
Distribution shift problem in adversarial training requires specific code examples
Abstract: Distribution shift is a ubiquitous problem in machine learning and deep learning tasks question. In order to deal with this problem, researchers have proposed the method of adversarial training. This article will introduce the distribution shift problem in adversarial training and give code examples based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
- Introduction
In machine learning and deep learning tasks, it is usually assumed that the data of the training set and the test set are independently sampled from the same distribution. However, in practical applications, this assumption does not hold true because there are often differences in distributions between training data and test data. This distribution shift (Distribution Shift) will lead to model performance degradation in practical applications. In order to solve this problem, researchers have proposed adversarial training methods. - Adversarial training
Adversarial training is a method of reducing the distribution difference between the training set and the test set by training a generator network and a discriminator network. The generator network is responsible for generating samples similar to the test set data, while the discriminator network is responsible for determining whether the input sample comes from the training set or the test set.
The process of adversarial training can be simplified to the following steps:
(1) Training generator network: The generator network receives a random noise vector as input and generates a test set data Similar samples.
(2) Training the discriminator network: The discriminator network receives a sample as input and is classified as coming from the training set or the test set.
(3) Backpropagation update generator network: The goal of the generator network is to trick the discriminator network into misclassifying the generated samples as coming from the training set.
(4) Repeat steps (1)-(3) several times until the generator network converges.
- Code example
The following is an adversarial training code example based on Python and TensorFlow framework:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# 定义生成器网络
def make_generator_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(256, input_shape=(100,), use_bias=False))
model.add(layers.BatchNormalization())
model.add(layers.LeakyReLU())
model.add(layers.Dense(512, use_bias=False))
model.add(layers.BatchNormalization())
model.add(layers.LeakyReLU())
model.add(layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation='tanh'))
model.add(layers.Reshape((28, 28, 1)))
return model
# 定义判别器网络
def make_discriminator_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(layers.Dense(512))
model.add(layers.LeakyReLU())
model.add(layers.Dense(256))
model.add(layers.LeakyReLU())
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
return model
# 定义生成器和判别器
generator = make_generator_model()
discriminator = make_discriminator_model()
# 定义生成器和判别器的优化器
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
# 定义损失函数
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
# 定义生成器的训练步骤
@tf.function
def train_generator_step(images):
noise = tf.random.normal([BATCH_SIZE, 100])
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=False)
gen_loss = generator_loss(fake_output)
gradients_of_generator = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_generator, generator.trainable_variables))
# 定义判别器的训练步骤
@tf.function
def train_discriminator_step(images):
noise = tf.random.normal([BATCH_SIZE, 100])
with tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
real_output = discriminator(images, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=True)
disc_loss = discriminator_loss(real_output, fake_output)
gradients_of_discriminator = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_discriminator, discriminator.trainable_variables))
# 开始对抗训练
def train(dataset, epochs):
for epoch in range(epochs):
for image_batch in dataset:
train_discriminator_step(image_batch)
train_generator_step(image_batch)
# 加载MNIST数据集
(train_images, _), (_, _) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1).astype('float32')
train_images = (train_images - 127.5) / 127.5
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_images).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
# 指定批次大小和缓冲区大小
BATCH_SIZE = 256
BUFFER_SIZE = 60000
# 指定训练周期
EPOCHS = 50
# 开始训练
train(train_dataset, EPOCHS)In the above code example, we define the generator and discriminator For the network structure of the optimizer, the Adam optimizer and binary cross-entropy loss function were selected. Then, we define the training steps of the generator and discriminator and train the network through the training function. Finally, we loaded the MNIST dataset and performed the adversarial training process.
- Conclusion
This article introduces the distribution shift problem in adversarial training and gives code examples based on generative adversarial networks. Adversarial training is an effective method to reduce the distribution difference between the training set and the test set, which can improve the performance of the model in practice. By practicing and improving code examples, we can better understand and apply adversarial training methods.
The above is the detailed content of Distribution shift problem in adversarial training. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何解决 VS Code 中 IntelliSense 不起作用的问题Apr 21, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
如何解决 VS Code 中 IntelliSense 不起作用的问题Apr 21, 2023 pm 07:31 PM最常称为VSCode的VisualStudioCode是开发人员用于编码的工具之一。Intellisense是VSCode中包含的一项功能,可让编码人员的生活变得轻松。它提供了编写代码的建议或工具提示。这是开发人员更喜欢的一种扩展。当IntelliSense不起作用时,习惯了它的人会发现很难编码。你是其中之一吗?如果是这样,请通过本文找到不同的解决方案来解决IntelliSense在VS代码中不起作用的问题。Intellisense如下所示。它在您编码时提供建议。首先检
 解决C++代码中出现的“error: redefinition of class 'ClassName'”问题Aug 25, 2023 pm 06:01 PM
解决C++代码中出现的“error: redefinition of class 'ClassName'”问题Aug 25, 2023 pm 06:01 PM解决C++代码中出现的“error:redefinitionofclass'ClassName'”问题在C++编程中,我们经常会遇到各种各样的编译错误。其中一个常见的错误是“error:redefinitionofclass'ClassName'”(类‘ClassName’的重定义错误)。这个错误通常出现在同一个类被定义了多次的情况下。本文将
 解决PHP报错:继承父类时遇到的问题Aug 17, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
解决PHP报错:继承父类时遇到的问题Aug 17, 2023 pm 01:33 PM解决PHP报错:继承父类时遇到的问题在PHP中,继承是一种重要的面向对象编程的特性。通过继承,我们能够重用已有的代码,并且能够在不修改原有代码的情况下,对其进行扩展和改进。尽管继承在开发中应用广泛,但有时候在继承父类时可能会遇到一些报错问题,本文将围绕解决继承父类时遇到的常见问题进行讨论,并提供相应的代码示例。问题一:未找到父类在继承父类的过程中,如果系统无
 机器学习模型的泛化能力问题Oct 08, 2023 am 10:46 AM
机器学习模型的泛化能力问题Oct 08, 2023 am 10:46 AM机器学习模型的泛化能力问题,需要具体代码示例随着机器学习的发展和应用越来越广泛,人们越来越关注机器学习模型的泛化能力问题。泛化能力指的是机器学习模型对未标记数据的预测能力,也可以理解为模型在真实世界中的适应能力。一个好的机器学习模型应该具有较高的泛化能力,能够对新的数据做出准确的预测。然而,在实际应用中,我们经常会遇到模型在训练集上表现良好,但在测试集或真实
 强化学习中的奖励设计问题Oct 08, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
强化学习中的奖励设计问题Oct 08, 2023 pm 01:09 PM强化学习中的奖励设计问题,需要具体代码示例强化学习是一种机器学习的方法,其目标是通过与环境的交互来学习如何做出能够最大化累积奖励的行动。在强化学习中,奖励起着至关重要的作用,它是代理人(Agent)学习过程中的信号,用于指导其行为。然而,奖励设计是一个具有挑战性的问题,合理的奖励设计可以极大地影响到强化学习算法的性能。在强化学习中,奖励可以被视为代理人与环境
 win10下载不了steam怎么办Jul 07, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
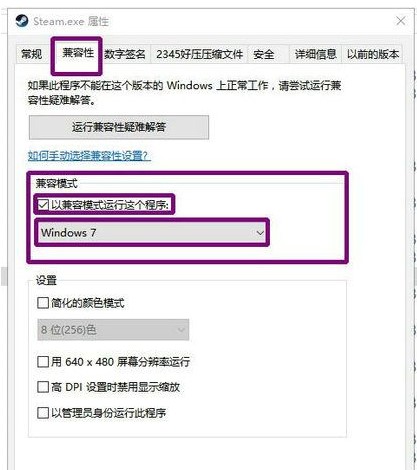
win10下载不了steam怎么办Jul 07, 2023 pm 01:37 PMSteam是十分受欢迎的一个平台游戏,拥有众多优质游戏,可是有些win10用户体现自己下载不了steam,这是怎么回事呢?极有可能是用户的ipv4服务器地址没有设置好。要想解决这个问题的话,你可以试着在兼容模式下安装Steam,随后手动修改一下DNS服务器,将其改成114.114.114.114,以后应当就能下载了。win10下载不了steam怎么办:WIn10下能够试着兼容模式下安装,更新后必须关掉兼容模式,不然网页将无法加载。点击程序安装的属性,以兼容模式运作运行这个程序。重启以增加内存,电
 弱监督学习中的标签获取问题Oct 08, 2023 am 09:18 AM
弱监督学习中的标签获取问题Oct 08, 2023 am 09:18 AM弱监督学习中的标签获取问题,需要具体代码示例引言:弱监督学习是一种利用弱标签进行训练的机器学习方法。与传统的监督学习不同,弱监督学习只需利用较少的标签来训练模型,而不是每个样本都需要有准确的标签。然而,在弱监督学习中,如何从弱标签中准确地获取有用的信息是一个关键问题。本文将介绍弱监督学习中的标签获取问题,并给出具体的代码示例。弱监督学习中的标签获取问题简介:
 win10浏览器自动关闭是怎么回事Jul 02, 2023 pm 08:09 PM
win10浏览器自动关闭是怎么回事Jul 02, 2023 pm 08:09 PMwin10浏览器自动关闭是怎么回事?我们在使用电脑的时候经常会去用到各种浏览器,而最近有不少用户在Win10电脑中使用浏览器的时候经常会出现自动关闭的情况,那么我们要是遇到这种问题应该怎么解决呢?很多小伙伴不知道怎么详细操作,小编下面整理了Win10系统浏览器自动关闭的解决教程,如果你感兴趣的话,跟着小编一起往下看看吧! Win10系统浏览器自动关闭的解决教程 1、针对浏览器崩溃的问题,可以借助电脑管家所提供的电脑诊所工具进行修复操作。只需要在其中搜索IE浏览器崩溃并点击如图所示立即修复


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






