近人们才意识到人工智能对人类的重要性。人工智能利用算法模拟人类,并随着时间的推移从经验中学习的能力,为这项技术与人类建立关系开辟道路。人类如何建立人际关系作为人类,我们倾向于只与少数人建立关系。我们试图确保不需要的和不相干的人从我们的生活中消失。在将我们的关系限制在少数人的同时,我们确保与那些对我们真正重要的人建立高质量的关系。然而,同样的方法在商业用语中可能不是理想的,并可能适得其反。尽管知道这
 盘点全球不错的七所机器人工程专业学校Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:31 PM
盘点全球不错的七所机器人工程专业学校Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:31 PM有抱负的工程师应该了解世界各地著名的机器人工程学院。现在是从事机器人和工程事业的最佳时机——从人工智能到太空探索,这一领域充满了令人兴奋的创新和进步。美国劳工统计局估计,未来10年,机械工程领域的职业总体上将保持7%的稳定增长率,确保毕业生将有大量的就业机会。机器人工程专业的学生平均工资超过9万美元,无需担心还助学贷款的问题。对于那些考虑投身机器人工程领域的人来说,选择一所合适的大学是非常重要的。世界上许多顶尖的机器人工程学院都在美国,尽管国外也有一些很棒的项目。这是7所世界上最好的机器人工程学
 让机器人学会咖啡拉花,得从流体力学搞起!CMU&MIT推出流体模拟平台Apr 07, 2023 pm 04:46 PM
让机器人学会咖啡拉花,得从流体力学搞起!CMU&MIT推出流体模拟平台Apr 07, 2023 pm 04:46 PM机器人也能干咖啡师的活了!比如让它把奶泡和咖啡搅拌均匀,效果是这样的:然后上点难度,做杯拿铁,再用搅拌棒做个图案,也是轻松拿下:这些是在已被ICLR 2023接收为Spotlight的一项研究基础上做到的,他们推出了提出流体操控新基准FluidLab以及多材料可微物理引擎FluidEngine。研究团队成员分别来自CMU、达特茅斯学院、哥伦比亚大学、MIT、MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab、马萨诸塞大学阿默斯特分校。在FluidLab的加持下,未来机器人处理更多复杂场景下的流体工作也都
 四足机器人学会“双腿站立下楼梯”!效率比腿式系统高83%Apr 09, 2023 am 11:21 AM
四足机器人学会“双腿站立下楼梯”!效率比腿式系统高83%Apr 09, 2023 am 11:21 AM还记得那个和特斯拉飙车的机器人吗?这是瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院衍生公司研发的与公司同名的四足轮腿式机器人——Swiss-Mile,前身是ANYmal四足机器人。距离它和特斯拉飙车还不到半年的时间,它又实现了重大升级。这次升级改进了机器人的算法,运动能力直接UP UP UP ! 可以双腿站立下楼梯:(小编内心OS:如果是我穿轮滑鞋下楼梯可能会摔个狗吃屎)楼梯爬累了,坐个电梯吧,用前脚按开电梯门:面对障碍物应对自如:它还能知道什么时候该站起来,什么时候该“趴下”,双腿直立与四足运动之间的切换更丝滑:
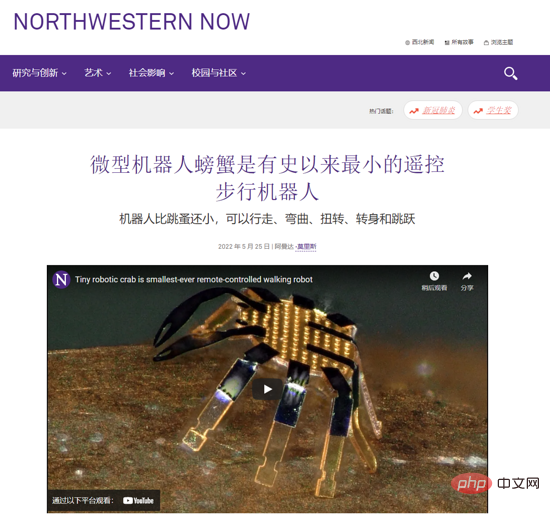 科学家展示世界上有史以来超小的“螃蟹”遥控步行机器人,体积比跳蚤还小Apr 09, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
科学家展示世界上有史以来超小的“螃蟹”遥控步行机器人,体积比跳蚤还小Apr 09, 2023 pm 10:41 PM日前,美国西北大学工程师开发出有史以来最小的遥控步行机器人,它以一种小巧可爱的螃蟹形式出现。这种微小的“螃蟹”机器人宽度只有半毫米,可以弯曲、扭曲、爬行、行走、转弯甚至跳跃,无需液压或电力。IT之家了解到,相关研究成果发表在《科学・机器人》上。据介绍,这种机器人是用形状记忆合金材料所制造的,然后可以变成所需的形状,当你加热后又会变回原来的形状,而热量消失时可以再次弹回变形时的样子。据介绍,其热量是由激光所带来的。激光通过“螃蟹”加热合金,但因为它们非常小,所以热量传播非常快,这使得它们的响应速度


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor





